
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Refers to Figure 18-1. Suppose the firm sells its output for $15 per unit, and it pays each of its workers $750 per week. When output increases from 210 units to 285 units, the
a. marginal cost is $10 per unit of output.
b. marginal revenue is $5 per unit of output.
c. value of the marginal product of labor is $4,275.
d. firm's profit decreases.
Please explain why the answer is a.
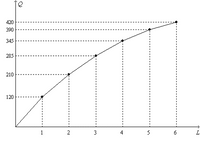
Transcribed Image Text:The image displays a line graph depicting the relationship between \( L \) and \( Q \).
**Axes and Labels:**
- The horizontal axis (\( x \)-axis) is labeled \( L \) and ranges from 0 to 6, marked in increments of 1 unit.
- The vertical axis (\( y \)-axis) is labeled \( Q \) and ranges from 0 to 420, with increments marked at 120, 210, 285, 345, 390, and 420.
**Graph Features:**
- A smooth curve passes through several plotted points, indicating a non-linear (concave upwards) relationship between \( L \) and \( Q \).
- The points of intersection with the vertical grid lines are at approximately (1, 120), (2, 210), (3, 285), (4, 345), (5, 390), and (6, 420).
- Dashed horizontal and vertical lines extend from each data point to the corresponding axis, aiding in visualization of exact values.
This graph can be used for educational purposes to illustrate how \( Q \) increases as \( L \) increases, demonstrating concepts such as production functions in economics or scalability in other fields. The shape of the curve suggests diminishing returns, where increases in \( L \) result in progressively smaller increases in \( Q \).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume coffee machine and labor are the only two inputs for a coffee shop. The labor demand elasticity will be larger if A. Coffee machine is the substitute for labor in the shop. in the short run. B. Coffee has a relative inelastic demand C. Labor cost is around 80% in the total cost of the shop. D. The supply of tea machine is quite elastic.arrow_forwardFill out chart am confusedarrow_forwardConsider a perfectly competitive market for a product Y and assume that the market is at the long run equilibrium. (a) Examine the cost structure and demand faced by an individual Y producer. Relate that producer to the Y market at the perfectly competitive long run equilibrium. Support with market and individual producer diagrams. (b) Analyze the effects of the following news on price and quantity in the Y market as well as the profit and output of the individual Y producer “It is discovered that consuming Y is beneficial to health and can prolong your life”. Explain both the short run and the long run equilibria and support your answers with suitable diagrams. Hi, I have the answer sheet but may I request for a more detailed explanation for part b? Thank you.arrow_forward
- Brody's firm produces trumpets in a perfectly competitive market. The table below shows Brody's total variable cost. He has a fixed cost of $240, and the price per trumpet is $60.-Calculate the average total cost of producing 6 trumpets. Show your work. -Calculate the marginal cost of producing the 11th trumpet. -What is Brody's profit-maximizing quantity? Use marginal analysis to explain your answer. -At the profit-maximizing quantity you determined in part (c), calculate Brody's profit or loss. Show your work. -Brody also produces saxophones at a loss in a perfectly competitive market. Draw a correctly labeled graph for Brody's firm showing the following at a market price of $200. -Brody's profit-maximizing quantity of saxophones -Brody's loss, completely shaded Quantity Total Variable cost 6 $120 7 $145 8 $165 9 $220 10 $290 11 $390arrow_forwardSuppose fixed costs are $10,000, variable costs are $40,000 and the price of the good is $10 and quantity of the good the firm sells is $10,000. A. Caluclate Total Costs. B. Caluclate Total Revenue. C. Calculate the Firm's Profits.arrow_forwardI'm not sure if I answered these questions correctly.arrow_forward
- Answer all partsarrow_forwardAnswer question 6D onlyarrow_forwardUse this table to answer the following question. Output Total Variable Cost $1 $20 $2 $24 $3 $33 $4 $40 $5 $45 $6 $60 $7 $77 $8 $96 $9 $180 $10 $200 The government just mandated that all firms must install new technology to reduce pollution. The new technology costs $13. The market price is $8. In the long run, will the firm stay open or shut down?arrow_forward
- 2. A competitive firm uses two variable factors to produce its output, with a production function q min{x₁, x₂}. The price of factor 1 is $8 and the price of factor 2 is $5. Due to a lack of warehouse space, the company cannot use more than 10 units of x₁. The firm must pay a fixed cost of $80 if it produces any positive amount but doesn't have to pay this cost if it produces no butput. What is the smallest integer price that would make a firm willing to produce a positive amount? b. d. $44 $41 $29 $13 $21arrow_forwardAnswer Question 6arrow_forward# Units Produced Total Revenue Total Costs 1 100 50 180 110 250 180 4 290 270 310 380 10. What is the marginal revenue of producing the 2nd unit? a) 50. b) 70. c) 90. d) 80. 2. 5.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education