
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:!
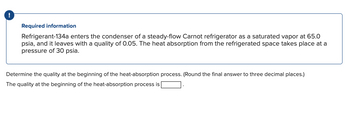
Required information
Refrigerant-134a enters the condenser of a steady-flow Carnot refrigerator as a saturated vapor at 65.0
psia, and it leaves with a quality of 0.05. The heat absorption from the refrigerated space takes place at a
pressure of 30 psia.
Determine the quality at the beginning of the heat-absorption process. (Round the final answer to three decimal places.)
The quality at the beginning of the heat-absorption process is
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The heat engine shown in the figure uses 2.0 mol of a monatomic gas as the working substance. (Figure 1) Figure p (kPa) 600 400 200 0 0 ہے۔ 0.025 0.050 -V (m³) 1 of 1 Part A Determine T₁, T2, and T3. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. Express your answer using two significant figures. T₁, T₂, T3 = Submit Request Answer Part B 17 ΑΣΦ AEth: Ws, Q = Submit Determine AEth, Ws, and Q for 1-2. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. Express your answer using two significant figures. [VD ΑΣΦ ? Request Answer K ? Jarrow_forwardIf feedwater is supplied at 50 degrees Celcius, a boiler generates 10,000 kg/hr of steam at 98% quality at 1 MPAA. Determine the (a) rated boiler horsepower if the boiler operates at 150% of its rating, and (b) what is its probable heating surface? Please provide the complete solution thank you. Don't just recopy the answers from other experts. Thank you.arrow_forwardUsing the tablearrow_forward
- Refrigerant 134a enters the condenser of a residential heat pump at 900 kPa and 40 degrees C at a rate of 0.02 kg/s and leaves at 900 kPa as a saturated liquid. If the compressor consumes 1.2 kW of power, determine the COP of the heat pump and the rate of absorption from the outside air.arrow_forwardConsider a condensing heat exchanger operating with two separate fluids, R-134a and the water. Assuming the operating conditions listed in the table below, and that the pressure drop of the fluids are negligible, find the mass flowrate of the water (kg/s) and Q (kW) transferred between the R-134a and the water. m Enters Exits Fluid Water ? Liquid at T₁ = 5 °℃ Liquid at T₂ = 25 °℃ T2 = 35 °C R-134a 10 kg/min P₁ = 1 MPa and T₁ = 70 °Carrow_forwardNitrogen gas at 90° F (MW=28) goes through a compressor, increasing its pressure from 10 psi to 65 psi. The temperature remained constant throughout. Determine the work in Hp for a steady flow process; ΔKE=0, ΔPE=0; mass flow rate of nitrogen is 2 lbm/min. Round up to 4 decimal places. Draw and label the P-V and T-S diagrams.arrow_forward
- In a household refrigerator, the condenser is vertically mounted at the outer backof the unit, the freezer (evaporator) on the topmost compartment, and thevegetable compartment at the very bottom. Explain why?arrow_forwardRefrigerant vapor rejects 70 kW of heat as it passes through an air-cooled condenser. The condenser has an air-side area of 210 m2 and, based on this area, has an overall heat transfer coefficient of 0.037 kW/m2∙°C. Cooling air flows at a rate of 7.59 kg/s. If condensation of the refrigerant occurs at 55°C, what is the inlet temperature (in °C) of the air? Take the specific heat of air to be 1.02 kJ/kg∙°C. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardIt is insulated against heat, except for a cylinder base B with a volume of 100 liters. This cylinder It is divided into two compartments by a heat-proof and frictionless piston. 100 kPa pressure in chamber A and air at 20 oC temperature, and neon gas at 30 oC in compartment B. Initially the volumes of both compartments are equal. Compartment A at 800 kPa and 20 oC inside it is connected to a pipe with air flow. The valve opens and when the pressure in chamber A reaches 800 kPa is closed. In compartment B, neon gas is inverted and the temperature changes in a steady state. a) Neon's final volume and compression work b) The temperature and mass of the air in the final chamber A c) Calculate the total entropy change of the entire system.arrow_forward
- Solve the following problems: Note: Draw the p-h diagram completely labeling the respective refrigerant conditions (pressures and temperatures) and define the properties of refrigerant (enthalpies and specific volume) needed to solve the respective problems. In an ammonia refrigeration system, the capacity is (1) 210 kW at a temperature of-20°C. The vapor from the evaporator is pumped by one compressor to the condensing pressure of 1431 kPa. Later, the system was revised to a two-stage compression operating on the cycle shown below with intercooling but no removal of flash at 555 kPa. (а) Calculate the power required by the single compressor in the original system. (b) Calculate the total power required by the two compressors in the revised system. Condenser 1431kPa High-stage compressor Intercooler 555kPa Evaporator 2í0kW -20°C Low-stage compresaorarrow_forwardIn a closed feedwater heater, steam warms the feedwater and the condensate leaves the heater through a trap or throttling value . What is the purpose of the trap or throttling value? It allows the liquid to flow to higher pressures with the same internal energy. It separates the liquid from the vapor. It allows the liquid to flow into a lower pressures without the loss of enthalpy. It allows the liquid to flow to higher pressures with the same enthalpy. It allows the liquid to flow into a lower pressures without the loss of internal energy.arrow_forwardThe maximum efficiency of a heat engine works between 660 K and 323 K isarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY