
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
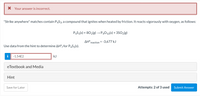
Transcribed Image Text:X Your answer is incorrect.
"Strike anywhere" matches contain P4S3, a compound that ignites when heated by friction. It reacts vigorously with oxygen, as follows:
P4S3(s) + 802(g) –→ P4010(s) + 3SO2(g)
AH°reaction = -3,677 kJ
Use data from the hint to determine AH°, for P4S3(s).
i
-1.54E2
kJ
eTextbook and Media
Hint
Save for Later
Attempts: 2 of 3 used
Submit Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q2) Calculate the lower heating value (LHV) for I mole CO, (g) for the following reaction from the given data: CO. (g) + 4 H. 25 C 2 H,O (1) + CH, (g) Compound Formula State (kJ/g mol) Hydrogen Water 8 - 285.00 H,0 8 -44.00 Water H,0 0.00 Methane Carbon dioxide CO, CH, ४ -890.00 0.00arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2NH3(g) + 202(g)→N20(g) + 3H20(1) AH° = -683 kJ and AS° = -366 J/K !! AG would be less than zero at temperatures (above, below) К. Enter above or below in the first box and enter the temperature in the second box. Assume that AH° and AS° are constant.arrow_forwardWhat is A H°rxn _for the following reaction, if given the three known reactions below: 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O (1) --> C2H, (g) + 02 (g); A H°rxn kJ (input numeric answer only) Given data: 2C (s, graphite) + 3H2 (g) --> C2H6 (g) A H°1= -68.29 kJ C (s, graphite) + O2 (g) --> CO2 (g) A H°2 = -393.5 kJ H2 (g) + O2 (g) --> H2O (I) A H°3= -285.8 kJarrow_forward
- Use your table of Heats of Formation to calculate the heat of reaction for the following reaction: C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) ⟶ 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)arrow_forwardTraduction: Given the reaction: determine the entalpy change for the next ecuation: 8. Dada la reaccion 4AICI3(s) + 302(g) → 2Al2O3(s) + 6CI2(g); AH= -529.0 kJ %3D determine AH para la siguiente rea ión Cl2(g) + %Al2O3(s) %AICI3(s) + ½O2(g) +529.0 kJ +88.2 kJ +176.3 kJ +264.5 kJ a)arrow_forwardThanks so much!arrow_forward
- 3) Calculate the reaction heat of formation of PbO from Pb and O2 at rxn temperatures of 500K and 800K seperately (using below reactions). Pb(s) + 1/2 O2(g) Pb(1) + 1/2 O2(g)- AH°298.PbO =-219400 J/mole Cp (PbO.s)-52.3 +8.66 x 10T- 8.2x10 T J/molK (298-1159 K) CP (Pb.s)-24.3 +8.7 x 10 T Cp (Pb.)= 32.5-3.1 x 10 T Cp(02g)-29.9 +4.18 x 10 T-1.7x10 T2 Pb(s)→ PbO(s) PbO(s) J/molK (298-600 K) J/molK (600-1300 K) J/molK (298-2500 K) Pb(1). AHmelting 4800 J/mole, Tmelting 600Karrow_forwardThe reaction we performed was: Na(s) + H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + 1/2H2(g) qreaction = rHo = -184 kJ/mol-rxn Assuming the dessicator jar is well insulated (like our coffee-cup calorimeter), the energy balance is: 0 = qsystem = qreaction + qwater qreaction = -qwater qreaction = -mwater*Cwater*Twater The data from the demonstration was: (a) 1.0 kg water, (b) 22.0oC, (d) Cwater = 4.18 J/g-K, (e) mNa = 0.21 g What is Tfinal in centigrade?arrow_forward9) One method for making ethanol, C2H5OH, involves the gas-phase hydration of ethylene, C2H4: Estimate AH for this reaction from the given average bond dissociation energies, D. Bond | D, kJ/mol C=C 615 H H H H С-Н 410 H C -C 0-H C-C 350 H H. 350 H H H H. 0–H 460arrow_forward
- For the reaction 4HCI(g) + O₂(g) 2H₂O(g) + 2Cl₂(g) AH° = -114 kj and AS = -129 J/K At standard conditions, this reaction would be product favored Oat all temperatures. at relatively high temperatures. at no temperature. at relatively low temperaturesarrow_forwardO-234 kJ 234 kJ -150. kJ -117 kJ Given: -1835kJ AH°, AHᵒf (kJ/mol) -941 -840 QUESTION 12 Use the standard reaction enthalpies given below to determine AH°rxn for the following reaction: P4(g) + 10 Cl₂(g) → 4 PC|5(s) PC15(s) → PC13(g) + Cl₂(g) P4(g) + 6 Cl₂(g) → 4 PCl3(g) rxn IF7(g) IF 5(9) 2(g) 62.42 = ? ΔΗ° rxn AH°rxn = +157 kJ = -1207 KJ QUESTION 13 Use the AH°f and AH°rxn information provided to calculate AH°f for IF: IF7(9) + 12(g) → IF5(g) + 2 IF(g) AH°rxn = -89 kJarrow_forwardGiven: 4AI(s) + 302(g) 2A1203(s) AH° = -3,340 kJ Determine AH for the reaction: 2AI(s) + 3/½02(g) Al203(s) O A. 6,680 kJ O B. -6,680 kJ O C. 1670 kJ O D. -1,670 kJ IIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY