
Appl Of Ms Excel In Analytical Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781285686691
Author: Crouch
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
How to calculate?
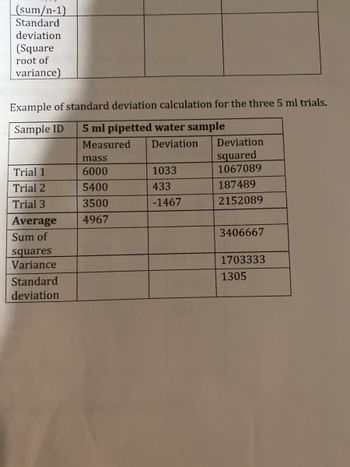
Transcribed Image Text:(sum/n-1)
Standard
deviation
(Square
root of
variance)
Example of standard deviation calculation for the three 5 ml trials.
Sample ID 5 ml pipetted water sample
Measured
Deviation
Trial 1
Trial 2
Trial 3
Average
Sum of
squares
Variance
Standard
deviation
mass
6000
5400
3500
4967
1033
433
-1467
Deviation
squared
1067089
187489
2152089
3406667
1703333
1305
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a certain species of fawns between 1 and 5 months old have a body weight that is approximately normally distributed with mean μ=28.6 kilograms and standard deviation σ=3.7 kilograms. Let x be the weight of a fawn in kilograms. Convert the following z interval to a x interval. 2.7 < z Choices x < 18.61 x < 38.59 x > 38.59 x > 18.61 x -38.59arrow_forwardIf you measure a quantity four times and the standard deviation is 1.0% of the average, can you be 90% confident that the true value is within 1.2% of the measured average?arrow_forwardCalculate the standard deviation of the four trials below. Trial 1: 49.59 grams Trial 2: 51.25 grams Trial 3: 49.78 grams Trial 4: 50.19 gramsarrow_forward
- A powder was prepared containing 3.00% NaCN and 97.00% NaCl. A sample obtained from that mixture containing 7.374×10^5 particles weighs 10.0 g. Determine the number and percent relative standard deviation of NaCN particles from a sample of the mixture weighing 6.30 g. I need nNaCN particles and %RSDarrow_forwardUse appropriate statistical tests to determine whether the results of replicatemeasurements (average ± standard deviation given below) by two methods are the sameor different at the 95% confidence level. Method A: 624.6 ± 0.8 (n = 10)Method B: 621 ± 3 (n = 5)arrow_forwardExplain the difference between the propagated uncertainty and the standard deviation. Which number would you use to describe the uncertainty in the measurement? if the standard deviation is 0.01 and the propagated uncertainty is 0.03arrow_forward
- Q 1 thank you!arrow_forwardPlease help me find the standard deviation for the given data.arrow_forwardUse a spreadsheet to calculate the mean and standard deviation of the data set. 54.99, 54.40, 54.60, 54.63, 54.36 The figure shows a suggested setup for your spreadsheet, where you enter the data in the highlighted cells and enter formulas in cells C4:D8 and B9:B11 to carry out the appropriate calculations. mean: standard deviation:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning



Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning