
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
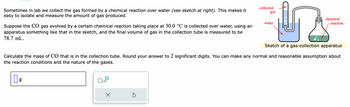
Transcribed Image Text:Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the CO gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 30.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be
78.7 mL.
g
x10
X
collected
S
gas
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
Calculate the mass of CO that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about
the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases.
water
chemical
reaction
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
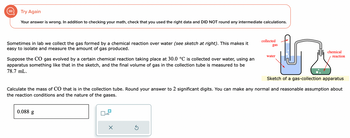
Transcribed Image Text:Try Again
Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations.
Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the CO gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 30.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be
78.7 mL.
0.088 g
x10
X
U
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
S
collected
gas
Calculate the mass of CO that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about
the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases.
water
chemical
reaction
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
the format of the answer is still incorrect, please give me the answer in decimal form .
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
That is not the correct answer and it must contain only 2 significant figures. Please try again!
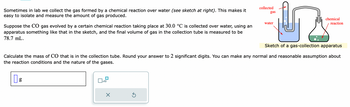
Transcribed Image Text:Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the CO gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 30.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be
78.7 mL.
g
x10
X
collected
S
gas
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
Calculate the mass of CO that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about
the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases.
water
chemical
reaction
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Try Again
Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations.
Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the CO gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 30.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be
78.7 mL.
0.088 g
x10
X
U
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
S
collected
gas
Calculate the mass of CO that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about
the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases.
water
chemical
reaction
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
the format of the answer is still incorrect, please give me the answer in decimal form .
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
That is not the correct answer and it must contain only 2 significant figures. Please try again!

Transcribed Image Text:Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the CO gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 30.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be
78.7 mL.
g
x10
X
collected
S
gas
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
Calculate the mass of CO that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about
the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases.
water
chemical
reaction
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- collected Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced. gas chemical reaction water Suppose the 0, gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0 °C is collected over water, using an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be 58.2 mL. Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus alo Calculate the mass of O, that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases. ? Explanation Check © 2021 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibilityarrow_forwardSometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced. Suppose the O2 gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0°C is collected over water, using an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be 76.9mL. Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus Calculate the mass of O2 that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases. = garrow_forwardetermine the total volume of all gases formed when 75.0 mL an explosive (C3H5(NO3)3 , d = 1.60 g/mL, molar mass = 227.10 g/mol) reacts according to the following reaction. Assume room temperature and pressure conditions. 4 C3H5(NO3)3(l) → 6 N2(g) + O2(g) + 12 CO2(g) + 10 H2O(g)arrow_forward
- Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced. Suppose the CO₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 55.0 °C is collected over water, using an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be 129. mL. g x10 177 Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus x collected gas Calculate the mass of CO₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases. water chemical reactionarrow_forwardSometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced. Suppose the O2 gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 35.0°C is collected over water, using an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be 48.7mL. Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus Calculate the mass of O2 that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases. = garrow_forwardSometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced. collected gas chemical water reaction Suppose the C0, gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 45.0 °C is collected over water, using 圖 an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be 32.9 mL. Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus Calculate the mass of CO, that is in the collection tube, Round your answer to 2 significant digits, You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases. Help Explanation Check étv 30 DII 110 F7 F3 & 24 % 09 %23 7 5 2 3arrow_forward
- Constants | Periodic Table A gas of unknown molecular mass was allowed to effuse through a small opening under constant-pressure conditions. It required 105 s for 1.0 L of the gas to effuse. Under identical experimental conditions it required 29 s for 1.0 L of O2 gas to effuse. ▾ Part A Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. (Remember that the faster the rate of effusion, the shorter the time required for effusion of 1.0 L; that is, rate and time are inversely proportional.) Express your answer in grams per mol to two significant figures. M = Ο ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer 3+ < Return to Assignment Provide Feedback a % ? g/mol MacBook Pro 曲 Carrow_forward1.541x10-4 mol of an unidentified gaseous substance effuses through a tiny hole in 83.7 s. Under identical conditions, 1.909×10-4 mol of argon gas takes 86.0 s to effuse. What is the molar mass of the unidentified substance (in g/mol)? g/mol 1 ptsarrow_forwardHow many grams of NaClO3 were decomposed?arrow_forward
- Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced. collected gas chemical reaction water Suppose the CÓ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 30.0 °C is collected over water, using an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be 131. mL. Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus alo Calculate the mass of CO that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases. Explanation Check O 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center| Acce: 12:05 AM ENG 42°F Cloudy 1/22/202 DELLarrow_forward#14arrow_forwardSometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced. Suppose the H₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 30.0 °C is collected over water, using an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be 116. mL. g G Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus X collected gas water Calculate the mass of H₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases. chemical reactionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY