
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
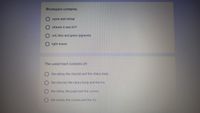
Transcribed Image Text:Rhodopsin contains:
opsin and retinal
vitamin A and ATP
red, blue and green pigments
light waves
The uveal tract consists of:
the retina, the choroid and the ciliary body
the choroid, the ciliary body and the iris
the retina, the pupil and the cornea
the sclera, the cornea and the iris
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Place the following into the correct order to represent the bleaching and regeneration of rhodopsin. Opsin and cis-retinal enzymatically combine to regenerate rhodopsin Trans-retinal is enzymatically converted back to cis-retinal Cis-retinal isomerizes to trans-retinal Trans-retinal separates from opsin Opsin triggers reaction cascade that breaks down cGMP Rhodopsin absorbs photon of light www Next >arrow_forwardAs light hits the rods and cones, they release molecules. This is interpreted as light by the brain. None of these is correct More neurotransmitter molecules More opsin molecules More rhodopsin molecules Fewer neurotransmitter moleculesarrow_forwardThe fovea centralis has many rod shaped receptors for detecting color O True False Previous Page Next Page Page 1 of 10arrow_forward
- Why does your eye have a blind spot? O There is only axons and blood vessels in that region of your eye The lens bends the light in such a way that it cannot reach a small portion of the retina. Light cannot reach the edges of the eye because the pupil is too small O The receptors in that region are obstructed Next Page Page 2 of 10 Previous Pagearrow_forwardThe lens tends to harden with age. This would make it difficult to focus on nearby objects make it harder for light to reach the photoreceptor cells increase the pressure on the retina causing blindnessarrow_forwarddescribe choroid, ciliary body and the iris. (easy and simple)arrow_forward
- What order does light pass through the structures of the eye, from superficial to deep? These are the strucutres i need put in order: Sclera – Cornea – Choroid – Ciliary body – Ciliary muscle – Iris – Pupil - Retina – Optic nerve – Vitreous humor – Optic chiasma Optic nerve – Optic tract –arrow_forwardThe membrane potential of cells within the visual system is recorded in the dark, then following a brief flash of light. During the flash of light you would expect __________ cells to _____________ a rod cell; hyperpolarize b bipolar cell; depolarize c ganglion cell; depolarize d all of the above are correctarrow_forwardList the following structures in the order that light passes through them: aqueous humor, cornea, lens, retina, pupil, vitreous humorarrow_forward
- Using the attached image of a diagram of an eye, lable what A, B, C, D, and E are of the following parts: 1. Retina: Pigmented layer 2. Retina: Photoreceptor layer 3. Choroid 4. Sclera 5. Retinaarrow_forwardI am a bit confused about the anatomy of hair cells. Is it just one hair cell or is it technically three 'cells' per hair cell: afferent neuron, senesory hair cell (cell body), and stereocilia?arrow_forwardWhat happens to voltage-gated Ca++ channels on hair cells when the hair cells move toward the shorter stereocilia? They open allowing Ca++ to exit They open allowing Ca++ entry They remain closed They go from open to closedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education