
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
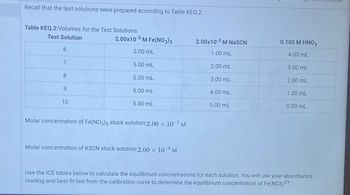
Transcribed Image Text:Recall that the test solutions were prepared according to Table KEQ.2.
Table KEQ.2:Volumes for the Test Solutions
Test Solution
6
7
8
9
10
2.00x10-3 M Fe(NO3)3
5.00 mL
5.00 mL
5.00 mL
5.00 mL
5.00 mL
Molar concentration of Fe(NO3)3 stock solution:2.00 × 10¯¹ M
Molar concentration of KSCN stock solution:2.00 × 10–³ M
2.00x10-³ M NaSCN
1.00 mL
2.00 mL
3.00 mL
4.00 mL
5.00 mL
0.100 M HNO3
4.00 mL
3.00 mL
2.00 mL
1.00 mL
0.00 mL
Use the ICE tables below to calculate the equilibrium concnetrations for each solution. You will use your absorbance
reading and best-fit line from the calibration curve to determine the equilibrium concentration of Fe(NCS)2+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 22 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nn.153. Subject :- Chemistryarrow_forwardIf you wish to precipitate Ag* from a 3.5 x 10-4 M solution, which of the following solutions could you use? Show the calculations that allowed you to determine the answer. There may be more than one correct choice. 5.0 x 10-5 M NaCI (Ksp for AgCl = 1.8 x 10-10) 5.0 x 10-5 M Na3PO4 (Ksp for Ag3PO4 = 8.9 x 1017) 5.0 x 10-5 M NaBr (Ksp for AgBr = 5.0 x 10-13) 5.0 x 10-5 M Na2CO3 (Ksp for Ag2CO3 = 8.1 x 10-12)arrow_forward9arrow_forward
- 44. You have three sodium carbonate solutions on a lab table in front of you. All of the solutions came from a 500.0-mL volumetric flask containing 3.00 M sodium carbonate. Solution 1: 100.0 mL of the 3.00 M solution. Solution 2: 50.0 mL of the 3.00 M solution. Solution 3: 10.0 mL of the 3.00 M solution. What is the new concentration of Solution 2 if 14.8 g of solid sodium carbonate is added and dissolved? (Assume no volume change.) a. 11.8 M b. 0.579 M c. 5.79 M d. 2.79 M e. 1.81 Marrow_forwardHow do I find the moles excess HCl titrated and Moles HCl absorbed by Tabletarrow_forward9arrow_forward
- Exactly 10.00-mL aliquots of a solution containing phenobarbital were measured into 50.00-mL volumetric flasks and made basic with KOH. The following volumes of a standard solution of phenobarbital containing 2.000μg/mL of phenobarbital were then introduced into each flask and the mixture was diluted to volume: 0.000, 0.500, 1.00, 1.50, 2.00 mL. The fluorescence of each of these solutions was measured with a fluorimeter, which gave values of 3.26, 4.80, 6.41, 8.02, 9.56, respectively. a. plot the data. b. derive a least squares equation for the data plotted in (a). c. find the concentration of phenobarbital from the equation in (b). d. calculate a standard deviation for the concentration obtained in (c).arrow_forward8 pleasearrow_forwardTo determine the concentration of a NaOH (39.997 g/mol) solution, 1.42 g of C8H5KO4 (a commonly used standard, 204.22 g/mol) was used. The volume of NaOH solution needed to reach the endpoint was 33.54 mL. What was the concentration (in molarity) of the NaOH solution? The mole:mole ratio for NaOH and KHP neutralization is 1:1. Report your answer to the thousandths place and do not include units.arrow_forward
- 280 mL of 1.08 M CrCl₂ is mixed with with 160 mL of 2.2 M KOH. Write out the balanced molecular, ionic, and net ionic equations. Then determine what mass of precipitate will form. Edit Format Table 12pt Paragraph V BIU A v T²V | V E✓ ✓ To ✓ √xarrow_forwardA student performed three H2SO4 titrations in Part 2 using their 0.1276 M NaOH solution which they previously standardized in Part 1. They reported the following measurements: Determination #1 Determination #2 Determination #3 Final NaOH Burette Reading 20.72 mL 41.54 mL 21.59 mL Initial NaOH Burette Reading 0.12 mL 20.72 mL 0.83 mL What was the total number of moles of H2SO4 in their second titration? Report your answer to the correct number of significant figures and only report the numerical value (no units).arrow_forwardA 12.7g sample of vinegar is titrated. It requires 19.75 mL of 0.205 M NaOH to neutralize the acetic acid (CH3COOH) in the vinegar. Calculate the weight percent (w/w) of acetic acid in the vinegar. Note: 1 mole of base neutralizes 1 mole of acid.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY