
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
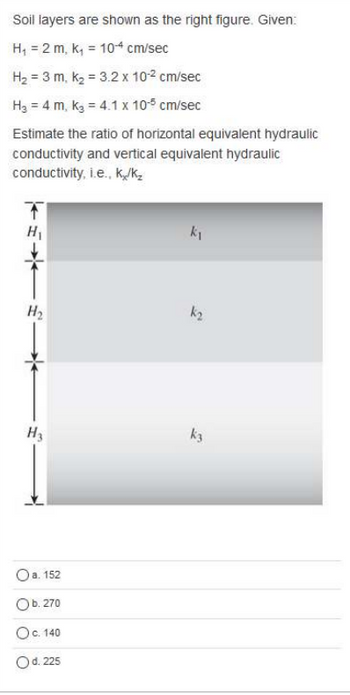
Transcribed Image Text:Soil layers are shown as the right figure. Given:
H₁ = 2 m, k₁ = 10-4 cm/sec
H₂ = 3 m, K₂ = 3.2 x 10-² cm/sec
H₂ = 4 m, K₂ = 4.1 x 10-5 cm/sec
Estimate the ratio of horizontal equivalent hydraulic
conductivity and vertical equivalent hydraulic
conductivity, i.e., k./k₂
T
*
H₂
H₂
a. 152
Ob. 270
O c. 140
O d. 225
k₁
k₂
k3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A constant head test is performed using a permeameter in the laboratory. The graduated cylinder collects 892 cm3 of water in 112 seconds. The soil specimen diameter = 18 cm , th elevation of water in upper-most piezometer is 181 com , the elevation of water in lowest piezometer is 116.6 cm and the piezometer inlets are evenly spaced at 16.7 cm on center. Compute the hydraulic conductivity, k and choose the correct answer below based on that. O A. 2.1 x 10^-3 cm/second O B. 1.5 x 10^-2 cm/second O C. 2.91 x 10^-2 cm/second O D. 2 x 10^-2 cm/second QUESTION 10 Given: -Applied stress on a soil = 122 kPa %3D -Influence Factor = 0.4 Compute the change in stress at 10 m below the edge of 25 m dimeter oil tank and select the correct answer from below: O A. Change in stress = 44 kPa O B. Change in stress = 49 kPa O C. Change in stress = 40 kPa O D. Change in stress = 42 kPa %3Darrow_forwardProblem (5) A layered soil is shown in following figure. a) Estimate the hydraulic conductivity for flow in the vertical direction. b) Estimate the equivalent hydraulic conductivity for flow in horizontal direction. c) calculate the ratio of ky(eg) /kh(eq) 1 m k = 10-3 cm/sec 1 m k = 2 × 10-4 cm/sec 1 m k = 10 cm/sec 1 m k = 2 × 10¬³ cm/secarrow_forwardAnswer in three decimal places pleasearrow_forward
- Consider a flow condition is given in figure below: % = 10 kN/m² 200 mm 100 mm 300 mm Yat = 20 kN/m² The head difference (in cm, in integer) which can cause the flow which can make effective stress zero in the soil at bottom would bearrow_forwardExplain and give answers pleasearrow_forwardIn the figure below, Dune sand is 100 60 80 60 Glacial till,- C₁ = 15.5 D10 =0.04 mm. Percent Finer by Weight 40 40 20 20 - Dune Sand C₁ = 1.8 D10 = 0.16 mm. Q ... Q Inorganic water deposited silt C₁₁ = 12.0 D10 = 0.001 mm. 0 10 5 1 0.5 0.1 0.05 0.01 0.005 0.001 0.0005 0.0001 Grain Size (mm) A poorly-graded soil B gap-graded soil well-graded soilarrow_forward
- Please do it in a complete way, so I can easily understand it. Thank you to all of youarrow_forwardSoil mechanicsarrow_forwardA cylindrical soil sample with length = 15cm and diameter = 4cm was taken from a site where a groundwater contamination piume was found. The sample was tested in the lab to determine its hydraulic conductivity. A hydraulic gradient of 0.05 was applied across the sample, and a flow rate of 0.025 cm³/sec was measured. Calculate the hydraulic conductivity of the soil sample using Darcy's law.arrow_forward
- For a falling head permeability test, the following values are given: Length of specimen: 200 mm Area of specimen:1000 sq. mm Area of standpipe: 40 sq. mm Head difference at t= 0: 500 mm Head difference at t= 180 sec : 300 mm Determine the hydraulic conductivity (cm/sec)arrow_forwarda. For Figure 2 below, calculate the effective hydraulic conductivity for flow parallel and perpendicular to layering. Show your work. Explain the difference in values. Figure 2 sand layer; K = 1 m/d; thickness = 5 d 10.5 m clay layer; K = 0.000001 m/d; thickness = 0.5 m sand laver: K = 1 m/d; thickness = 5 m b. Figure 3 below shows the effects of groundwater refraction, assuming that groundwater flow in the top layer is almost horizontal i.e., a = 89.8°, what is B and what can you say about the flow in the clay layer? a a K, b B K Figure 3.arrow_forwardThe soil under a dam consists of five layers as follows: Hydraulic conductivity (cm/hr) Layer Depth (m) 1 5 4.8 2 2 8.0 3 0.6 18.0 4 1.0 3.0 5 3.5 1 Calculate: v What is the average vertical (perpendicular to flow) hydraulic conductivity of the soil? V What is the transmissivity of the soil, given the water table is at the ground surface?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning