
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
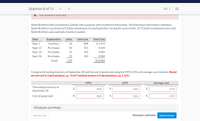
Transcribed Image Text:Question 8 of 13
< >
0/1
Your answer is incorrect.
Splish Brothers sells a snowboard, EZslide, that is popular with snowboard enthusiasts. The following is information relating to
Splish Brothers's purchases of EZslide snowboards during September. During the same month, 107 EZslide snowboards were sold.
Splish Brothers uses a periodic inventory system.
Date
Explanation
Units
Unit Cost
Total Cost
Sept. 1
Inventory
13
$98
$ 1,274
Šept. 12
Purchases
44
101
4,444
Sept. 19
Purchases
52
102
5,304
Sept. 26
Purchases
20
103
2.060
Totals
129
$13,082
Compute the ending inventory at September 30 and the cost of goods sold using the FIFÓ, LIFÓ, and average-cost methods. (Round
per unit cost to 3 decimal places, e.g. 15.647 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,125.)
FIFO
LIFO
Average-cost
The ending inventory at
September 30
2$
2060
2$
2266
$
1274
Cost of goods sold
2060
2$
2266
2$
1274
eTextbook and Media
Save for Later
Attempts: unlimited
Submit Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- REI sells snowboards. Assume the following information relates to REI's purchases of snowboards during September. During the same month, 106 snowboards were sold. REI uses a periodic inventory system. Date Sept. 1 Sept. 12 Sept. 19 Sept. 26 Explanation Units Unit Cost Inventory Purchases Purchases Purchases Totals 15 42 57 21 135 $100 103 104 105 Total Cost $1,500 4,326 5,928 2,205 $13,959arrow_forwardABC Company employs a periodic inventory system and sells its inventory to customers for $20 per unit. ABC Company had the following inventory information available for May: May 1 May 3 May 8 May 13 May 18 May 20 May 24 May 30 Beginning inventory 1,900 units @ $10.20 cost per unit Purchased 2,100 units @ $11.60 cost per unit Sold 1,400 units Purchased 3,700 units @ $8.10 cost per unit Sold 2,600 units Purchase 4,100 units @ $14.70 cost per unit Sold 2,900 units Purchased 2,200 units @ $12.60 cost per unit During May, ABC Company reported operating expenses of $14,000 and had an income tax rate of 36%. Calculate the amount of net income shown on ABC Company's income statement for May using the LIFO method.arrow_forwardplease answer within the format by providing formula the detailed workingPlease provide answer in text (Without image)Please provide answer in text (Without image)Please provide answer in text (Without image)arrow_forward
- Dorothy's Boards sells a snowboard, Xpert, that is popular with snowboard enthusiasts. Information relating to Dorothy's purchases of Xpert snowboards during September is shown below. During the same month, 126 Xpert snowboards were sold. Dorothy's uses a periodic inventory system. Date Sept. 1 Sept. 12 Sept. 19 Sept. 26 (a) Explanation Inventory Purchases (b) Purchases Purchases Totals Units Unit Cost 29 Cost of goods sold 45 20 Your Answer Correct Answer (Used) 50 e Textbook and Media 144 $95 102 104 105 The ending inventory at September 30 $ Total Cost $ $ 2,755 Compute the ending inventory at September 30 and cost of goods sold using the FIFO and LIFO methods. 4,590 2,080 5,250 $14,675 FIFO The sum of ending inventory and cost of goods sold $ 1,890 12,785 For both FIFO and LIFO, calculate the sum of ending inventory and cost of goods sold. $ FIFO $ LIFO 1.710 12.965 LIFOarrow_forwardVaughn Boards sells a snowboard, Xpert, that is popular with snowboard enthusiasts. Information relating to Vaughn's purchases of Xpert snowboards during September is shown below. During the same month. 98 Xpert snowboards were sold. Vaughn's uses a periodic inventory system. Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Cost Sept. 1 Inventory 23 HK$970 HK$ 22,310 Sept. 12. Purchases 37 1,020 37,740 Sept. 19 Purchases 13 1.040 13,520 Sept. 26 Purchases 47 1,050 49.350 Totals 120 HK$122.920 (a) Compute the ending inventory at September 30 and cost of goods sold using the FIFO and average-cost methods. (Round per unit cost to 3 decimal places, eg. 15.125 and final answers to O decimal places, eg. 125) FIFO Average-Cost The ending inventory at September 30 HK$ HK$ Cost of goods sold HK$ HK$ (b) For both FIFO and average-cost, calculate the sum of ending inventory and cost of goods sold. (Round per unit cost to 3 decimal