
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
![!
Required information
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. For specific identification,
ending inventory consists of 340 units from the January 30 purchase, 5 units from the January 20 purchase, and 15 units
from beginning inventory.
Date
January 1
January 10
January 20
January 25
January 30
Activities
Beginning inventory
Sales
Purchase
Sales
Purchase
Totals
Units Acquired at Cost
210 units @ $13.50 =
$12.50 =
340 units @ $ 12.00 =
700 units
150 units @
$ 2,835
1,875
4,080
$ 8,790
Units sold at Retail
$ 22.50
160 units @
@ $ 22.50
180 units
340 units
Record journal entries for Laker Company's sales and purchases transactions. Assume for this assignment that the company uses a
perpetual inventory system and FIFO. All sales and purchases are made on account, and no discounts are offered.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/70dabe61-0fe7-42ab-bbbe-26eb7a4bc637/c041778d-2ee5-4d94-b211-638ae1682f5e/u5z4shm_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:!
Required information
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. For specific identification,
ending inventory consists of 340 units from the January 30 purchase, 5 units from the January 20 purchase, and 15 units
from beginning inventory.
Date
January 1
January 10
January 20
January 25
January 30
Activities
Beginning inventory
Sales
Purchase
Sales
Purchase
Totals
Units Acquired at Cost
210 units @ $13.50 =
$12.50 =
340 units @ $ 12.00 =
700 units
150 units @
$ 2,835
1,875
4,080
$ 8,790
Units sold at Retail
$ 22.50
160 units @
@ $ 22.50
180 units
340 units
Record journal entries for Laker Company's sales and purchases transactions. Assume for this assignment that the company uses a
perpetual inventory system and FIFO. All sales and purchases are made on account, and no discounts are offered.
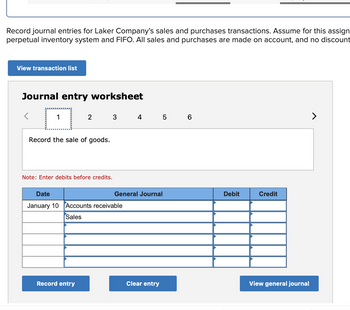
Transcribed Image Text:Record journal entries for Laker Company's sales and purchases transactions. Assume for this assign
perpetual inventory system and FIFO. All sales and purchases are made on account, and no discount
View transaction list
Journal entry worksheet
2
Record the sale of goods.
Note: Enter debits before credits.
Record entry
3
Date
January 10 Accounts receivable
Sales
4 5 6
General Journal
Clear entry
Debit
Credit
View general journal
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units sold at Retail Jan. 1 Beginning inventory 150 units @ $ 7.50 = $ 1,125 Jan. 10 Sales 110 units @ $ 16.50 Jan. 20 Purchase 80 units @ $ 6.50 = 520 Jan. 25 Sales 90 units @ $ 16.50 Jan. 30 Purchase 200 units @ $ 6.00 = 1,200 Totals 430 units $ 2,845 200 units The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 230 units, where 200 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 25 are from beginning inventory. Required:1. Complete the table to determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using specific identification.2. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using…arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Hemming Company reported the following current-year purchases and sales for its only product. Date January 1 January 10 March 14 March 151 July 30 October 5 October 26 Activities beginning inventory Sales Purchase Sales Purchase Sales Purchase Totals Required: Hemming uses a perpetual inventory system. Units Acquired at Cost $11.40- 235 units 360 units 435 units 135 units 1,165 units $16.40- $21.40- $26.40- $ 2,679 5,904 9,309 3,564 $ 21,456 1. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO. 2. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO. 3. Compute the gross profit for FIFO method and LIFO method. Units Sold at Retail 170 units 290 units 410 units 870 units $41.40 $41.40 @$41.40arrow_forwardLaker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units sold at Retail Jan. 1 Beginning inventory 145 units @ $ 7.00 = $ 1,015 Jan. 10 Sales 105 units @ $ 16.00 Jan. 20 Purchase 70 units @ $ 6.00 = 420 Jan. 25 Sales 85 units @ $ 16.00 Jan. 30 Purchase 190 units @ $ 5.50 = 1,045 Totals 405 units $ 2,480 190 units The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 215 units, where 190 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 20 are from beginning inventory. Exercise 5-4 Perpetual: Income effects of inventory methods LO A1 Required:1. Complete comparative income statements for the month of January for Laker Company for the four inventory methods. Assume expenses are $1,300…arrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Units Acquired at Cost 100 units@ $56.00 per unit 400 units@ $61.00 per unit Date Activities Units Sold at Retail 1 Beginning inventory 5 Purchase 9 Sales Mar. Mar. Mar. 420 units @ $91.00 per unit 120 units @ $66.00 per unit 200 units @ $68.00 per unit Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales 160 units @ $101.00 per unit Totals 820 units 580 units 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory. Ending inventory unitsarrow_forwardRequired information Use the following information for the Exercises 3-7 below. (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 300 units from the January 30 purchase, 5 units from the January 20 purchase, and 25 units. from beginning inventory. Date January 11 January 10 January 201 January 25, January 30 Activities Beginning inventory Sales Purchase Sales Purchase Totals Exercise 5-3 (Algo) Perpetual: Inventory costing methods LO P1 Assume the perpetual inventory system is used. Required: Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Purchase Date January 11 FIFO Units Acquired at Cost. 200 units @ $12.50 130 units@ $ 11.50 = 300 units @ $ 11.00 = 630 units 1. Complete the table to determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using specific identification. 2.…arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail March 1 March 5 Beginning inventory Purchase 250 units @ $54.00 per unit 300 units March 9 Sales March 18 Purchase March 25 Purchase 160 units 300 units @ $59.00 per unit $64.00 per unit 410 units @ $89.00 per unit @ $66.00 per unit March 29 Sales Totals 280 units $99.00 per unit 1,010 units 690 units 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods. For specific identification, units sold include 140 units from beginning inventory, 270 units from the March 5 purchase, 120 units from the March 18 purchase, and 160 units from the March 25 purchase. Note: Round weighted average cost per unit to two decimals and final answers to nearest whole dollar. Gross Margin FIFO LIFO…arrow_forward
- Required information Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 400 units from the January 30 purchase, 5 units from the January 20 purchase, and 15 units from beginning inventory. Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units sold at Retail January 1 Beginning inventory 230 units @ $ 15.50 = $ 3,565 January 10 Sales 180 units @ $ 24.50 January 20 Purchase 190 units @ $ 14.50 = 2,755 January 25 Sales 220 units @ $ 24.50 January 30 Purchase 400 units @ $ 14.00 = 5,600 Totals 820 units $ 11,920 400 units Assume the perpetual inventory system is used. Required: Compute gross profit for the month of January for Laker Company for the four inventory methods. Which method yields the highest gross profit? Does gross profit using weighted average fall between that using FIFO and LIFO? If costs were rising…arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Date March 1 March 5 March 9 March 18 March 25 March 29 Activities Beginning inventory Purchase Sales Purchase Purchase Sales Totals Perpetual FIFO |Perpetual LIFO Units Acquired at Cost 60 units @ $50.20 per unit 205 units @ $55.20 per unit Weighted Average 65 units 110 units Specific Id 440 units Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. @ $60.20 per unit @ $62.20 per unit 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification. For specific identification, units sold include 45 units from beginning inventory, 175 units from the March 5 purchase, 25 units from the March 18 purchase, and 65 units from the March 25 purchase. Units Sold at Retail 220 units @ $85.20 per unit…arrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Hemming Co. reported the following current-year purchases and sales for its only product. Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail Jan. 1 Beginning inventory 195 units @ $13.80 = $ 2,691 Jan. 10 Sales 185 units @ $43.80 Mar. 14 Purchase 345 units @ $18.80 = 6,486 Mar. 15 Sales 235 units @ $43.80 July 30 Purchase 495 units @ $23.80 = 11,781 Oct. 5 Sales 205 units @ $43.80 Oct. 26 Purchase 695 units @ $28.80 = 20,016 Totals 1,730 units $ 40,974 625 units Required: Hemming uses a perpetual inventory system. Compute the gross margin for FIFO method. Sales revenue Less: cost of goods sold Gross Margin…arrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] A company began January with 7,000 units of its principal product. The cost of each unit is $6. Inventory transactions for the month of January are as follows: Date of Purchase January 10 January 18 Totals Total * Includes purchase price and cost of freight. Date of Sale January 5 January 12 January 20 Total Sales LIFO Beginning Inventory Purchases: Units 6,000 7,000 13,000 January 10 January 18 Units 10,000 units were on hand at the end of the month. 3,000 3,000 4,000 10,000 2. Calculate January's ending inventory and cost of goods sold for the month using LIFO, periodic system. Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Available for Sale Number Cost per of units unit Purchases Unit Cost* $7 8 7,000 $ 6.00 6,000 $ 7.00 7,000 $ 8.00 20,000 $ $ 42,000 Total Cost $ 42,000 56,000 $ 98,000 42,000 56,000 140,000 Cost of Goods Sold - Periodic LIFO Cost of Goods Sold Number of units sold Cost per…arrow_forwardVipularrow_forwardVikrambhaiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education