
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
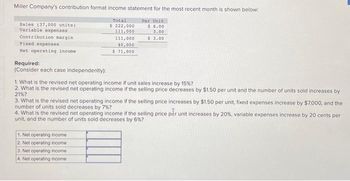
Transcribed Image Text:Miller Company's contribution format income statement for the most recent month is shown below:
Per Unit
$ 6.00
3.00
$ 3.00
Sales (37,000 units)
Variable expenses
Contribution margin
Fixed expenses
Net operating income
Required:
(Consider each case independently):
Total
$ 222,000
111,000
1. Net operating income
2. Net operating income.
3. Net operating income
4. Net operating income
111,000
40,000
$ 71,000
1. What is the revised net operating income if unit sales increase by 15% ?
2. What is the revised net operating income if the selling price decreases by $1.50 per unit and the number of units sold increases by
21%?
3. What is the revised net operating income if the selling price increases by $1.50 per unit, fixed expenses increase by $7,000, and the
number of units sold decreases by 7%?
4. What is the revised net operating income if the selling price per unit increases by 20 %, variable expenses increase by 20 cents per
unit, and the number of units sold decreases by 6%?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Sales revenue from product X is $9,000, variable costs are $6,000, and allocated fixed costs are $4,500. If you drop product X in the short term, profit will: decrease by $1,500 O decrease by $5,250 increase by $3,000 O increase by $1,500 decrease by $3,000arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Henna Co. produces and sells two products, T and O. It manufactures these products in separate factories and markets them through different channels. They have no shared costs. This year, the company sold 46,000 units of each product. Sales and costs for each product follow. Product 0 $ 800,400 160,080 640,320 512,320 128,000 44,800 Product T $ 800,400 640,320 Sales Variable costs Contribution margin 160,080 32,080 128,000 44,800 $ 83,200 Fixed costs Income before taxes Income taxes (35% rate) Net income $ 83, 200arrow_forwardCullumber Company is considering two alternatives. Alternative A will have sales of $158,500 and costs of $100,100. Alternative B will have sales of $180,900 and costs of $133,200. Compare alternative A with alternative B showing incremental revenues, costs, and net income. (If an amount reduces the net income then enter with a negative sign preceding the number, e.g. -15,000 or parenthesis, e.g. (15,000).) Revenues Costs Net income $ $ Alternative A $ $ Alternative B $ $ Net Income Increase (Decrease)arrow_forward
- Question Part Score If it holds the sales price constant and makes the suggested changes, how many units of product will Wildhorse have to sell to make the same operating Income before taxes as last year? Required sales units If Wildhorse wishes to maintain the same contribution margin ratio, what selling price per unit of product must it charge next year to cover the increased materials costs? (Round answer to 2 decimal places, e.g. 15.25) Selling price per unit $arrow_forwardVariable costs as a percentage of sales for Lemon Inc. are 64%, current sales are $691,000, and fixed costs are $180,000. How much will operating income change if sales increase by $41,800?arrow_forwardplease answer 4a,b,c and 5 only. 4-a. What will be the new breakeven point if the additional $213,280 is spent on advertising? 4-b. Prepare a contribution income statement at the new breakeven point. 4-c. What is the percentage change in both fixed costs and in the breakeven point? 5. If the additional $213,280 is spent for advertising in the next year, what is the sales level (in units) needed to equal the current year’s operating profit at 60,000 unitsarrow_forward
- 1-Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that variable expenses will increase by $3 per ball next year. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25, what will be the new CM ratio and break-even point in balls? 2. Refer to the data in (2) above. If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $90,000, as last year? 3. Refer again to the data in (2) above. The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year, what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs?arrow_forwardAssume the following information: Amount Per Unit Sales $ 600,000 $ 40 Contribution margin $ 360,000 $ 24 Net operating income $ 240,000 If the selling price per unit increases by 8% and unit sales drop by 6%, then the best of estimate of the new net operating income is: Multiple Choice $263,520. $243,520. $253,520. $233,520.arrow_forward3) If demand for 2022 is instead 2,500 units should the company pay to increase their capacity? Why? Please explain your calculations and reference to the chart in Figure 1. Assume units are sold at the normal price. Please mention the concept of incremental profits. Hint: If you expand capacity, you will have to pay additional fixed costs of $25,000. Remember that fixed costs are fixed within the relevant range. If you expand capacity then you are outside this range. If you expand capacity then you can make revenue on 500 additional units at the normal price and would pay variable costs on 500 additional units. Please consider the incremental profit or loss of expanding capacity. The incremental profit is the increase in revenues minus the increase in costs of adding 500 more units. If the incremental profit of expanding capacity is positive then you should do so.arrow_forward
- e. 5,000 XYZ company is studying the profitability of a change in operation and has gathered the following information. Current Operation: Fixed Costs: $38,000, Selling Price: $16, Variable Cost: $10, and Sales (Units): 9,000. Anticipated Operation: Fixed Costs: $48,000, Selling Price: $22, Variable Cost: $12, and Sales (Units): 6,000. Should XYZ company make the change? Select one: O a. No, because sales will drop by 3,000 units. Ob. It is impossible to judge because additional information is needed. Oc. No, because the company will be worse off by $4,000. O d. Yes, the company will be better off by $6,000. Oe. No, because the company will be worse off by $22000. Next pagearrow_forwardAccounting Questionarrow_forwardD) Brolin Company sells a single product. The product has a selling price of $50 and variable expenses of 80% of sales. If the company's fixed expenses total $150,000 per year, what is the company's break-even point in sales dollars? per unit $750,000 A) $187,500 B) $15,000 C) $3,750 D) Page 2 of 4 O 48°F Sunny re to searcharrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education