
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:(15) What is the minimum price needed by the firm to break even (i.e., earn zero economic
profits)? Explain.
(16) What is the shutdown price? Explain.
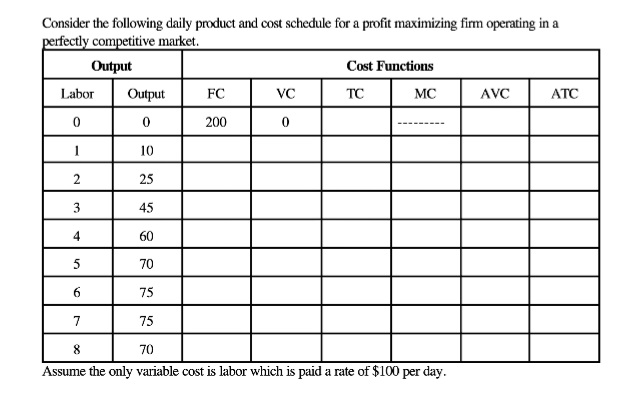
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following daily product and cost schedule for a profit maximizing firm operating in a
perfectly competitive market.
Output
Labor Output
0
0
1
10
2
25
45
3
4
5
6
7
607075
75
FC
200
VC
0
Cost Functions
TC
MC
8
70
Assume the only variable cost is labor which is paid a rate of $100 per day.
AVC
ATC
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The intersection of the average variable cost curve and the marginal cost curve, which shows the price where the firm would lack enough revenue to cover its variable costs, is called the: Shutdown point Equilibrium Profit Lossarrow_forwardA firm sells its product in a perfectly competitive market where other firms charge a price of $90 per unit. The firm’s total costs are C(Q) = 50 + 10Q + 2Q2. [NOTE à MC(Q) = 10+4Q] a) How much output should the firm produce in the short run? b) What price should the firm charge in the short run? c) What are the firm’s short run profits?arrow_forwardFigure 1 shows the short-run cost curves of a toy producer. The market has 1,000 identical producers and Table 1 shows the market demand schedule for toys. At what market prices would the firm shut down temporarily? What is the market price of a toy in long-run equilibrium? How many firms will be in the toy market in the long run? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- Suppose that the jackfruit industry is initially operating in long-run equilibrium at a price level of $5 per pound of jackfruit and quantity of 75 million pounds per year. Suppose a top medical journal publishes research that animal-alternative protein sources such as jackfruit could decrease your expected lifespan by 5 years. The publication is expected to cause consumers to demand jackfruit at every price. In the short run, firms will respond by Shift the demand curve, the supply curve, or both on the following graph to illustrate these short-run effects of the publication. 2 1 10 9 8 Supply Demand 0 0 + 15 30 45 60 75 90 105 120 135 150 QUANTITY (Millions of pounds) In the long run, some firms will respond by + 1 } Demand Supply until Shift the demand curve, the supply curve, or both on the following graph to illustrate both the short-run effects of the publication and the new long- run equilibrium after firms and consumers finish adjusting to the news. 2 1 10 9 Supply Demand B…arrow_forwardA firm operates in a perfectly competitive market. The firm’s total cost of production is given by the following equation: TC(q) = 100 + 48q2 + 5q, where q is the quantity supplied. What is the shutdown point for this firm in the short run, or in other words, what is the market price below which a firm is better off not supplying any units in the short run? [Advice: draw AVC and MC]arrow_forwardUse the following statements to answer this question: 1) The firm’s decision to produce zero output when the price is less than the average variable cost of production is known as the shutdown rule 2)The firm’s supply decision is to generate zero output for all prices below the minimum AVC. A) 1 and 2 are true b)1 is true and 2 is false c)2 is true and 1 is false d) 1 and 2 are falsearrow_forward
- 7. Short-run supply and long-run equilibrium Consider the perfectly competitive market for copper. Assume that, regardless of how many firms are in the industry, every firm in the industry is identical and faces the marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves shown on the following graph. COSTS (Dollars per kilogram) 80 72 64 56 48 40 32 16 8 0 0 4 MC 8 ATC AVC □ 12 16 20 24 28 32 QUANTITY (Thousands of kilograms) 36 The following diagram shows the market demand for copper. □ 40 ? Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the initial short-run industry supply curve when there are 10 firms in the market. (Hint: You can disregard the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output since this is the industry supply curve.) Next, use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 20 firms. Finally, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the short-run industry…arrow_forwardQuestion 23 A competitive firm has a total cost function in dollars of the form C(q)= 100–4q + q^2, where q is output. Suppose the market price is $10 per unit of output. What is the firm’s short run point elasticity of supply? a) 20/7 b) 5/7 c) 10/7 d) 0.5 e) 2arrow_forwardIf a firm operates at a loss, the loss is equal to TC - TR. If the firm shuts down instead, its loss is equal to FC. Given this, show that price must exceed AVC for the firm to operate at a loss and not shut downarrow_forward
- Marginal cost= 2x+3 Average variable cost= x+3 Variable cost=x^2 + 3x x is the daily output. Product's price is 13 dollars. Part a) Calculate the level of output that will be produced. Part b) Calculate the producer surplus of the firm. Part c) The fixed costs are 5 dollars. In the short run, is the firm making a 0 economic profit, a positive profit, or a negative profit? Explain why.arrow_forwardWill, Jill, and Phil are all wheat farmers. The wheat industry is perfectly (purely) competitive. The first chart shows how much each farmer produces at different price levels. The second chart shows each farmer's minimum average total cost (ATC), average variable cost (AVC), and marginal cost (MC). Based on this data (assuming these three are the only producers), answer the questions that follow. Short-run quantity supplied Price Will Jill Phil $2.00 4 2 0 $4.00 6 4 2 $6.00 9 5 4 $8.00 12 8 6 Firm a. What is the cause of the divergence in the short-run Minimum ATC and long-run supply curves? Minimum AVC Minimum MC $1.00 $2.00 Will Jill Phil $2.50 $5.00 $7.00 $2.50 $0.50 $1.00 $2.00 government regulation changes in the market differing individual cost structures b. Suppose that the market price dips to $2.25 in the short run before ultimately settling at $2.50 per bushel. Who exits immediately, and who exits in the long-run when costs are no longer fixed? Phil exits immediately, Jill…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education