places, eg. 15.125 and final answers to O decimal places, eg 125) FIFO…arrow_forwardHans Inc. is a merchandising company that resells equestrian saddles. The company’s inventory data is as follows: Cost of Goods Available for Sale Jan. 1 Beginning Balance 3 units @ $200 = $600 Jan. 5 Purchase 2 units @ $400 = $800 Jan. 20 Purchase 3 units @ $500 = $1,500 Retail Sales of Goods Jan. 15 Sales 2 units @ $800 = $1,600 Jan. 31 Sales 1 units @ $1,000 = $1,000 For the January 15th sale, the company sold 1 unit that originally cost $200 and 1 unit that cost $400. For the January 31st sale, the 1 unit sold originally had a cost of $500. Using the Weighted Average method, the cost of goods sold for January would be: Answer formatting -when typing in your answer please include a dollar sign, a comma if necessary, use whole numbers, omit any periods, and make sure your response has no spaces. For example, $1,200arrow_forward
- Bonita Company sells one product. Presented below is information for January for Bonita Company. Jan. 1 4 11 13 20 27 Inventory 109 units at $4 each 85 units at $8 each 137 units at $7 each 109 units at $9 each 151 units at $7 each 93 units at $11 each Sale Purchase Sale Purchase Sale Bonita uses the FIFO cost flow assumption. All purchases and sales are on account.arrow_forwardREI sell snowboards. Assume the following information relates to REI's purchases of snowbourds during tegnember During the same month, 100 snowboards were sold REloses a periodic inventory system Dale Sept. 1 Sept. 12 Sept 19 Sept. 26 Explanation Unit Unit Cont Inventory 15 $110 Purchases 48 113 Purchases 33 114 Purchases 24 115 Totals 140 Compute the ending inventory at September 30 using FIFO LIFO, and average-cost. (Round average cost per 3 decimal places eg. 125.153 and final answers to 0 decimal places 125 Ending inventory at September 30 eTextbook and Media FIFO Your answer is incorrect Cost of goods sold 2775 FIFO $1.630 5,424 6042 3.760 $15.876 13654 LIFO Compute the cost of goods sold for the month using the FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost methock Mound average cost per unit to 3 decimal ploces, eg 125 153 end final enmers to 0 alecimal places, 1253 1344 UFD ETDA AVERAGE-COST $ 3402 AVERAGE-COST 130825arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Trey Monson starts a merchandising business on December 1 and enters into the following three inventory purchases. Monson uses a perpetual inventory system. Also, on December 15, Monson sells 15 units for $34 each. Purchases on December 7 Purchases on December 14 10 units @ $20.00 cost 20 units @ $26.00 cost Purchases on December 21 15 units @ $28.00 cost Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on the LIFO method.arrow_forward
- Mary's Boards sells a snowboard, Xpert, that is popular with snowboard enthusiasts. Information relating to Mary's purchases of Xpert snowboards during September is shown below. During the same month, 119Xpertsnowboards were sold. Mary's uses a periodic inventory system. Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Cost Sept 1 Inventory 25 $95 $2,375 Sept. 12 Purchases 45 100 4.500 Sept 19 Purchases 20 102 2,040 Sept. 26 Purchases 50 103 5.150 Totals 140 $14.065 (a) Compute the ending inventory at September 30 and cost of goods sold using the FIFO and LIFO methods. FIFO LIFO The ending inventory at September 30 Cost of goods soldarrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardHans Inc. is a merchandising company that resells equestrian saddles. The company’s inventory data is as follows: Cost of Goods Available for Sale Jan. 1 Beginning Balance 3 units @ $200 = $600 Jan. 5 Purchase 2 units @ $400 = $800 Jan. 20 Purchase 3 units @ $500 = $1,500 Retail Sales of Goods Jan. 15 Sales 2 units @ $800 = $1,600 Jan. 31 Sales 1 units @ $1,000 = $1,000 For the January 15th sale, the company sold 1 unit that originally cost $200 and 1 unit that cost $400. For the January 31st sale, the 1 unit sold originally had a cost of $500. Using the LIFO method, the cost of goods sold for January would be: Answer formatting -when typing in your answer please include a dollar sign, a comma if necessary, use whole numbers, omit any periods, and make sure your response has no spaces. For example, $1,200arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education