
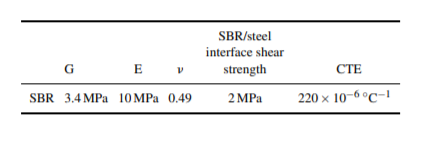
Concept explainers
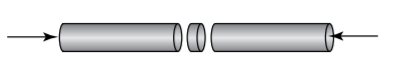
A disk of SBR elastomer 3.0 cm in diameter 0.5 cm
thick is used as a cushioning surface between two steel rods of
the same diameter, as shown below (not to scale). a. If the rods are brought together with an axial force
of 100 N such that the SBR is compressed
elastically between them, what is the thickness
of the SBR under load?
b. Under the same conditions as part (a), what is the
greatest possible diameter of the SBR under load?
c. If the SBR is bonded to the rods, how far can one
rod be rotated with respect to the other before the
SBR/rod interface fractures? Assume that the
rods are essentially rigid and the distance
between them remains constant. Please answer
in degrees of rotation.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- hi, can you help me with all parts of this question. thank youarrow_forwardThe cable of hoist has a cross sectional of 80mm2.The hoist is used to lift a crate weighining 500 kg.The free length of of the cable is 30 m.Assume all deformation is elastic. (a) what is the stress on the cable. (b) How much will the cable extend if it is made from steel(E-200 Gpa)? (c) How much will the cable extend if it is made from polypropylene(E-1.2 Gpa)?arrow_forwardA cable is made of two strands of different materials, A and B, and cross sections as follows: For material A: K=70,000 psi, n=0.5, A0=0.6 in2. For material B: K=25,000 psi, n=0.5, A0=0.3 in2 Calculate the maximum tensile force that this cable can withstand.arrow_forward
- A rectangular polypropylene [E = 6.200 MPa] bar (1) is connected to a rectangular nylon [E = 1,400 MPa] bar (2) at flange B. The assembly (shown in the figure) is connected to rigid supports at A and C. Bar (1) has a cross-sectional area of A₁ = 920 mm² and a length of L₁ = 1220 mm. Bar (2) has a cross-sectional area of A₂ = 2630 mm² and a length of L₂ = 570 mm. After two loads of P = 3.8 kN are applied to flange B, determine: (a) the forces in bars (1) and (2). (b) the deflection of flange B. (a) F₁ = F₂ = (b) UB = i i i A kN KN mm L₁ (1) P B L₂ (2)arrow_forwardA rubber ball is inflated to a pressure of 60KPa. At that pressure, the diameter of the ball is 230mm and the wall thickness is 1.2mm. The rubber has a modulus of elasticity of E = 3.5MPa and Poisson’s ratio of 0.45. (a)Compute the maximum tensile stress. (b)If the allowable tensile stress of the rubber ball wall is 2.5MPa, compute the internal pressure the rubber ball could be inflated.arrow_forwardPlease answer in proper unitsarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





