
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Mr. Conti died from a smallpox infection. The graphs (pictured) illustrate Anne's immune response and Mr. Conti's immune response. What differences do you see between these two graphs, and how do these differences explain why Anne survived and Mr. Conti died?
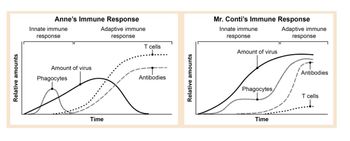
Transcribed Image Text:Relative amounts
Innate immune
response
Anne's Immune Response
Adaptive immune
response
T cells
Amount of virus
Phagocytes
Antibodies
Time
Relative amounts
Mr. Conti's Immune Response
Innate immune
response
Amount of virus
Adaptive immune
response
Antibodies
Phagocytes
T cells
Time
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Which of the following destroys virus-infected cells? Question 6 options: A) cytotoxic T cells B) B cells C) T helper cells D) dendritic cellsarrow_forwardPart E - Characteristics of Lymphocytes Drag and drop the correct type of immunity on the left to complete the sentence that describes the targets, actions, or cell associated with that type of immunity. Immunity types may be used more than once, but each sentence has only one correct type of immunity associated with the description. View Available Hint(s)arrow_forwardSelect the best answer or answers from the choices given: Cells that can directly attack target cells include all of the following except (a) macrophages, (b) cytotoxic T cells, (c) helper T cells, (d) natural killer cells.arrow_forward
- __________________________________________________ cells can help prevent autoimmune diseases. The antigen receptor on a B cell is essentially a membrane-bound ____________________________. If a cell of yours lacks MHCs, ______________________________________ (specific kind of cell) might cause its death _________________________________ is the name of the migration activity by a neutrophil, e.g., when it is physiologically driven to move toward molecules at an area of injury. Its temporary binding and unbinding to sticky endothelial cell adhesion molecules on their way is called _______________________________________. When it enters the injured or infected tissue space from the capillary this is called ____________________________________. When identical plasma cells start being made, in great abundance, from a single specific immune cell, the originally chosen immune cell has undergone ______________________ - ______________________________________. What are a few things discussed…arrow_forwardSelect the correct answer from the answers provided. The cross-linkage of antigens by antibodies is known as a. opsonization b. a cross-reaction c. agglutination d. complement fi xationarrow_forwardMatch the type of lymphocyte cell with its main function in the immune system. Generates antibodies [ Choose] [Choose ] T cells Secretes cytokines Antibody B Cells NK cells Secretes cytotoxic granuales [ Choose ] Binds specific antigen [ Choose ]arrow_forward
- NK Activity (% lysis) 100 80 40 20 O ooo O O BOQ 10 00 20 Depression O 30 p=0.0001 R=0.604 40 FIGURE 4 | Correlation between natural killer (NK) cell activity and depression. There is a significant correlation between NK activity and depression (p = 0.001; R = -0.604).arrow_forwardJohnny has just been infected and needs your help in letting him know how his body is fighting the infection. To do so, describe how the innate and adaptive immune systems work together. You should address the following: 1. define adaptive and innate immunity; 2. Describe the role of natural killer cells (how do they work); 3. what are antigen presenting cells and what is their function, what are MHCs?; 4. describe the role of the complement system; 5. what is the role of interferons?; 6. How do helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells and B lymphocytes work make sure you address adaptive immunity memory?; 7. Define HIV, which cells do they attack and why do some individuals develop persistent lymphadenopathy (swollen or enlarged lymph nodes)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education