
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
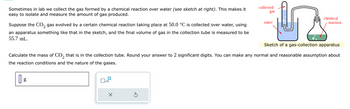
Transcribed Image Text:Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the CO₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0 °C is collected over water, using
an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be
55.7 mL.
g
☐
☐x10
15
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
X
collected
gas
Calculate the mass of CO₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about
the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases.
water
chemical
reaction
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reaction: 4 PH3 (g) → P4 (g) + 6 H2 (g) In the reaction above, 0.075 mole of H2 is produced in a 2.0-L container over some time period. What concentration of PH3 is consumed over the same time period?arrow_forwardreceive ceredit. 1. Calculate the volume of gas at 175°C if its volume is 132 mL at 24°C at a constant pressure. 2. A tank contains 725 mL of compressed air at 1350. mmHg. Calculate the volume the compressed air will occupy at a pressure of 1860. mmHg at the same temperature. 6s Aus boo in . A sample of neon gas has a volume of 365 mL at 18°C and 675 torr. Calculate 855 m Hg and 38°C.arrow_forwardA gas system has initial volume and moles of 7.56 L and 0.537 moles. If the volume changes to 8.93 L, under conditions P and T, determine the number of moles.arrow_forward
- Which statement best describes why increasing pressure of a reaction involving gases will increase the rate of reaction? Increasing the pressure increases the surface area of the reactants. Increasing the pressure increases the kinetic energy of the reactants and will lead to more effective collisions. Increasing the pressure decreases the relative space of the reaction vessel and will lead to more collisions. Increasing the pressure increases the amount of reactants and will lead to more collisions.arrow_forwardDinitrogen monoxide gas is collected at 28.0 °C in an evacuated flask with a measured volume of 30.0 L. When all the gas has been collected, the pressure in the flask is measured to be 0.290 atm. Calculate the mass and number of moles of dinitrogen monoxide gas that were collected. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. mass: g dlo mole: |mol I Don't Know Submit O 2021 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward** 16. If nitrogen gas and oxygen gas are combined in a tank, they will be at the same tem- perature and fill the same volume. a) Basing your explanation on the kinetic theory of gases, as derived in Section 15.1, explain why you would find the total pressure in the tank by adding together the indi- vidual pressures of the nitrogen and oxygen acting alone. This conclusion is known as Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures. b) A 1-m³ tank contains 0.8 moles of nitrogen and 0.2 moles of oxygen at 300 K. What is the total pressure in the tank?arrow_forward
- [18]arrow_forwardwhat does STP stand for in chemistry what are the values of each letter explaining my STP is important to chemists working with gasesarrow_forwardIII. Que 1. Suppose you wanted to perform this experiment using aluminum metal. As- suming a volume of hydrogen of 65 mL, a final gas temperature of 25°C, and of aluminum, in grams, to be reacted. (Hint: Use the information about the a gas pressure of approximately 720 torr, calculate the appropriate amount hydrogen gas and work backwards. Be sure to include a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of aluminum with HCl to produce hydrogen gas.) Show your work. answer: grams Al =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY