
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
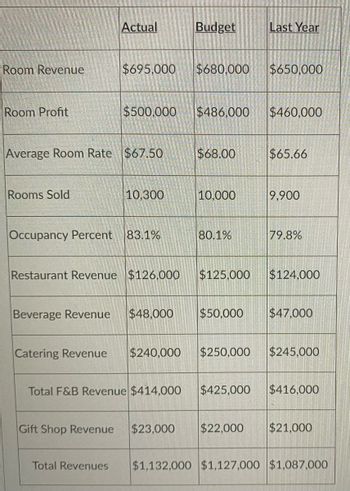
Transcribed Image Text:Room Revenue
Room Profit
Rooms Sold
Actual
$695,000
Average Room Rate $67.50
$500,000
Catering Revenue
10,300
Occupancy Percent 83.1%
Budget Last Year
$680,000
$240,000
$486,000
$68.00
10,000
Restaurant Revenue $126,000 $125,000
80.1%
$250,000
$650,000
$460,000
Gift Shop Revenue $23,000 $22,000
$65.66
Beverage Revenue $48,000 $50,000 $47,000
9,900
79.8%
$124.000
$245,000
Total F&B Revenue $414,000 $425,000 $416,000
$21,000
Total Revenues $1,132,000 $1,127,000 $1,087,000
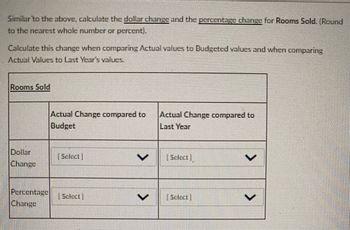
Transcribed Image Text:Similar to the above, calculate the dollar change and the percentage change for Rooms Sold. (Round
to the nearest whole number or percent).
Calculate this change when comparing Actual values to Budgeted values and when comparing
Actual Values to Last Year's values.
Rooms Sold
Dollar
Change
Actual Change compared to
Budget
Percentage Select
Change
Actual Change compared to
Last Year
[Select
Select
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Break-Even Sales Anheuser-Busch InBev SA/NV (BUD) reported the following operating information for a recent year: Sales $7,344,000 Cost of goods sold $1,836,000 Selling, general, and administrative expenses 510,000 2,346,000 Operating income $4,998,000* *Before special items In addition, assume that Anheuser-Busch InBev sold 51,000 barrels of beer during the year. Assume that variable costs were 75% of the cost of goods sold and 50% of selling, general, and administrative expenses. Assume that the remaining costs are fixed. For the following year, assume that Anheuser-Busch InBev expects pricing, variable costs per barrel, and fixed costs to remain constant, except that new distribution and general office facilities are expected to increase fixed costs by $21,400. a. Compute the break-even number of barrels for the current year. Round to the nearest whole barrel.fill in the blank 1 barrels b. Compute the anticipated break-even number of barrels for the…arrow_forwardHD marketing channel team estimated Net sales and other expenses and created a profit-and-loss statement. Complete the statement using the following information (Q4-6). • Cost of goods sold (50% of net sales) • Sales salaries : 6 millions • 8% commission on sales • advertising and promotion : $10 millions • 3% of sales for cooperative advertising allowances to retailers freight and delivery charges (8% of sales) Managerial salaries and expenses: 3 millions • Indirect overhead: 2 millions Profit-and-loss statement | Net sales Cost of goods sold Gross Margin Marketing Expenses Sales expenses Promotion expenses $238,000,000 $119,000,000 $119,000,000 04 Q5 Freight General and Administrative Q6 expenses Managerial salaries and expenses Indirect overhead $3,000,000 $2,000,000 $5,000,000 $52,780,000 Net Profit before tax Q7. What is the total fixed costs? Q8. What is the total variable costs? Q9 What is the contribution margin (%) ? Q10 What is the break-even sales ($)?_arrow_forwardHelp me please asaparrow_forward
- Break-Even Sales Anheuser-Busch InBev Companies, Inc., reported the following operating information for a recent year: Sales $4,992,000 Cost of goods sold $1,248,000 Selling, general and administration 520,000 $1,768,000 Income from operations $ 3,224,000* *Before special items In addition, assume that Anheuser-Busch InBev sold 52,000 barrels of beer during the year. Assume that variable costs were 75% of the cost of goods sold and 50% of selling, general, and administration expenses. Assume that the remaining costs are fixed. For the following year, assume that Anheuser-Busch InBev expects pricing, variable costs per barrel, and fixed costs to remain constant, except that new distribution and general office facilities are expected to increase fixed costs by $17,200. a. Compute the break-even number of barrels for the current year. Round to the nearest whole barrel.fill in the blank 1 barrels b. Compute the anticipated break-even number of barrels for the following…arrow_forwardDuring Heaton Company’s first two years of operations, it reported absorption costing net operating income as follows: Year 1 Year 2 Sales (@ $64 per unit) $ 1,088,000 $ 1,728,000 Cost of goods sold (@ $35 per unit) 595,000 945,000 Gross margin 493,000 783,000 Selling and administrative expenses* 303,000 333,000 Net operating income $ 190,000 $ 450,000 * $3 per unit variable; $252,000 fixed each year. The company’s $35 unit product cost is computed as follows: Direct materials $ 8 Direct labor 12 Variable manufacturing overhead 2 Fixed manufacturing overhead ($286,000 ÷ 22,000 units) 13 Absorption costing unit product cost $ 35 Forty percent of fixed manufacturing overhead consists of wages and salaries; the remainder consists of depreciation charges on production equipment and buildings. Production and cost data for the first two years of operations are: Year 1 Year 2 Units produced…arrow_forwardIncome for Profit Center The centralized computer technology department of Crutchfield Company has costs of $982,500. The department has provided a total of 13,100 hours of service for the period. The Retail Division has used 5,900 hours of computer technology service during the period, and the Commercial Division has used 7,200 hours of computer technology service. Additional data for the two divisions is following below: RetailDivision CommercialDivision Sales $6,320,000 $4,950,000 Cost of goods sold 3,190,000 2,220,000 Selling expenses 502,000 489,000 Determine the divisional income from operations for the Retail Division and the Commercial Division.arrow_forward
- I want correct answerarrow_forwardDuring Heaton Company’s first two years of operations, it reported absorption costing net operating income as follows: Year 1 Year 2 Sales (@ $61 per unit) $ 1,159,000 $ 1,769,000 Cost of goods sold (@ $34 per unit) 646,000 986,000 Gross margin 513,000 783,000 Selling and administrative expenses* 305,000 335,000 Net operating income $ 208,000 $ 448,000 * $3 per unit variable; $248,000 fixed each year. The company’s $34 unit product cost is computed as follows: Direct materials $ 7 Direct labor 13 Variable manufacturing overhead 2 Fixed manufacturing overhead ($288,000 ÷ 24,000 units) 12 Absorption costing unit product cost $ 34 Production and cost data for the first two years of operations are: Year 1 Year 2 Units produced 24,000 24,000 Units sold 19,000 29,000 Required: 1. Using variable costing, what is the unit product cost for both years? 2. What is the variable costing net operating income in Year 1 and in Year 2? 3. Reconcile the…arrow_forwardThe following date relates to Your Company: Total Store 1 Store 2 Sales $2,100,000 $1,300,000 $800,000 VC $1,065,000 $585,000 $480,000 CM $1,035,000 $715,000 $320,000 Traceable fixed costs $497,500 $165,000 $332,500 Segment margin $537,500 $550,000 ($12,500) Common fixed costs $370,000 $210,000 $160,000 $167,500 $340,000 ($172,500) NI Your Company is considering closing Store 2. If Store 2 is closed, 65% of its traceable fixed expenses could be avoided. Also, the closing of Store 2 would result in a 15% increase in sales in Store 1. Your Company allocates common fixed expenses on the basis of sales dollars and none of these costs would be saved if a store were shut down. What is the increase or (decrease) in the net income if Store I is closed? Enter an increase as a positive number and a decrease wtih a minus sign in front.arrow_forward
- Sales Cost of goods sold Gross margin Selling and administrative expenses: Selling expense 99,000 Administrative expense* 44,500 Total selling and 143,500 administrative expenses Net operating income *Includes $22,000 of depreciation each month. April May June July $510,000 $1,040,000 $490,000 $390,000 357,000 728,000 343,000 273,000 312,000 147,000 117,000 153,000 9,500 $ b. Sales are 20% for cash and 80% on account. c. Sales on account are collected over a three-month period with 10% collected in the month of sale; 70% collected in the first month following the month of sale; and the remaining 20% collected in the second month following the month of sale. February's sales totaled $205,000, and March's sales totaled $245,000. 1. Inventory purchases are paid for within 15 days. Therefore, 50% of a month's inventory purchases are paid for in the month of purchase. The remaining 50% is paid in the following month. Accounts payable at March 31 for Inventory purchases during March total…arrow_forwardPlease help me with show all calculation thankuarrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education