
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Refer to the diagram above. The shift of the aggregate
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
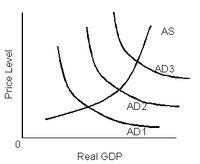
Transcribed Image Text:AS
AD3
AD2
AD1
Real GDP
Price Level
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The United States enters a recession: Use the money market supply and demand model to explain, in the "Keynesian Transmission Mechanism", what the Fed could do in open market operation to help the the economy recover. - Be sure to show what would happen to the money supply, interest rates, investment, and aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS) in the goods and services market.arrow_forwardSuppose the economy is experiencing inflation. If the Federal Reserve enacts contractionary monetary policy, interest rates will likely Multiple Choice rise causing prices to decrease. fall causing prices to increase. fall causing prices to decrease. rise causing prices to increasearrow_forwardApplied Problems on Monetary Policy and Interest Rates 1. For each of the following questions, draw the Money Demand curve (MD) and Money Supply curve (MS) and label the equilibrium interest rate as i*. Also show how the MS- MD graph changes due to the given events and as a result how the equilibrium interest rate changes. (In your answer you should clearly state and show what happens to the MS and MD curves and also what happens to the interest rate).arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements is true? Group of answer choices To increase the interest rate, the Reserve Bank conducts expansionary open market operations. The central bank should reduce the price of bonds for a contractionary monetary policy. Reducing the supply of money will lead to a decrease in the interest rate. An increase in money demand leads to a fall in the interest rate.arrow_forwardDuring a period of inflation, an appropriate pair of policies for the Fed to implement would be to Group of answer choices raise the legal reserve requirement and lower the discount rate sell government securities and raise the discount rate increase the federal funds rate by purchasing government securities raise the discount rate and lower the legal reserve requirementarrow_forwardExplain how lowering the reserve requirement ratio by the central bank will affect the aggregate demand at any given price level. Use relevant graphs to support your answer.arrow_forward
- As a response to high inflation, in March 2022, the Federal Reserve System (Fed) approved its first interest rate hike since December 2018. However, inflation rate still remained very high and piked in June 2022. The last time inflation ran that high was in the 1980s. To bring down inflation, the Fed implemented more restrictive monetary policy and approved another interest rate hike of 0.75 percent in November 2022. The Fed decided to maintain the federal funds rate at a target level of 4%. What the Fed need do to achieve a higher target federal funds rate (how to implement monetary policy)? If CPI increased from 287.7 in the 2nd quarter (Q2) 2022 to 298.1 in the 3rd (Q3) 2022. Using CPI-based inflation rate, how much is real interest rate if the Fed sets nominal interest rate at 4%. Note: we assume velocity of money supply is constant.arrow_forwardBoblandia produces no oil. It starts at potential GDP with inflation equal to the Central Bank's inflation target. Boblandia then sees a significant increase in the price of oil. Which of the following is true (according to our models) if the Central Bank engages in inflation targeting? The Central Bank will enact expansionary monetary policy. This action will put upward pressure on read GDP. The Central Bank will enact expansionary monetary policy. This action will put downward pressure on read GDP. The Central Bank will enact contractionary monetary policy. This action will put upward pressure on read GDP. The Central Bank will enact contractionary monetary policy. This action will put downward pressure on read GDP.arrow_forwardWhat does the Taylor rule imply that policymakers should do to the fed funds rate under the following scenarios? Unemployment rises due to a recession. An oil price shock causes the inflation rate to rise by 1% and output to fall by 1%. The economy experiences prolonged increases in productivity growth while actual output growth is unchanged. Potential output declines while actual output remains unchanged. The Fed revises its (implicit) inflation target downward. The equilibrium real fed funds rate decreases.arrow_forward
- Assume the monetary policy curve is given by r = 1.5 +0.75π. a) Calculate the real interest rate when the inflation rate is at 2%, 3%, and 4%. b) Plot the monetary policy curve and identify the points from part (a).arrow_forwardSuppose that the money demand function is (M/P)d = 1,000 − 100r, where r is the interest rate in percent. The money supply M is 1,000 and the price level P is 2. If the Fed wishes to raise the interest rate to 7 percent, what money supply should it set?arrow_forwardSuppose the Federal Reserve (the US central bank) increases the money stock. Create a graph that explains the effect of the Fed's expansionary monetary policy in the Short Run.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education