
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
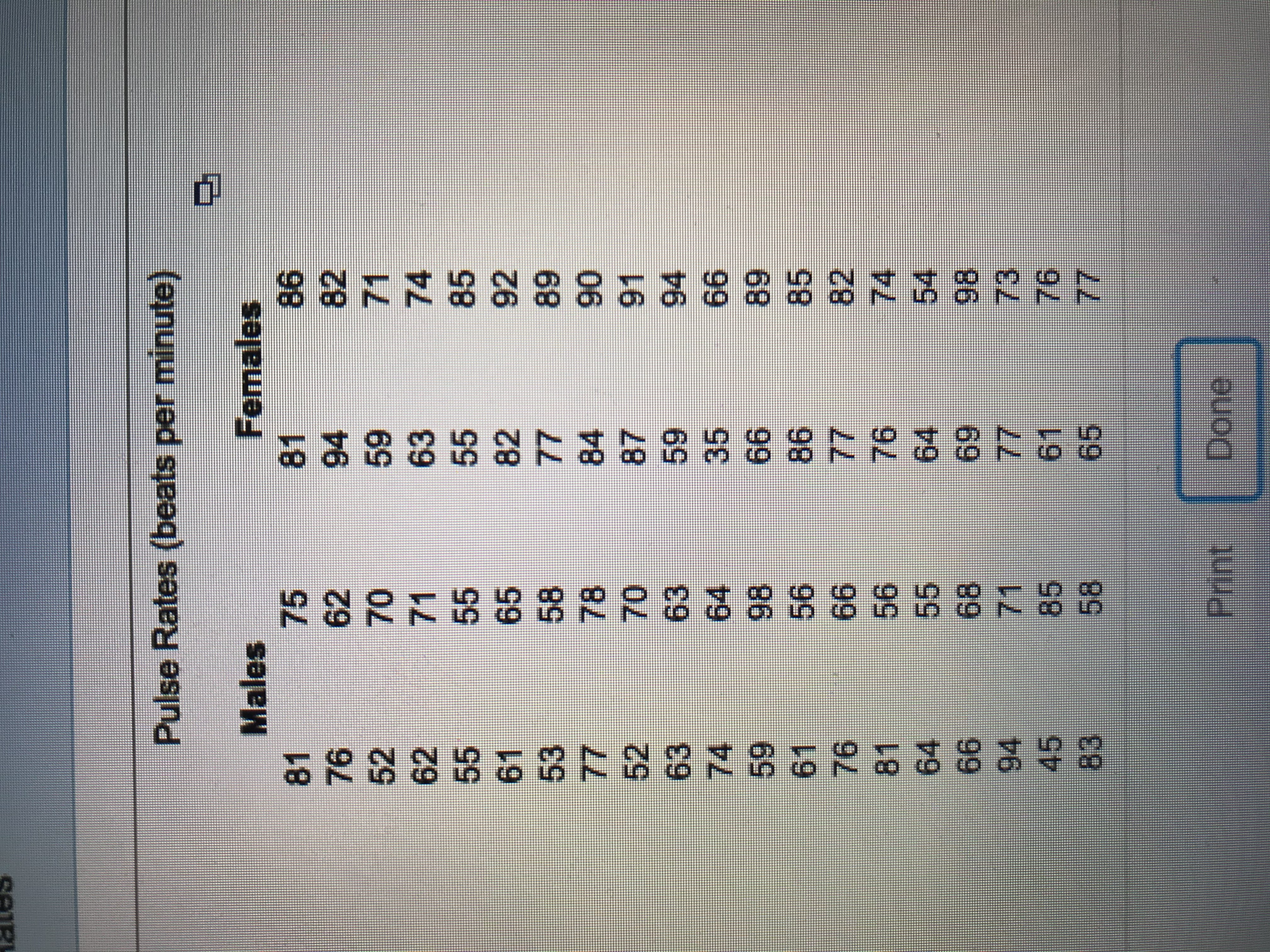
Transcribed Image Text:**Pulse Rates Analysis (Beats Per Minute)**
This data presents pulse rates, measured in beats per minute, for two groups, Males and Females. The pulse rates are listed in columns under each group.
**Males:**
- 81, 76, 52, 62, 55, 61, 53, 77, 52, 63
- 74, 59, 61, 76, 81, 64, 66, 94, 45, 83
**Females:**
- 75, 62, 70, 71, 55, 65, 58, 78, 70, 63
- 64, 98, 56, 66, 56, 55, 68, 71, 85, 58
**Females (continued):**
- 81, 94, 59, 63, 55, 82, 77, 84, 59, 35
- 66, 86, 86, 77, 76, 64, 69, 77, 61, 66
**Females (continued):**
- 86, 82, 71, 74, 85, 92, 89, 90, 59, 66
- 85, 82, 94, 54, 98, 73, 76, 77
This data can be used for comparative studies of average pulse rates between genders, or for statistical analysis such as finding means, medians, and ranges for each gender group. The variability in pulse rates can be further explored to understand factors affecting heart rates in different individuals.
![Refer to the accompanying data set and construct a 90% confidence interval estimate of the mean pulse rate of adult females; then do the same for adult males. Compare the results.
- Click the icon to view the pulse rates for adult females and adult males.
1. **Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult females.**
\[ \underline{\hspace{2cm}} \, \text{bpm} < \mu < \underline{\hspace{2cm}} \, \text{bpm} \]
*(Round to one decimal place as needed.)*
2. **Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult males.**
\[ \underline{\hspace{2cm}} \, \text{bpm} < \mu < \underline{\hspace{2cm}} \, \text{bpm} \]
*(Round to one decimal place as needed.)*
**Compare the results.**
- **A.** The confidence intervals overlap, so it appears that there is no significant difference in mean pulse rates between adult females and adult males.
- **B.** The confidence intervals do not overlap, so it appears that adult females have a significantly higher mean pulse rate than adult males.
- **C.** The confidence intervals do not overlap, so it appears that there is no significant difference in mean pulse rates between adult females and adult males.
- **D.** The confidence intervals overlap, so it appears that adult males have a significantly higher mean pulse rate than adult females.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/121bf263-4a6e-46d9-9385-c90d802499da/861d99f8-6ce1-4af9-82ba-dcbd6b7ae5d0/tyvpawt_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:Refer to the accompanying data set and construct a 90% confidence interval estimate of the mean pulse rate of adult females; then do the same for adult males. Compare the results.
- Click the icon to view the pulse rates for adult females and adult males.
1. **Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult females.**
\[ \underline{\hspace{2cm}} \, \text{bpm} < \mu < \underline{\hspace{2cm}} \, \text{bpm} \]
*(Round to one decimal place as needed.)*
2. **Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult males.**
\[ \underline{\hspace{2cm}} \, \text{bpm} < \mu < \underline{\hspace{2cm}} \, \text{bpm} \]
*(Round to one decimal place as needed.)*
**Compare the results.**
- **A.** The confidence intervals overlap, so it appears that there is no significant difference in mean pulse rates between adult females and adult males.
- **B.** The confidence intervals do not overlap, so it appears that adult females have a significantly higher mean pulse rate than adult males.
- **C.** The confidence intervals do not overlap, so it appears that there is no significant difference in mean pulse rates between adult females and adult males.
- **D.** The confidence intervals overlap, so it appears that adult males have a significantly higher mean pulse rate than adult females.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pulse Rates (beats per minute) Males Females 82 71 82 82 73 61 97 81 50 75 58 70 60 75 68 72 52 56 58 86 61 64 82 91 50 55 80 86 78 79 85 91 50 69 85 90 64 66 53 97 70 66 37 68 58 95 65 92 65 60 84 83 78 64 74 80 84 57 79 75 66 55 66 54 68 68 64 98 94 73 77 74 41 82 58 74 85 60 67 74arrow_forwardRefer to the accompanying data set and construct a 90% confidence interval estimate of the mean pulse rate of adult females; then do the same for adult males. Compare the results. Click the icon to view the pulse rates for adult females and adult males. Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult females. bpm < µ< bpm (Round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forwardRefer to the accompanying data set and construct a 90% confidence interval estimate of the mean pulse rate of adult females; then do the same for adult males. Compare the results. Click the icon to view the pulse rates for adult females and adult males. Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult females. bpm <μarrow_forward
- Translate the statement into a confidence interval. Approximate the level of confidence. In a survey of 900 adults in a country, 80% think teaching is one of the most important jobs in the country today. The survey's margin of error is +3%. The confidence interval for the proportion is (OD (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse the confidence interval to find the estimated margin of error. Then find the sample mean. A biologist reports a confidence interval of (1.9.3.1) when estimating the mean height (in centimeters) of a sample of seedlings. The estimated margin of error is The sample mean isarrow_forwardRefer to the accompanying data set and construct a 90% confidence interval estimate of the mean pulse rate of adult females; then do the samé for adult males. Compare the results. A Click the icon to view the pulse rates for adult females and adult males. Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult females. 69.9 bpmarrow_forward
- Refer to the accompanying data set and construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the mean pulse rate of adult females; then do the same for adult males. Compare the results. Click the icon to view the pulse rates for adult females and adult males. Pulse Rates Construct a 95% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult females. bpm bpm <µ< (Round to one decimal place as needed.) Pulse Rates (beats per minute) Males Females 87 71 78 86 75 62 93 79 49 73 61 72 71 76 54 51 54 84 61 68 84 90 54 55 81 91 77 78 86 87 52 70 86 89 60 61 53 94 75 66 35 71 61 96 63 88 67 55 81 83 76 69 79 82 84 58 77 76 65 57 62 58 69 66 64 99 99 67 77 75 Enter your answer in the edit fields and then click Check Answer. 42 87 61 76 88 56 64 73arrow_forwardRefer to the accompanying data set and construct a 90% confidence interval estimate of the mean pulse rate of adult females; then do the same for adult males. Compare the results. Click the icon to view the pulse rates for adult females and adult males. Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult females. | bpm<µ<| bpm (Round to one decimal place as needed.) Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult males. |bpm<μ< bpm (Round to one decimal place as needed.) Compare the results. A. The confidence intervals overlap, so it appears that there is no difference in mean pulse rates between adult females and adult males. B. The confidence intervals do not overlap, so it appears that adult females have a higher mean pulse rate than adult males. C. The confidence intervals overlap, so it appears that adult males have a higher mean pulse rate than adult females. D. The confidence intervals do not overlap, so it appears that there is no…arrow_forwardThe distribution of heights in a population of women is approximately normal. Sixteen percent of the women have heights less than 62 inches. About 97.5% of the women have heights less than 71 inches. Use the empirical rule to estimate the mean and standard deviation of the heights in this population. Mean: K inches Standard Deviation: inchesarrow_forward
- Use the confidence interval to find the estimated margin of error. Then find the sample mean. A biologist reports a confidence interval of (4.0,4.8) when estimating the mean height (in centimeters) of a sample of seedlings. The estimated margin of error isarrow_forwardRefer to the accompanying data set and construct a 90% confidence interval estimate of the mean pulse rate of adult females; then do the same for adult males. Compare the results. Click the icon to view the pulse rates for adult females and adult males. i Pulse Rates Construct a 90% confidence interval of the mean pulse rate for adult females. | bpm<µ< bpm (Round to one decimal place as needed.) Pulse Rates (beats per minute) Males Females 82 74 78 86 75 64 95 82 47 72 55 70 59 75 65 77 53 52 57 84 60 69 80 93 53 56 79 88 78 80 88 90 52 75 88 93 65 65 59 95 73 64 37 68 60 98 66 92 65 56 85 80 80 68 78 82 80 60 76 76 65 58 63 56 66 67 66 99 99 69 81 73 41 83 59 75 85 56 63 74 Enter your answer in the edit fields and then click Check Answer.arrow_forwardCereals sodium values have a mean of 167 and a standard deviation of 77.3. Find the z-score for the cereal that has a sodium value of 0. How would you interpret this z-score?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman