
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
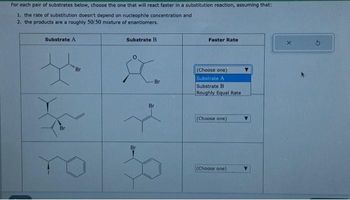
Transcribed Image Text:For each pair of substrates below, choose the one that will react faster in a substitution reaction, assuming that:
1. the rate of substitution doesn't depend on nucleophile concentration and
2. the products are a roughly 50/50 mixture of enantiomers.
Substrate A
F
Br
Br
Substrate B
&
Br
Br
Br
Faster Rate
(Choose one)
Substrate A
Substrate B
Roughly Equal Rate
(Choose one)
(Choose one)
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- After drawing a mechanism for this reaction determine which intermediate cannot be formedarrow_forwardWrite the mechanism for the reaction. ůl 1. H 2. H+ H NaOMe MeOHarrow_forwardReaction Time (s) 0.000 26.01 37.57 54.23 [A](M) 0.192 0.114 0.0780 0.0300 Which best describes the order of this reaction? Ozeroth O first Osecondarrow_forward
- What amount of catalyst is necessary to significantly change the reaction rate of peroxide hydrogen decomposition? O A catalyst does not influence the rate of reaction O Equal to hydrogen peroxide O Half of hydroxide peroxide O Small DD 000 החמ F9 F10arrow_forwardSKIP IF YOU ALREADY DID THIS OR ELSE DOWNVOTEarrow_forwardStep 1) X(g) + Y(g) A(g) fast, reaches equilibrium (For Step 1, k1 = forward rate constant & k-1 = reverse rate constant.)Step 2) A(g) + Z(g) B(g) slow (k2 = rate constant) Step 3) B(g) P(g) fast (k3 = rate constant) a) What is the overall reaction? b) What is the rate law supported by this mechanism? Explain your answer. c) The following is experimental data found for this reaction: Initial [X] (M) Initial [Y] (M) Initial [Z] (M) Initial Rate (M/day) Exp 1 0.150 0.150 0.150 0.569 Exp 2 0.250 0.150 0.150 0.948 Exp 3 0.250 0.300 0.150 3.793 Exp 4 0.300 0.350 0.200 6.196 i) What is the experimentally determined rate law? ii) Determine the rate constant and include units. d) Does your experimentally determined rate law support the proposed mechanism? Explain your answer. e) ΔΔHo = -347 kJ/mol for the overall reaction. Draw a reasonable reaction profile for the proposed mechanism. Label your profile with the proper reactants,…arrow_forward
- Which of the four reactions does NOT proceed through the same intermediate as the others?arrow_forward1. What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate?arrow_forwardIn comparing these two reactions, which one would occur faster via the SÃ2 mechanism and why? Reaction I CI OH- Reaction II CI 1 NH₂arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction and predict the new rate of the reaction if the concentration of A is doubled and the concentration of B was quadrupled. The new rate will be how many times greater than the original rate?arrow_forwardAnother common component of reaction mechanism is a catalyst. These are compounds that change the reaction mechanism and provide a pathway with a lower activation energy, and correspondingly faster reaction rate. They are a reactant in an early step in the mechanism and a product in a later step. They do not appear in the overall reaction but do appear in the rate law. 3. A reaction occurs by the following mechanism; Step 1 Ce4+ + Mn²+ →→ Ce³+ + Mn³+ Step 2 Ce4+ + Mn³+ → Ce³+ + Mn²+ Step 3 Tit+ Mn+→ Ti³+ + Mn²+ a. Write the overall reaction. b. Identify each of the components as a reactant, product, intermediate, or catalyst; Mn²+ Mn³+ Ce4+ Ce ³+ Mn4+ Tit Ti³+ C. Assuming that the catalyst is involved in the rate determining step, what is the rate law for this reaction? 4. Under certain conditions, the reaction: 2 NO + Cl₂ → 2 NOCI is found to be second order in NO and first order Cl₂. Given the following mechanism; Step 1 NO + Cl2 → NOCI₂ Step 2 NOCI₂ + NO 2 NOCI a. What are the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY