
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
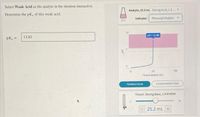
Transcribed Image Text:Select Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration interactive.
Analyte, 25.0 ml Strong Acid, 1.0.
Determine the pK, of this weak acid.
Indicator
Phenolphthalein
pink
14
pH=11.60
pK =
13.82
25
50
Titrant Added (ml)
Titration Curve
Concentration Chart
Titrant: Strong Base, 1.0 M MOH
50
25.2 mL +
Hd
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 25.00 mL of a weak monoprotic acid is titrated with a 2.00 M solution of NaOH. The following data is collected mL NaOH added PH 5.55 half-way point 2.50 equivalence point 5.00 saved Use the pH at the half-way point point to estimate the pK, of the acid. 00000 5.55 6.43 05.12 8.76 6.01 O 5.92arrow_forwardA Consider the pH titration curve above (pH vs volume in ml). The pk, of the weak base being titrated and the pH of the equivalence point are, respectively: 12 11 10 8 7 5 4 2 1 10 20 30 40 O 2.5 and 4.0 • 5.4 and 4.5 O 11.2 and 5.4 O 11.2 and 4.5 O 4.5 and 5.4 Based on the indicator information above, which of the following indicators could be used successfuly in the titration in Part A? (Select all correct responses. Indicator Colour (low pH – high pH) pK, methyl yellow red-yellow 3.1 methyl orange red-yellow 3.7 bromophenol blue yellow-blue 4.2 bromocresol green yellow-blue 4.7 methyl red pink-yellow 5.1 bromocresol purple bromothymol blue yellow-purple 6.3 yellow-blue 7.0 phenol red yellow-red 7.9 O phenol red cresol red yellow-red 8.3 O bromocresol purple thymol blue yellow-blue 8.9 O methyl yellow thymolphthalein colourless-blue 9.2 O bromothymol blue O thymol blue O thymolphthalein Part C Baseu on the table above, what colour is methyl orange at pH3? Submit Request Answer Part…arrow_forwardBuild a titration curve for the following scenarios. Make sure to label your accesses and anyother appropriate pieces of data. Each curve should have a minimum of 4 data points, but youcan use the following to help structure your curvea) Initial pHb) pH at Veqc) pH=pka (if applicable)d) pH when excess titrant is addede) Additional pH point near Veq for Strong Acid/Strong Base titrations (in order to see thesteepness of the slope) OR additional pH point in buffer zone for titrations with a Weakcompound.arrow_forward
- Consider how best to prepare one liter of a buffer solution with pH = 3.79 using one of the weak acid/conjugate base systems shown here. Weak Acid Conjugate Base Ka pKa HC2O4- C2O42- 6.4 x 10-5 4.19 H2PO4- HPO42- 6.2 x 10-8 7.21 HCO3- CO32- 4.8 x 10-11 10.32 How many grams of the sodium salt of the weak acid must be combined with how many grams of the sodium salt of its conjugate base, to produce 1.00 L of a buffer that is 1.00 M in the weak base?grams sodium salt of weak acid = grams sodium salt of conjugate base =arrow_forwardSelect Weak Acid as the analyte in the titration interactive. Analyte, 25.0 ml. Weak Acid, 1.0 ... Determine the pK, of this weak acid. Indicator No Indicator colorless 14 4.79 pKa Incorrect pH = 2.50 25 50 Titrant Added (mL) Titration Curve Concentration Chart Titrant: Strong Base, 1.0 M MOH 50 0.0 mL +arrow_forwardFind moles of NaOH added and equivalence pointarrow_forward
- A 100.0 mL acetic acid buffer solution contains 0.50 M CH3COOH and 0.50 M CH3COONa. What will the pH be after 0.020 mol of HCI has been added to the buffer solution? pk, of acetic acid = 4.74 5.11 4.74 8.89 None of these 9.62 4.38arrow_forwardM of NaOH: 0.100 Volume of HCI 25mL = 0.025L Moles of HCI = 2.5 mol What is the Volume of NaOH equivalence point: What is Moles of NaOH equaivalence point: What is pH at equivalence point? What is calculated pH and experimental pH of NaOH at 0.00 mL , 12.50 mL, 25mL, and 30 mL. Also what is the Error percentage for each one?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY