
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
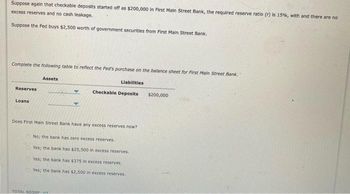
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose again that checkable deposits started off as $200,000 in First Main Street Bank, the required reserve ratio (r) is 15%, with and there are no
excess reserves and no cash leakage.
Suppose the Fed buys $2,500 worth of government securities from First Main Street Bank.
Complete the following table to reflect the Fed's purchase on the balance sheet for First Main Street Bank.
Reserves
Loans
Assets
TOTAL SCORP
Liabilities
Checkable Deposits
Does First Main Street Bank have any excess reserves now?
No; the bank has zero excess reserves.
Yes; the bank has $25,500 in excess reserves.
Yes; the bank has $375 in excess reserves.
Yes; the bank has $2,500 in excess reserves.
$200,000
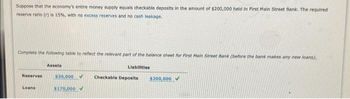
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that the economy's entire money supply equals checkable deposits in the amount of $200,000 held in First Main Street Bank. The required
reserve ratio (r) is 15%, with no excess reserves and no cash leakage.
Complete the following table to reflect the relevant part of the balance sheet for First Main Street Bank (before the bank makes any new loans).
Liabilities
Reserves
Loans
Assets
$30,000
$170,000 V
Checkable Deposits
$200,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume that the required reserve ratio is 7.00%, that banks do not keep excess reserves, and that all the money loaned out from Bank Uno is deposited into Bank Duo (whose loans go to other banks not shown here). Bank Uno has $2,167 in reserves and $2,167 in deposits. Once the lending and depositing process is complete, what will Bank Uno have in reserves, loans, and deposits?arrow_forwardIf a bank that faces a 25 percent reserve ratio received a deposit of $30,000 and makes a loan to a customer for $10,000, what is the consequence if the bank then deposits the rest of the funds at the Federal Reserve? Excess reserves increase by $30,000. Excess reserves increase by $20,000 and required reserves increase by $10,000. Excess reserves increase by $12,500 and required reserves increase by $7,500. Required reserves increase by $17,500. Reserves are not affected.arrow_forwardConsider a system of banking in which the Federal Reserve uses required reserves to control the money supply (as was the case in the United States before 2008). Assume that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency, so the only money exists in the form of demand deposits. To further simplify, assume the banking system has total reserves of $400. Determine the money multiplier as well as the money supply for each reserve requirement listed in the following table. Reserve Requirement (Percent) 20 10 Simple Money Multiplier A higher reserve requirement is associated with a Money Supply (Dollars) money supply. Suppose the Federal Reserve wants to increase the money supply by $200. Maintain the assumption that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency. If the reserve requirement is 10%, the Fed will use open-market operations to $ worth of U.S. government bonds. Now, suppose that, rather than immediately lending out all…arrow_forward
- What is the maximum impact on the money supply from the bond liquidation in the previous problem(Use positive or negative to show growth or contraction)? Required Reserve Ratio=20% Assets Liabilities Total Reserves=$50 Demand Deposits=$100 Loans=$20 Bonds=$30arrow_forwardIf a bank has $32 million in deposits and the required reserve ratio is 4 percent, the bank's required reserves equal $0.8 million. True Falsearrow_forwardYou are given the following balance sheet of the Summer Bank (21) Balance sheet of the Winter bank Assets Liabilities Cash $ 8,000 Deposited with the Fed $ 5,000 Loans $ 117,000 Deposits $ 80,000 Capital $ 50,000 Total $ 130,000 Total $ 130,000 The required reserve ratio (RRR) on all deposits is 5% What, if any, are this bank's excess reserves? How much new amount of loan will this bank be able to create because of the excess reserves? How much new amount of loan the entire banking system be able to create because of the excess reserves? What would be the excess reserves of this bank after the RRR is changed to 4%? How much new amount of loan will this bank be able to create with the RRR of 4%? How much new amount of loan the entire banking system be able to create because of the excess reserves? What happened to the money supply after the…arrow_forward
- One effect of the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks was to temporarily prevent banks from accessing reserves they needed to meet the demands of their customers. (This occurred because the attacks destroyed many records as well as the computers required to access backup records, and it took affected banks several weeks to become fully operational.) In response, the Fed made many billions of dollars of reserves available to banks, gradually withdrawing the new reserves from the banking system as that system returned to normal. Suppose the Fed had not injected reserves in this way. What would likely have happened to interest rates as a result? What would have been the likely impact on the stock market and on spending by consumers and businesses? Would the unemployment rate have gone up or down? Explain your reasoning in each case.arrow_forwardUsing the supply and demand analysis of the market for reserves, determine what happens to the federal funds rate, borrowed reserves, and non-borrowed reserves, holding everything else constant, if: The economy is surprisingly strong, leading to an increase in the amount of checkable deposits. The fed reduces reserve requirements and the federal funds rate is initially at the discount rate.arrow_forwardUsing the supply and demand analysis of the market for reserves, indicate what happens to the federal funds rate, borrowed reserves, and nonborrowed reserves, holding everything else constant, under the following situations. Be sure to fully explain the shifts in reserve demand, reserve supply, and changes in the federal funds rate. Please include a picture of your graphs in the folder below.arrow_forward
- Consider a system of banking in which the Federal Reserve uses required reserves to control the money supply (as was the case in the United States before 2008). Assume that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency, so the only money exists in the form of demand deposits. To further simplify, assume the banking system has total reserves of $100. Determine the money multiplier as well as the money supply for each reserve requirement listed in the following table. Reserve Requirement (Percent) 15 10 Simple Money Multiplier Money Supply (Dollars) A lower reserve requirement is associated with a money supply. Suppose the Federal Reserve wants to increase the money supply by $100. Maintain the assumption that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency. If the reserve requirement is 10%, the Fed will use open-market operations to $ worth of U.S. government bonds. Now, suppose that, rather than immediately lending out all excess…arrow_forwardInitially, the banking system has a required reserve ratio of 20.0 percent, $450,000 in total deposits, and no excess reserves. If the Fed reduces the required reserve ratio to 15.0, how much unused lending capacity does the banking system now have? Multiple Choice $750,000 $3,000,000 $337,500 $150,000arrow_forwardmacmillan learning Suppose that the legal reserve ratio set by the Fed is 10% and that the Fair Bank in Fairdealing, Missouri, initially has checkable deposit equal to $240 and a reserve account of $70. A customer of Fair Bank deposits $100 into her checking account. Fair Bank loans 80% of the deposit and places the rest in its reserves at the St. Louis Fed. For simplicity, assume the borrower received the loan as cash. How much does Fair Bank have in excess reserves after the deposit and loan? Number Place the figures below to represent changes in the accounts of Fair Bank and the Federal Reserve of St. Louis' balance sheets resulting from the deposit and loan. Hint Cash: Reserves: Loans: Property: $ +$100 +$80 Balance Sheet: Fair Bank Liabilities: Net equity: +$20 -$100 -$20 +$10 -$80 -$10 Balance Sheet: Saint Louis Fed Liabilities: Cash: Property: Loans: Previous Check Answer Next Exitarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education