
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:34
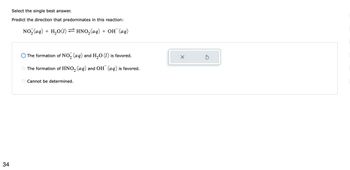
Select the single best answer.
Predict the direction that predominates in this reaction:
NO₂ (aq) + H₂O(1) ⇒ HNO₂(aq) + OH¯ (aq)
The formation of NO₂ (aq) and H₂O (1) is favored.
The formation of HNO₂ (aq) and OH(aq) is favored.
Cannot be determined.
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) is a strong base. Dissociation of potassium hydroxide follows the reaction equation given. KOH(s) --H20--> K+(aq) OH-(aq) a) Write down the reaction equation for a neutralization reaction where potassium hydroxide (KOH) reacts with sulphuric acid (H2SO4) producing potassium sulphate (K2SO4) and water (H2O). Balance if needed! b) Calculate pH for the solution where 0,2 mol of KOH is dissolved into water so that the total volume of the solution is 0,5 L.arrow_forwardGiven the equilibrium reactions below and their equilibrium constants. H3O+ (aq) + A (aq) ⇒ HA(aq) + H₂O (1) Kc1 = 2.5 x 104 A™ + H₂O(1) OH- (aq) (aq) + HA(aq) 2.5 x 10-10 What is the value of Kc for the reaction 2 H₂O) H3O+ + OH (aq) (aq) 1.0 x 10¹4 6.3 x 10-6 1.0 x 10-14 none of the answers are correct Kc2 =arrow_forwardPhosphoric acid, H3PO4, is a polyprotic acid. What is the THIRD ionization reaction for phosphoric acid in water? HPO (aq) → H+ (aq) + PO³ (aq) ○ H3PO4 (aq) → 3 H+ (aq) + PO¾- (aq) 4 H₂PO (aq) → HPO²¼¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) H3PO4 (aq) → H₂PO (aq) + H+ (aq)arrow_forward
- D Four solutions of an acid dissolved in water are sketched below, as if under a microscope so powerful individual atoms could be seen. The same volume of solution is shown in each sketch. Rank the solutions by the strength of the dissolved acid. That is, select 1 under the solution of the strongest acid, 2 under the solution of the next strongest acid, and so on. Note: Solution 1 (Choose one) 2 = H₂O Explanation Solution 3 (Choose one) ▼ W S ▼ Check 3 747 E D (Choose one) Solution 2 $ (Choose one) 4 Solution 4 R % 5 T X 80 G 6 3 MacBook Pro Y & 7 H © 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | A U 8 J 1 ( 9 ➡ K ) O O P Oarrow_forwardSodium reacts violently with water according to the equation: 2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) → 2 NaOH(aq) + H2(g) The resulting solution has a higher temperature than the water prior to the addition of sodium. What are the signs of AH° and AS° for this reaction? C) AH° is positive and AS is negative. A) AH° is negative and AS° is negative. OB) AH° is negative and AS° is positive. D) AH° is positive and AS° is positive.arrow_forwardHydrosulfuric acid, also known as hydrogen sulfide, is a diprotic acid. Its two stages of ionization are shown below: H2S (aq) = H* + HS'(aq) HS (aq) SH* + S² (aq) Kaj = 5.70 x 108 Kaz = 1.00 x 10 %3D Calculate the concentration of HS ion in a 0.222 M H2S solution. x 10 Enter your answer in scientific notation with three significant figures.arrow_forward
- 8:35 : Question 22 of 23 Submit Which one of the following correctly shows the weak acid equilibrium for trichloroacetic acid, CCl,COOH? A) CCl,COOH (aq) = CCl;CO* (aq) + OH- (aq) В) Cli,COOH (аq) + H,0 (I) — СCl,COOH, (aд) + ОН- (аф) C) CCl,COOH (aq) + H20 (1) = CCI,COO- (aq) + H30* (aq) D) CCl;COOH (aq) + H2O (I) CCl,CO(OH), (aq) + H* (aq) Tap here or pull up for additional resourcesarrow_forwardMethanoic acid is also called formic acid. It has the chemical formula HCOOH(l). It is a colourless fuming liquid that is mainly used as a preservative. It exhibits the following equilibrium in water:HCOOH(aq) + H2O(l) → HCOO–(aq) + H3O+(aq) 3) A 35.0 mL sample of (monoprotic) lactic acid, C3H6O3, is titrated with 20.0 mL of a 4.0 x 10-4 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution. What is the pH of the resulting solution at the equivalence point, if Ka for lactic acid is 1.4 x 10-4? PLEASE HELP THIS IS VERY URGENTarrow_forwardMatch the acid to the correct chemical equation showing its reaction with water. hydrochloric acid hypochlorous acid chlorous acid chloric acid perchloric acid A. HClO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ ClO2−(aq) + H3O+(aq) B. HCl(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ Cl−(aq) + H3O+(aq) C. HClO2(aq) + H2O(l) → ClO2−(aq) + H3O+(aq) D. HClO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ ClO3−(aq) + H3O+(aq) E. HClO(aq) + H2O(l) → ClO−(aq) + H3O+(aq) F. HClO(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ ClO−(aq) + H3O+(aq) G. HClO4(aq) + H2O(l) → ClO4−(aq) + H3O+(aq) H. HClO3(aq) + H2O(l) → ClO3−(aq) + H3O+(aq) I. HClO4(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ ClO4−(aq) + H3O+(aq) J. HCl(aq) + H2O(l) → Cl−(aq) + H3O+(aq)arrow_forward
- The balanced reaction between aqueous potassium hydroxide and aqueous acetic acid is ________. explain me. Please! KOH (aq) + HC2H3O2 (aq) → OH- (l) + HC2H3O2+ (aq) + K (s) KOH (aq) + HC2H3O2 (aq) → H2O (l) + KC2H3O2 (aq) KOH (aq) + HC2H3O2 (aq) → H2C2H3O3 (aq) + K (s) KOH (aq) + HC2H3O2 (aq) → KC2H3O3 (aq) + H2 (g) KOH (aq) + HC2H3O2 (aq) → H2KC2H3O (aq) + O2 (g)arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate K for the following acid/base reaction? H25 (aq) +F (aq) ++ HF (aq) +HS (aq) ACID BASE HCI C H2SO4 HNO3 H30 (aq) HSO H3PO4 HSO NO3 H2O so, H,PO, F HF CH3COOH H,CO3 H,S H,PO, NH, CH;COO HCO, HS HPO, NH, CO PO OH HCO HPO. 1,0 OH H, CH CH, OA unable to determine OB. K.<1 Base strength increasing Acid strength increasingarrow_forwardThe pH of an aqueous solution of formic acid (HCOOH) is 3.318. What is the initial molar concentration of HCOOH, if its acid ionization constant is Ka=1.78 × 10-4? Reaction: HCOOH (aq) ↔ HCOO- (aq) + H+ (aq).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning