
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Attached is a graph diagram depicting the market for soft drinks. If an excise tax equal to $1 per liter is levied on soft drink sellers, please answer the following questions:
1. Buyers would spend a total of $___________ million on soft drinks.
2. Sellers would receive a total of $____________ million (after-tax) from selling soft drinks.
3. The government revenue from this tax would be $____________ million.
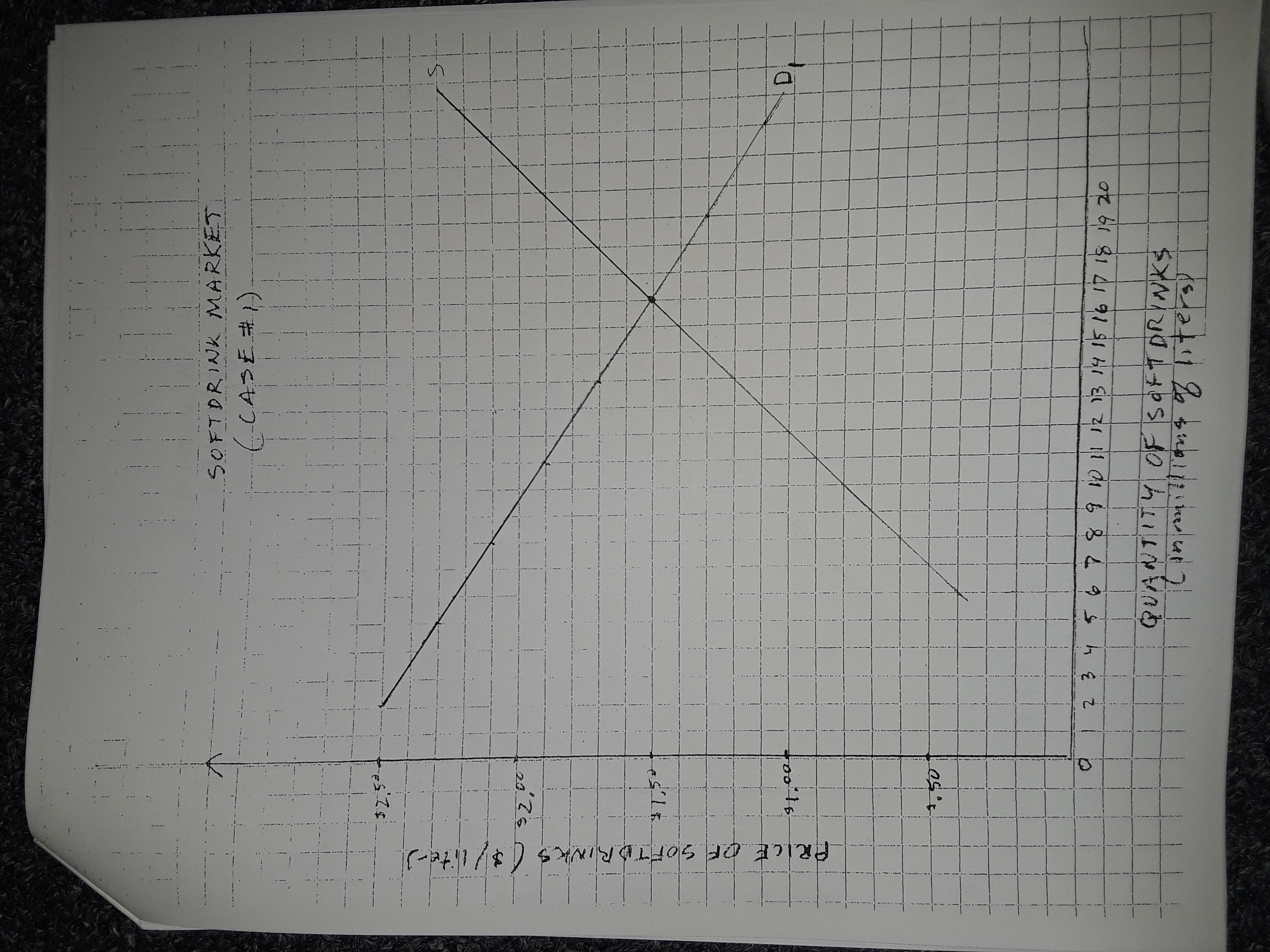
Transcribed Image Text:SOFTDRINK MARKET
(.CASE#1)
$2.52
too16
2 3 4 56 7891012 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20
QUANTIT
८१ ६ প
OF SOFTDRINKS
PRICE OF SOFTDRINKS ($/ite-)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If the state government would like to increase tax revenue, please give three examples of products/commodities that the government should impose tax on so that they can collect the highest amount of tax revenue. Please explain your reasons clearly.arrow_forward5arrow_forwardTo answer Questions #1-3, refer to the following diagram, which shows the monthly cigarette market in Wake County, North Carolina and the demand for, and supply of, cigarettes before and after the imposition of a $5.00-dollar per unit excise tax. Exam 2, Figure1-The Wake County Market for Cigarettes Per Pack Price Supply with tax 20.00 Supply before tax 18.00 16.00 Demand 10.00 Quantity Per Year (Milions of Packs) Ceteris paribus, how much will the government collect in annual tax revenue from this tax? Select one: a. $5 million b. $10 million C. $15 million d. $20 millionarrow_forward
- Q)Economics If the tax elasticity of supply is 0.16, by how much will the quantity supplied increase when the marginal tax rate decreases from 40 to 36 percent?arrow_forwardThe market supply and demand for a product are shown in the diagram below. Now supose the government imposes a per-unit tax of $1 on producers. (i) What happens to total revenue received by producers after they pay the tax to the government? Explain. (ii) Will producer surplus increase, decrease, or stay the same? (iii) Will total surplus increase, decrease, or stay the same? Explain.arrow_forward9) The following graph shows the effect of a per-ticket tax on plane tickets from Boston to Tampa. Use the graph to answer questions 5 to 10. $30 $20 $10 Price (P) of airline tickets (in dollars per ticket) How much of the per-ticket tax is paid by passengers? $40 230 200 190 2850 3000 Swith tax Sno tax D Figure 14 Image author created Quantity (Q) of airline tickets (thousands per day)arrow_forward
- 4 Is it true, as many people claim, that taxes assessed on producers are passed along to consumers? That is, do consumers pay for the entire tax?arrow_forward6) The following graph shows the effect of a per-ticket tax on plane tickets from Boston to Tampa. Use the graph to answer questions 5 to 10. O $10 $30 $40 Price (P) of airline tickets (in dollars per ticket) What is the amount of the tax per ticket from Boston to Tampa? $20 230 200 190 2850 3000 with tax D Sno tax Figure 14 Image author created Quantity (Q) of airline tickets (thousands per day)arrow_forwardols 4. The Laffer curve Government-imposed taxes cause reductions in the activity that is being taxed, which has important implications for revenue collections. To understand the effect of such a tax, consider the monthly market for champagne, which is shown on the following graph. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph, Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. PRICE (Dollars per case) 22***RES 40 35 Show Transcribed Text AX REVENUE (Dolan) 018 27 345 54 63 72 81 00 QUANTITY (Cases) Suppose the government imposes a $10-per-case tax on suppliers. At this tax amount, the equilibrium quantity of champagne is [ . 648 576 504 432 360 204 3214 144 72 D Supply . Demand Now calculate the government's tax revenue if it sets a tax of $0, $10, $20, $25, $30, $40, or $50 per case. (Hint: To find the equilibrium quantity…arrow_forward
- Suppose that the local government of Santa Fe decides to institute a tax on soda consumers. Before the tax, 45,000 liters of soda were sold every week at a price of $10 per liter. After the tax, 38,000 liters of soda are sold every week; consumers pay $14 per liter (including the tax), and producers receive $8 per liter. The amount of the tax on a liter of soda is 3 that falls on producers is 5 per liter. True or False: The effect of the tax on the quantity sold would have been the same as if the tax had been levied on producers. True per liter. Of this amount, the burden that falls on consumers is 3 O False per liter, and the burdenarrow_forwardSuppose that the demand for digital pianos is price inelastic and the supply of digital pianos is price elastic. By what amount will a tax of $1.00 per piano levied on buyers of pianos increase the equilibrium price paid by buyers of digital pianos? by $1.00 by less than $0.50 by more than $0.50 but less than $1.00 by more than $1.00arrow_forwardQuestion 5 Suppose that the government imposes a tax on cigarettes. Use the diagram below to answer the questions. D is the demand curve before tax, S is the supply curve before tax and St is the supply curve after the tax. Price 18 12 10 10 12 Qua (a) For the market for cigarettes without the tax. Indicate: Price paid by consumers (1) Price paid by producers (ii) Quantity of cigarettes sold (iv) Buyer's reservation price (v) Seller's reservation price Seller's reservation price Choose. + Choose. + Choose. Price paid by consumers Choose. + 12 18 Quantity of cigarettes sold Choose. 10 7 Buyer's reservation price 3 Choose. 8 Price paid by producers Choose.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education