
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:* 00
T
# 3
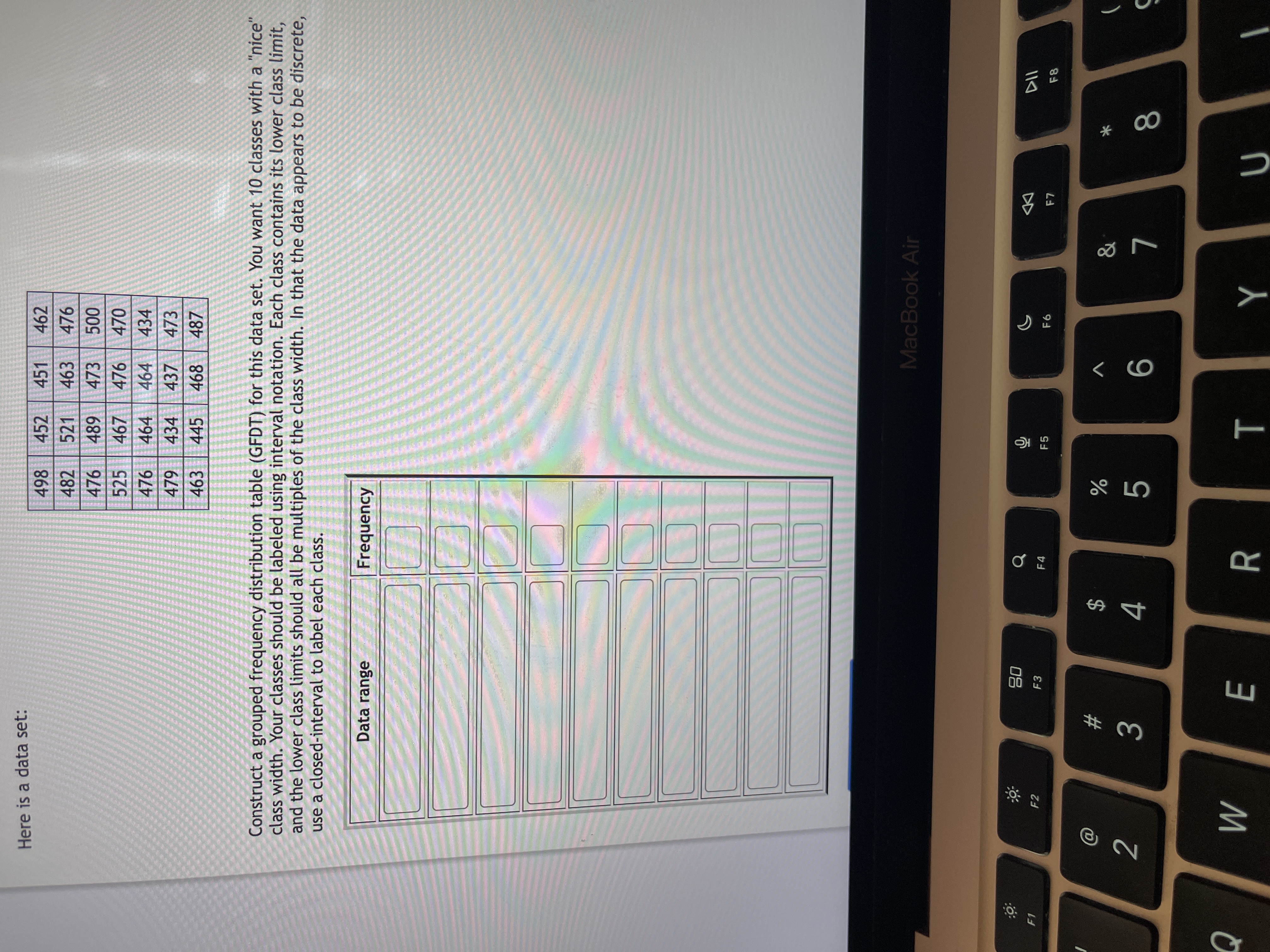
Here is a data set:
498
452
451
462
482
521
463
476
476 489
000
470
473
525
467
476
476
464
464
434
479
434
437
473
463
445
468
487
Construct a grouped frequency distribution table (GFDT) for this data set. You want 10 classes with a "nice'
class width. Your classes should be labeled using interval notation. Each class contains its lower class limit,
and the lower class limits should all be multiples of the class width. In that the data appears to be discrete,
use a closed-interval to label each class.
