
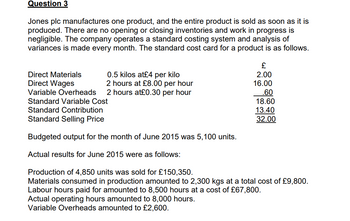
Required:
Calculate all variances and prepare an operating statement for the month ended
June 2015 by using the following table format.
|
Sales variances |
£ |
Favourable (F)/Adverse (A) |
|
Sales price variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales volume variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total sales variance |
|
|
|
Direct material variances |
£ |
Favourable (F)/Adverse (A) |
|
Material price variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Material usage variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total direct material variance |
|
|
|
Direct labour variances |
£ |
Favourable (F)/ Adverse (A) |
|
Labour rate variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Labour efficiency variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total direct labour variance |
|
|
|
Variable |
£ |
Favourable (F)/ Adverse (A) |
|
Variable overhead rate variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable overhead efficiency variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Variable overhead variance |
|
|
|
Variable overhead variances |
£ |
Favourable (F)/ Adverse (A) |
|
Variable overhead rate variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable overhead efficiency variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Variable overhead variance |
|
|
|
Direct labour variances |
£ |
Favourable (F)/ Adverse (A) |
|
Labour rate variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Labour efficiency variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total direct labour variance |
|
|
|
Direct material variances |
£ |
Favourable (F)/Adverse (A) |
|
Material price variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Material usage variance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total direct material variance |
|
|
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- Subject: accountingarrow_forwardWhich method of closing out the fixed MOH volume variance will have no effect on the financial statements, no matter the capacity used? Question options: a) Prorating the fixed MOH volume variance to FG inventory and COGS. b) Allocating the fixed MOH volume variance equally among WIP Inventory, FG inventory and COGS. c) Prorating the fixed MOH volume variance to WIP Inventory, FG inventory and COGS. d) Allocating the fixed MOH volume variance to COGS.arrow_forwardPlease help me with show calculation thankuarrow_forward
- Select all that were the source for the Indirect Costs favorable efficiency variance. a. Actual indirect costs per direct labor hour was less than budgeted indirect cost per direct labor hour. b. Actual indirect costs per direct labor hour was greater than budgeted indirect cost per direct labor hour. c. Actual number of jobs completed was less than budgeted number of jobs. d. Actual number of jobs completed was greater than budgeted number of jobs. e. Actual number of direct labor hours per job was less than budgeted direct labor hours per job. f. Actual number of direct labor hours per job was greater than budgeted direct labor hours par job. QUESTION 5 Select all that were the source for the Sales Activity favorable variance. a. Actual number of units completed was greater than budgeted number of units. b. Actual selling price per unit was less than budgeted. c. Actual number of units completed was less than budgeted number of units. d. Actual selling price per unit was greater than…arrow_forwardFind the values of the missing items (a) through (x). Assume the actual sales volume equals actual production volume. Marketing and Administrative Sales Price Variance Variance Units Sales Revenue Less: Variable Manufacturing Costs Variable marketing and administrative costs Contribution margin Fixed manufacturing costs Fixed marketing and administrative costs Operating Profit PreviousNext Reported income statement (based on actual sales volume) Manufacturing variance (a) (g) (n) (q) (r) (t) $4,320 $3,600 (0) $1,800 U $ 400 F (u) (p) (s) (v) (w) $3,600 F (X) $3,600 F Flexible Budget (based on actual sales volume (b) (h) (m) Sales Activity Variance 4,000 F (1) $19,200 (i) $4,800 $800 U $12,000 (k) $3,000 $4,000 (1) Master Budget (based on budgeted sales volume) 20,000 $30,000 (c) (d) (e) (f) $16,000 $10,000arrow_forwardPrimara Corporation has a standard costing system in which it applies overhead to products on the basis of the standard direct labour- hours allowed for the actual output of the period. Data concerning the most recent year appear below: Total budgeted fixed overhead cost for the year Actual fixed overhead cost for the year Budgeted standard direct labour-hours (denominator level of activity) Actual direct labour-hours Standard direct labour-hours allowed for the actual output $ 500,000 $ 508,000 50,000 54,000 52,000 Required: 1. Compute the fixed portion of the predetermined overhead rate for the year. Predetermined overhead rate per DLHarrow_forward
- Which statement is true? A. Gross profit (GP) variance analysis, is an essential part of financial statements analysis that is used to evaluate the performance of a firm's departments responsible for the firm's line activities (functions). B. Increases and decreases in sales and cost of sales have direct relationship with increases and decreases in GP. C. If there is a negative sales price variance and there is no cost variance, the gross profit variance will be equal to the sales price variance. D. A zero cost variance indicates that there is no difference between the standard cost prices and actual cost prices. E. none of the abovearrow_forwardWhich of the following is true? Multiple Choice If a company has an unfavorable spending variance, it must have an unfavorable price variance. If a company has a favorable spending variance, it may have a favorable or unfavorable rate variance. If a company has a favorable quantity variance, it will have a favorable price variance. If a company has an unfavorable efficiency variance, it spent more per labor hour than budgeted.arrow_forwardPlease help with the following question,arrow_forward
- Assume the labor rate variance is $400 unfavorable and the labor spending variance is $200 unfavorable. Given these assumptions, which of the following statements is true? Multiple Choice The labor efficiency variance must be $600 favorable. The labor efficiency variance must be $600 unfavorable. The labor efficiency variance must be $200 favorable. The labor efficiency variance must be $200 unfavorable.arrow_forwardTotal Flexible Budget Product Cost Variance (a) Total Direct Total Direct Total Manufacturing Materials Variance Labor Variance Overhead Variance (b) (c) (d) Direct Materials Direct Materials Direct Labor Direct Labor Total Variable Total Fixed Cost Variance Efficiency Variance Cost Variance Efficiency Variance Overhead Variance Overhead Variance $540 F $155 U $180 U $425 F (e) (f) Variable Overhead Variable Overhead Fixed Overhead Cost Variance Efficiency Variance Cost Variance $225 U $575 F $110 Farrow_forward1. Compute for Spending Variance 2. Compute for Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance 3. Compute for Controllable Variancearrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





