
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
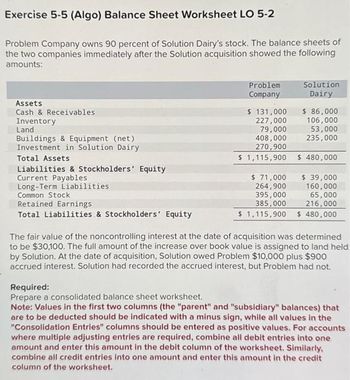
Transcribed Image Text:Exercise 5-5 (Algo) Balance Sheet Worksheet LO 5-2
Problem Company owns 90 percent of Solution Dairy's stock. The balance sheets of
the two companies immediately after the Solution acquisition showed the following
amounts:
Assets
Cash & Receivables
Inventory
Land
Buildings & Equipment (net)
Investment in Solution Dairy
Total Assets
Liabilities & Stockholders' Equity
Current Payables
Long-Term Liabilities
Common Stock
Retained Earnings
Total Liabilities & Stockholders' Equity
Problem
Company
Solution
Dairy
$ 131,000
$ 86,000
106,000
227,000
79,000 53,000
408,000 235,000
270,900
$ 1,115,900 $ 480,000
$ 71,000
264,900
395,000
385,000
$ 39,000
160,000
65,000
216,000
$ 1,115,900 $ 480,000
The fair value of the noncontrolling interest at the date of acquisition was determined
to be $30,100. The full amount of the increase over book value is assigned to land held
by Solution. At the date of acquisition, Solution owed Problem $10,000 plus $900
accrued interest. Solution had recorded the accrued interest, but Problem had not.
Required:
Prepare a consolidated balance sheet worksheet.
Note: Values in the first two columns (the "parent" and "subsidiary" balances) that
are to be deducted should be indicated with a minus sign, while all values in the
"Consolidation Entries" columns should be entered as positive values. For accounts
where multiple adjusting entries are required, combine all debit entries into one
amount and enter this amount in the debit column of the worksheet. Similarly,
combine all credit entries into one amount and enter this amount in the credit
column of the worksheet.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For each of the tollowing transactions or adjustments, indicate the effect of the transaction or adjustment on assets, liabilities, and net income by entering for each account affected the account name and amount and indicating whether it is an nddition () or a subtraction ( Transaction a has been done as an illustration. Net income is not affected by every transaction. In some cases, only one column may be affected because all of the specific accounts affected by the transaction are included in that category. a. Recorded $200 of depreciation expense. b. Sold land that had originally cost $9,000 for $14,000 in cash. c. Acquired a new machine under a financing lease. The present value of future lease payments, discounted at 10%, was $10,000. d. Recorded the first annuai payment of $2.200 for the leased machine (in part c). e. Recorded a $5,100 payment for the cost of developing and registering a trademark. f. Recognized periodic amortization for the trademark (in part e) using a 34-year…arrow_forwardPrepare an answer sheet with the column headings shown here. For each of the following transactions or adjustments, indicate the effect of the transaction or adjustment on the appropriate balance sheet category and on net income by entering for each account affected the account name and amount and indicating whether it is an addition (+) or a subtraction (-). Transaction a has been done as an illustration. Net income is not affected by every transaction. In some cases only one column may be affected because all of the specific accounts affected by the transaction are included in that category. a. Accrued interest revenue of $30 on a note receivable. b. Determined that the Allowance for Bad Debts account balance should be increased by $2,050. c. Recognized bank service charges of $22 for the month. d. Received $29 cash for interest accrued in a prior month. e. Purchased 3 units of a new item of inventory on account at a cost of $31 each. Perpetual inventory is maintained. f. Purchased…arrow_forwardProblem Company owns 90 percent of Solution Dairy's stock. The balance sheets of the two companies immediately after the Solution acquisition showed the following amounts: Assets Cash & Receivables. Inventory Land Buildings & Equipment (net) Investment in Solution Dairy Total Assets Liabilities & Stockholders' Equity Current Payables Long-Term Liabilities Common Stock Retained Earnings Total Liabilities & Stockholders' Equity Problem Company $ 149,000 217,000 77,000 396,000 273,600 $ 1,112,600 Solution Dairy $ 76,000 266,600 390,000 380,000 $ 71,000 91,000 60,000 238,000 $ 460,000 $ 28,000 158,000 62,000 212,000 $ 1,112,600 $ 460,000 The fair value of the noncontrolling interest at the date of acquisition was determined to be $30,400. The full amount of the increase over book value is assigned to land held by Solution. At the date of acquisition, Solution owed Problem $13,000 plus $1,500 accrued interest. Solution had recorded the accrued interest, but Problem had not.arrow_forward
- Posting errors are identified in the following table. In column (1), enter the amount of the difference between the two trial balance columns (debit and credit) due to the error. In column (2), identify the trial balance column (debit or credit) with the larger amount if they are not equal. In column (3), identify the account(s) affected by the error. In column (4), indicate the amount by which the account(s) in column (3) is under- or overstated. Item (a) is completed as an example. Note: Select "None" if there is no effect. (1) Difference between Description of Posting Error Debit and Credit Columns Larger Total (2) Column with the (3) Identify Account(s) Incorrectly Stated (4) Amount of account over- or understatement a. $1,720 debit to Rent Expense is posted as a $1,270 debit. $ 450 Credit Rent Expense Rent Expense is understated by $450 b. $3,440 credit to Cash is posted twice as two credits to Cash. c. $1,570 debit to Prepaid Insurance is posted as a debit to Insurance Expense.…arrow_forwardWhat is the purpose of a double-line rule in a balance sheet? O to show a balance sheet was checked by a manager O to show that the columns need to be totaled O to verify that all transactions have been listed O to show that totals have been verifiedarrow_forwardMatch the statements below with the accounting assumption, characteristic, or principle to which the statement relates. Assumptions/characteristics/principles may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Recorded when the performance obligation is satisfied. a. Revenue recognition principle V The reason for recording accruals and deferrals in adjusting entries. b. Matching principle Valuing assets at amounts originally paid for them. C. Historical cost principle Entity assumed to have a long life d. Going concern assumption Description of significant accounting policies and unusual events. e. Full disclosure principle v Information has predictive and confirmatory value. T. Relevance characteristic 8. Consistency characteristicarrow_forward
- Identify the correct pair of formula from the following column I and II: (Choose the correct alternative) Column I Column II A Current Account Surplus i. Receipts Payments C Balance Current Account i. Receipts + Payments D Current Account Deficit iv. Receipts < Payments Alternatives: а) А -i b) В - ii c) C - ii d) D - ivarrow_forwardIdentify the type of account (Asset, Liability, Equity, Revenue, Expense), normal balance (Debit, Credit), financial statement (Balance Sheet, Income Statement), and whether the account is closed at the end of the period (Yes, No) by selecting the letter that best describes those attributes. If an account is a contra or adjunct account, the answer will show the account type in parentheses. Answer items may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Retained Earnings 1. Equity, Credit, Balance Sheet, No 2. Freight-Out Liability, Credit, Balance Sheet, No V Loss on Impairment of Intangible Assets 3. Expense, Debit, Income Statement, Yes 4. Gain on Acquisition of Business (Equity), Debit, Balance Sheet, No 5. Amortization of Copyrights Asset, Debit, Income Statement, Yes Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 6. Expense or Loss, Credit, Income Statement, Yes Land 7. Revenue or Gain, Credit, Income Statement, Yes Federal Income Tax Withheld 8. (Revenue or Gain), Debit, Income Statement, Yes…arrow_forwardplease step by step solution. please introductio of this solution.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education