
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
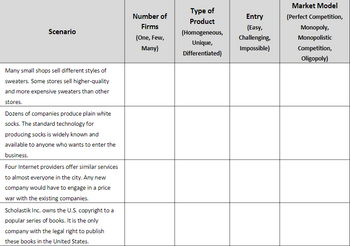
Transcribed Image Text:Scenario
Many small shops sell different styles of
sweaters. Some stores sell higher-quality
and more expensive sweaters than other
stores.
Dozens of companies produce plain white
socks. The standard technology for
producing socks is widely known and
available to anyone who wants to enter the
business.
Four Internet providers offer similar services
to almost everyone in the city. Any new
company would have to engage in a price
war with the existing companies.
Scholastik Inc. owns the U.S. copyright to a
popular series of books. It is the only
company with the legal right to publish
these books in the United States.
Number of
Firms
(One, Few,
Many)
Type of
Product
(Homogeneous,
Unique,
Differentiated)
Entry
(Easy,
Challenging,
Impossible)
Market Model
(Perfect Competition,
Monopoly,
Monopolistic
Competition,
Oligopoly)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Comparing Market Types Another Name for Firms Special Traits Number of Kind of Type of Market Barriers to Entry Producers Competition One None No entry possible Price-setter Only one firm Monopoly Primarily non-price competition Firms can collude and behave as a monopolist Medium barriers Oligopoly A few (difficult entry) N/A Non-price competition; price competition Product differentiation and branding Low barriers Monopolistic Competition Many (easy entry) Price-maker No barriers (free entry) Perfectly elastic demand Perfect A great many Price competition Price-taker Competition Using the chart above, if you were a buyer (consumer) which of the four market structures would you want to buy from? Explain the benefits that come from this level of competition.arrow_forwardSome years ago, two intercity bus companies, Greyhound Lines, Inc. and Trailways Transportation System, wanted to merge. One possible definition of the market in this case was “the market for intercity bus service.” Another possible definition was “the market for intercity transportation, including personal cars, car rentals, passenger trains, and commuter air flights.” Which definition do you think the bus companies preferred, and why?arrow_forwardHow do you find the profit maximizing PRICE (not level of output) on a graph for a monopoly with demand, marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost curves. Group of answer choices Find the minimum point on the ATC curve and go straight over to the price axis. Find the point where MR = MC and go straight over to the price axis. Find the point where MR = MC, go straight up until you hit the demand curve, and then go straight over to the price axis. Find the point where demand hits marginal cost and go straight over to the price axis.arrow_forward
- Match the statements to complete a correct sentence A market structure with only one seller called Monopoly A market structure with few sellers called Oligopoly If the income elasticity of demand for bananas is 3.45, then banana's considered as Choose. The cost that is declining as output increase Choose. The quantity that consumer is willing and able to buy at a given price and time period is Quantity demanded The quantity that producer is willing and able to sell at a given price and time period is Quantity supplied The cost that remain unchanged regardless of of level of production called Choose. The time frame at which at least one input is fixed called Choose.. If the elasticity of demand is infinity, then the demand curve is Choose. If the elasticity of demand is zero, then the demand curve is Choose. The time frame at which all inputs are variables called Choose. If the cross elasticity of demand between good A and B is -2.7, then A and B are Choose.arrow_forwardPlesco is planning to establish a subsidiary in the US. This subsidiary will employ up to 50 workers, will have an office and a special storage for laptops. When designing the corporate form of the subsidiary Plesco wishes to limit its own liability so that the subsidiary is fully liable for all debts and obligations before its clients. At the same time, Plesco does not want this subsidiary to become a public company –- all shares should belong to Plesco so that Plesco could exercise full control. In addition, Plesco does not want a complicated organizational structure. An optimal tax regime would also be preferable for the owners of Plesco. One of the Plesco's plans includes registering a trademark “Plesco" for laptops. As laptops are the company's most successful product, Plesco is not planning to sell anything else in the US. However, having monitored the market, Plesco found that a trademark "Plesco" had already been registered for chocolates by USPTO. The owner of trademark in the…arrow_forwardA perfectly competitive firm is expected to make a $0 economic profit in the long-run. What type(s) of profit would you expect a monopolist to earn in the long-run? Why the difference? Use the editor to format your answerarrow_forward
- Subject:arrow_forwardIf due to a change in the price of a commodity from Tk. 250 to Tk. 200 per unit, its quantity demanded increases by 20% per year for a family, then what is the price elasticity of demand for the good? Please comment on the type of its price elasticity.arrow_forwardMarket structure grid?arrow_forward
- Please consider firms in the following types of markets: Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Pure Competition Pure Monopoly Check All That Apply The following questions will ask you to check all of the market types that has each characteristic. There may be only one market type or there may be more than one market type for each characteristic. Price is equal to marginal revenue Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Pure Monopoly Pure Competition Has high barriers to entry Monopolistic Competition Pure Competition Pure Monopoly Oligopoly Charges the lowest price Pure Monopoly Pure Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Produces the lowest quantity Monopolistic Competition Pure Monopoly Pure Competition Oligopoly Achieves allocative efficiency in the long run equilibrium Monopolistic Competition Pure Competition Oligopoly Pure Monopoly O O O Oarrow_forwardThe grapharrow_forward1. Two companies, Klaren Electronics, a monopoly, and the Yarn Barn, a perfectly competitive firm, are interested in increasing their profits by using price discrimination. What is price discrimination? Will it help each company to accomplish their goal? Why or why not?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education