Data range
Frequency
MacBook Air
08
F3
F1
F2
F4
DD
F5
F8
$
)
2.
M
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A sample of size 50 will be drawn from a population with mean 76 and standard deviation 14. Find the 69th percentile of x.arrow_forward43arrow_forwardA data set with whole numbers has a low value of 20 and a high value of 110. Find the class width for a frequency table with seven classes. Find the class limits for a frequency table with seven classes. Lower class limit - Upper class limit First class Second class Third class Fourth class Fifth class Sixth class Seventh classarrow_forward
- Here is a data set: 589 301 420 232 390 385 372 326 312 449 307 459 589 105 271 589 292 337 410 314 366 231 309 423 382 425 457 273 Construct a grouped frequency distribution table (GFDT) for this data set. You want 10 classes with a "nice" class width. Your classes should be labeled using interval notation. Each class contains its lower class limit, and the lower class limits should all be multiples of the class width. In that the data appears to be discrete, use a closed-interval to label each class.arrow_forwardHere is a data set: 262 143 161 311 307 150 234 204 174 210 128 273 228 183 184 260 128 243 209 311 190 169 197 179 190 155 188 311 Construct a grouped frequency distribution table (GFDT) for this data set. You want 10 classes with a "nice" class width. Each class contains its lower class limit, and the lower class limits should all be multiples of the class width. Note: the data ranges will be hand graded after the due date for this assignment. If your frequencies are marked correct, you most likely have the classes correct.arrow_forwardHere is a data set: Data range 210-229 230-249 250-269 270-289 290-309 214 217 219 223 228 238 241 245 247 253 253 254 X Construct a frequency distribution table for this data set. • Number of classes: 10 • Use a "nice" class width, such as a multiple of 5 or 10. • Label classes using interval notation. • For example, if the class is 70-79, label it as [70,79]. The lower class limit should be a multiple of the class width. • • For example, if the class width is 10, the lower class limit should be a number like 30 or 40 (depending on the data). X 5 263 265 286 291 X 4 50 11 250 X 2 256 X 8 10% Frequency 28 266 269 287 290 291 303 305 307 56 259 262 Xarrow_forward
- Here is a data set: 430 584 450 343 458 737 498 265 665 412 643 466 356 338 644 599 466 577 495 436 456 476 516 503 497 675 421 334 Construct a grouped frequency distribution table (GFDT) for this data set. You want 10 classes with a "nice" class width. Your classes should be labeled using interval notation. Each class contains its lower class limit, and the lower class limits should all be multiples of the class width. In that the data appears to be discrete, use a closed-interval to label each class.arrow_forwardIdentify the lower class limits, upper class limits, class width, class midpoints, and class boundaries for the given frequency distribution. Also identify the number of individuals included in the summary. Blood Platelet Count of Females (1000 cells/uL) Frequency 100-199 200-299 24 91 26 300-399 400-499 1 500-599 4 Identify the lower class limits. 00000 (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. Use ascending order.) Identify the upper class limits. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. Use ascending order.) Identify the class width. Enter your answer in each of the answer boxes.arrow_forward* 00 T O LO R Question 18 Here is a data set: 218 75 129 105 35 133 98 95 37 112 61. 154 696 LL 114 167 35 09 06 174 167 124 83 98 Construct a grouped frequency distribution table (GFDT) for this data set. You want 10 classes with a "nice" class width. Your classes should be labeled using interval notation. Each class contains its lower class limit, and the lower class limits should all be multiples of the class width. In that the data appears to be discrete, use a closed-interval to label each class. Data range Frequency MacBook Air 08 F3 F1 F2 F4 F 7 #3 24 1 2 3. 4. A H. Z B. W Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman