
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
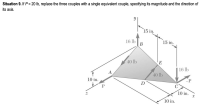
Transcribed Image Text:Situation 9. If P = 20 lb, replace the three couples with a single equivalent couple, specifying its magnitude and the direction of
its axis.
15 in.
16 lb
В
15 in.
40 lb
E
16 lb
A
40 lb
10 in.
-P
D
C
10 in.
10 in.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q1/ The weights of the various components of the truck are shown. Replace this system of forces by an equivalent resultant force and specify its location measured from B? Ans: R=- 10750 lb, d= 13.7 ft 3500 lb B 5500 lb) A 1750 lb tont -14 ft- 3 ft 2 ft ...arrow_forward4.4.4.4.4.4.4arrow_forwardReplace the loading acting on the frame by an equivalent resultant force and specify where the resultant's line of action intersects member AB (Figure 1). Suppose that F₁ = 200 lb, F2 = 100 lb, and M = 400 lb. ft. Figure x F₂ M 30⁰ -3 ft B 2 ft 4 ft 1 of 1 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. FR = Submit Part B 0 = Submit Part C Determine the angle between the resultant force and the x axis. Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures. y = ΠΑΣΦ Submit Provide Feedback Request Answer ↓↑ ΑΣΦ Request Answer ΑΣΦ vec ↓↑ vec Specify where the resultant's line of action intersects member AB, measured from A. Express your answer in feet to three significant figures. Request Answer ? vec ? lb O , measured counterclockwise from the positive x axis ft below Aarrow_forward
- Problem 3: If µs = 0.35 between all surfaces (but pulleys remain frictionless), then find the smallest force P required to move the blocks. P 60 lb B 40 lbarrow_forward2. Given the equations from Joint B Solve for the force in BD and BE. 600 lb 600 lb 600 lb 600 lb BD D 300 lb B. F 2 ft 4 in. 300 lb| 6 ft 1500 lb ВЕ E G H. 8 ft 8 ft→-8 ft→-8 ft 8. BD 8. ΣΕ-0= 1500| 8. BE 10 10 6. = 0 =1500 10 1, 600 – BD 8 6. + BE 10 3. Solve for x and y. 1200 lb 30°arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning