
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
refer to figure 23.6. if aggregate income is $1,000, aggregate consumption is
Note:-
- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism.
- Answer completely.
- You will get up vote for sure.
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 2
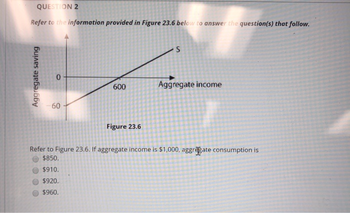
Refer to the information provided in Figure 23.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow.
Aggregate saving
0
60
600
Figure 23.6
S
Aggregate income
Refer to Figure 23.6. If aggregate income is $1,000, aggregate consumption is
$850.
$910.
$920.
$960.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Show full answers to the questions and steps to this exercisearrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardax policy is one used not only for economic purposes but also for political purposes. It is the opinion of some economists and politicians that the rich should pay more of their income in taxes, and that the resulting fairness from this rise in taxes will lead to more economic growth and a rise in employment. Using the simple expenditure model (Y and Ep, not IS-LM) answer these two questions: One, would a lump-sum tax increase on many high-income households cause GDP to rise in the short run as predicted by the politicians? Why or why not? And two, are there macroeconomic conditions in the simple model under which such a tax increase would be fully warranted? Draw the graphs and explain the outcomes for both cases.arrow_forward
- Assume the following model of the expenditure sector: S=C+I+G+Nx TR=100 C=420+(4/5)YD I=160 G=180 Nx=-40 YD=Y+TR-TA TA=(1/6)Y Assume you increase both government purchases (G) and taxes (TA) by the same lump sum of deltaG=deltaTA=+300. Would this be sufficent to reach the full employment level of output at Y*=2700? Why or why not?arrow_forwardA media company wants to know how much consumers spend in a closed economy. The answer is not readily available, but we know the following: Consumption: C = 50 + 0.6(Y - T) • Investment: 1 = 40-500 i • Taxes: T = 2C . Government spending: G = 20 where Y is GDP and i is the interest rate. At the time of the analysis, the central bank made sure that the interest rate. was 4% What is the level of consumption C? Select one: a 155 b. 170 c. 195 d. 220arrow_forwardGiven the scatter diagram in Figure 8-1, what is the MPC (your best estimate)? a. 1 b. 2/3 c. 1/2 d. 1/3 I know the answer of this question answer is 2/3 but can you please give the explanation how 2/3 is the answer of the problemarrow_forward
- If the increase in government spending is $500 and the marginal propensity to consume is .75 then the change in real gross domestic domestic product will be ___arrow_forwardOne last time, please consider a closed economy with the following information: • Economic investment = $4500 • Private savings = $3000 Output (income) = $16,000 Consumption = $11,000 This economy has no transfer payments; in other words, total taxes and "net taxes" are the same thing. Carefully following all numeric instructions, calculate this economy's taxes (T). Note that there are no transfer payments.arrow_forwardeconomicsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education