
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please show full steps and explain
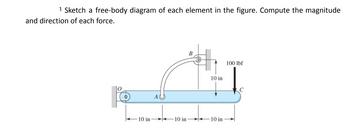
Transcribed Image Text:### Mechanics: Analyzing Forces on a Beam
#### Problem Statement:
**Sketch a free-body diagram of each element in the figure. Compute the magnitude and direction of each force.**
#### Diagram Description:
The diagram illustrates a beam with multiple forces and pivots. The beam is horizontally aligned and fixed at one end (O) to a wall. The distance from O to point A is 10 inches, from A to B is another 10 inches, and from B to C is 10 inches.
- **Dimensions:**
- O to A: 10 inches
- A to B: 10 inches
- B to C: 10 inches
- **Forces:**
- A vertical force of 100 lbf is acting downward at point C.
- **Other Elements:**
- The beam is supported by a curved member connected at point B.
- The vertical distance from point B to the beam at point C is 10 inches.
#### Steps for Solving the Problem:
1. **Sketch a Free-Body Diagram:**
- Identify and indicate all forces acting on the beam.
- Include reaction forces at the support point O.
- Mark the applied load at point C and the directions of the forces.
- Show the points of application of forces and distances between these points.
2. **Compute the Magnitude and Direction of Each Force:**
- Apply the equations of static equilibrium to solve for unknown forces:
- Sum of Vertical Forces (`ΣFy = 0`)
- Sum of Horizontal Forces (`ΣFx = 0`)
- Sum of Moments about any point (`ΣM = 0`)
3. **Detailed Analysis:**
- Calculate the reactions at the fixed support (O).
- Calculate the forces in the curved member connected at point B by considering the geometry and the external force applied at point C.
- Break down forces into their components if necessary, especially if calculating moments around a point.
#### Graph/Diagram Explanation:
- **Graph:** The beam is shown with a horizontal alignment. Each measurement and force is labeled for clarity.
- **Connections:** The beam is fixed at one end (O) with a pin support and has a curved member at B, stressing the beam through C.
- **Load Applied:** A vertical force of 100 lbf acting downward at point C.
By carefully analyzing the forces and using principles of statics,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For moments if there is any take anti-clockwise as positive and clockwise as negative.For All answer are correct to 3 significant figures and if it starts with a 1 it must be rounded to 4 significant figures Please give asap I will give a likearrow_forwardI need these three parts answered (Multiple Choice). If you can not answer all three parts please leave it for another tutor to answer. Thank you. For the two holes identified as datum D, what is the total size tolerance specified for those holes? (Multiple Choice)a. .002'b. .003'c. .004'd. .006' The two holes identified as datum D have a counterbore on one end. What size toleranceis specified for the counterbore diameter? (Multiple Choice)a. .010″ (±.005″; see title block)b. .020″ (±.010″; see title block)c. .030″ (±.015″; see title block) What letter represents the revision status of this print? (Multiple Choice)ABCDarrow_forwardIf all of the words in the image shown below are supposed to have a common theme, then which of the following words is the best choice to replace the question mark in the image? Knuckles Palm Fingers Wrist ? Select the single best answer: A. ankle B. leg C. ear D. nails E. nosearrow_forward
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Please help ASAP. Rate will be given accordingly. Please write your answer on paper. Thank you so much. Note: The tolerance is ±1 in the third significant digit.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardTest-II. Write down all the operations or step by step procedure on how to create the object below. Write down also the name of the machines and the tools that you will use to complete the drawing below. 824 020 015 22 15 35 40 100 NOTE: ALL DIMENSIONS ARE IN MM ALL CHAMFERS ARE 1X 45arrow_forward
- Problem-AA: Consider the following system of equations: -123 = 1.5a + 25n 5 = -21a +n Calculate the two unknows.arrow_forwardCan someone please help to solve this question following the directions and showing neat work and formulas and drawing all needed diagrams. PLEASE AND THANK YOU!!!arrow_forwardOrthographics: Add missing lines and complete any missing views. Draw the isometricarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY