
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
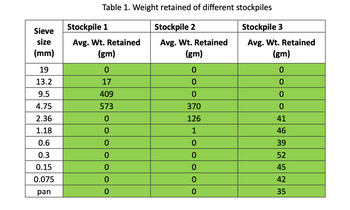
below shows the sieve size and corresponding weight retained for 3 different stockpiles. Calculate the percent passing for all the 3 aggregate stockpiles.
Transcribed Image Text:Sieve
size
(mm)
19
13.2
9.5
4.75
2.36
1.18
0.6
0.3
0.15
0.075
pan
Table 1. Weight retained of different stockpiles
Stockpile 2
Stockpile 3
Avg. Wt. Retained
Avg. Wt. Retained
(gm)
(gm)
Stockpile 1
Avg. Wt. Retained
(gm)
0
17
409
573
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
370
126
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
41
46
39
52
45
42
35
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- (c) Asphalt concrete mixture of AC 14 will be used to construct the wearing course layer. The coarse aggregate, fine aggregate and filler are used as materials to produce the asphalt concrete mixture. The aggregate gradation will be blended to fulfill the gradation limit according to JKR standard specification as shown in Table Q1(c)(i). Based on this statement, conclude the result of sieve analysis test of blended aggregate as shown in Table Q1(c)(ii). I Table Q1(c)(i): Gradation specification for AC 14 mixture BS Sieve Size (mm) Percentage passing by weight 28.0 20.0 14.0 10.0 5.0 3.35 1.18 0.425 0.150 0.075 100 90-100 76-86 50-62 40-54 18-34 12-24 6-14 4-8 I Act Go toarrow_forwardCoarse aggregate is placed in a rigid bucket and rodded with a tamping rod to determine its unit weight. The following data are obtained:Volume of bucket = 14 LWeight of empty bucket = 9.21 kgWeight of bucket filled with dry rodded coarse aggregate:Trial 1 = 34.75 kgTrial 2 = 34.06 kgMeasureSampleA B CWet Mass (g) 521.0 522.4 523.4Dry Mass (g) 491.6 491.7 492.1Absorption (%) 2.5 2.4 2.3Table P 5 . 9 determine the amount of water required to increase the moisture content of aggregate to reach absorption?5.9 Three samples of fine aggregate have the properties shown in Table Trial 3 = 35.74 kga. Calculate the average dry-rodded unit weightb. If the bulk dry specific gravity of the aggregate is 2.620, calculate thepercent voids between aggregate particles for each trial.arrow_forwardQuartering (or splitting) means reducing sample sizes into reasonable volumes. Would you expect every after each quartering (or splitting) process, the weight of the original aggregates would be reduced to half or almost half? Why or why not? Defend your reason.arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning