
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781337398909
Author: Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
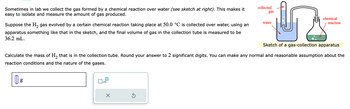
Transcribed Image Text:Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the H₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be
36.2 mL.
x10
X
y
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
Ś
collected
gas
Calculate the mass of H₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the
reaction conditions and the nature of the gases.
|| g
water
chemical
reaction
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
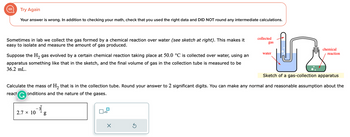
Transcribed Image Text:Try Again
Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations.
Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the H₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube measured to be
36.2 mL.
2.7 × 10
_3__8
g
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
Calculate the mass of H₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the
react G onditions and the nature of the gases.
x10
X
collected
Ś
gas
water
chemical
reaction
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Try Again
Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations.
Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the H₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube measured to be
36.2 mL.
2.7 × 10
_3__8
g
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
Calculate the mass of H₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the
react G onditions and the nature of the gases.
x10
X
collected
Ś
gas
water
chemical
reaction
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Many nitrate salts can be decomposed by heating. For example, blue, anhydrous copper(II) nitrate produces the gases nitrogen dioxide and oxygen when heated. In the laboratory, you find that a sample of this salt produced a 0.195-g mixture of gaseous NO2 and O2 with a total pressure of 725 mm Hg at 35 C in a 125-mL flask (and black, solid CuO was left as a residue). What is the average molar mass of the gas mixture? What are the mole fractions of NO2 and O2 in the mixture? What amount of each gas b in the mixture? Do these amounts reflect the relative amounts of NO2 and O2 expected based on the balanced equation? Is it possible that the fact that some NO2 molecules combine to give N2O4 plays a role? Heating copper(II) nitrate produces nitrogen dioxide and oxygen gas and leaves a residue of copper(ll) oxide.arrow_forward47 HCl(g) reacts with ammonia gas, NH3(g), to form solid ammonium chloride. If a sample of ammonia occupying 250 mL at 21 C and a pressure of 140 torr is allowed to react with excess HCl, what mass of NH4Cl will form?arrow_forwardYou have a 550.-mL tank of gas with a pressure of 1.56 atm at 24 C. You thought the gas was pure carbon monoxide gas, CO, but you later found it was contaminated by small quantities of gaseous CO2 and O2. Analysis shows that the tank pressure is 1.34 atm (at 24 C) if the CO2 is removed. Another experiment shows that 0.0870 g of O2 can be removed chemically. What are the masses of CO and CO2 in the tank, and what is the partial pressure of each of the three gases at 25 C?arrow_forward
- Pyruvic acid, HC3H3O3, is involved in cell metabolism. It can be assayed for (that is, the amount of it determined) by using a yeast enzyme. The enzyme makes the following reaction go to completion: HC3H3O3(aq)C2H4O(aq)+CO2(g) If a sample containing pyruvic acid gives 21.2 mL of carbon dioxide gas, CO2, at 349 mmHg and 30C, how many grams of pyruvic acid are there in the sample?arrow_forwardA mixture contained zinc sulfide, ZnS, and lead sulfide, PbS. A sample of the mixture weighing 6.12 g was reacted with an excess of hydrochloric acid. The reactions are ZnS(s)+2HCL(aq)ZnCl2(aq)+H2S(g)PbS(s)+2HCL(aq)PbCl2(aq)+H2S(g) If the sample reacted completely and produced 1.049 L of hydrogen sulfide, H2S, at 23C and 762 mmHg, what were the percentages of ZnS and PbS in the mixture?arrow_forwardYou have a gas, one of the three known phosphorus-fluorine compounds (PF3, PF3, and P2F4). To find out which, you have decided to measure its molar mass. (a) First, yon determine that the density of the gas is 5.60 g/L at a pressure of 0.971 atm and a temperature of 18.2 C. Calculate the molar mass and identify the compound. (b) To check the results from part (a), you decide to measure the molar mass based on the relative rales of effusion of the unknown gas and CO2. You find that CO2 effuses at a rate of 0.050 mol/min, whereas the unknown phosphorus fluoride effuses at a rate of 0.028 mol/min. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas based on these results.arrow_forward
- Plot the data given in Table 5.3 for oxygen at 0C to obtain an accurate molar mass for O2. To do this, calculate a value of the molar mass at each of the given pressures from the ideal gas law (we will call this the apparent molar mass at this pressure). On a graph show the apparent molar mass versus the pressure and extrapolate to find the molar mass at zero pressure. Because the ideal gas law is most accurate at low pressures, this extrapolation will give an accurate value for the molar mass. What is the accurate molar mass?arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide, CO2, was shown lo effuse through a porous plate at the rate of 0.033 mol/min. The same quantity of an unknown gas, 0.033 moles, is found to effuse through the same porous barrier in 104 seconds. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas.arrow_forwardA 21.4-mL volume of hydrochloric acid reacts completely with a solid sample of MgCO3. The reaction is 2HCl(aq)+MgCO3(s)CO2(g)+H2O(l)+MgCl2(aq) The volume of CO2 formed is 159 mL at 23C and 731 mmHg. What is the molarity of the HCl solution?arrow_forward
- What volume, in milliliters, of hydrogen gas at 1.33 atm and 33 C is produced by the reaction of 0.0223 g lithium metal with excess water? The other product is LiOH.arrow_forward54 One way to generate oxygen is to heat potassium chlorate, KClO3. (The other product is potassium chloride.) If 386 mL of oxygen at 41 C and 97.8 kPa is generated by this reaction, what is the minimum mass of KClO3used?arrow_forward105 The decomposition of mercury(II) thiocyanate produces an odd brown snake-like mass that is so unusual the process was once used in fireworks displays. There are actually several reactions that take place when the solid Hg(SCN)2 is ignited: 2Hg(SCN)2(s)2HgS(s)+CS2(s)+C3N4(s)CS2(s)+3O2(g)CO2(g)+2SO2(g)2C3N4(s)3(CN)2(g)+N2(g)HgS(s)+O2(g)Hg(l)+SO2(g) A 42.4-g sample of Hg(SCN)2 is placed into a 2.4-L vessel at 21°C. The vessel also contains air at a pressure of 758 torr. The container is sealed and the mixture is ignited, causing the reaction sequence above to occur. Once the reaction is complete, the container is cooled back to the original temperature of 21°C. (a) Without doing numerical calculations, predict whether the final pressure in the vessel will be greater than, less than, or equal to the initial pressure. Explain your answer. (b) Calculate the final pressure and compare your result with your prediction. (Assume that the mole fraction of O2 in air is 0.21.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning