
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
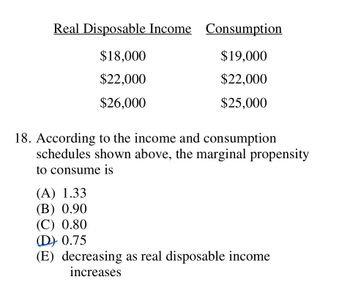
18. According to the income and consumption schedules shown above, the marginal propensity to consume is
(A) 1.33
(B) 0.90
(C) 0.80
(D) 0.75
(E) decreasing as real disposable income
How come MPC equals 0.75?
Transcribed Image Text:Real Disposable Income Consumption
$18,000
$19,000
$22,000
$22,000
$26,000
$25,000
18. According to the income and consumption
schedules shown above, the marginal propensity
to consume is
(A) 1.33
(B) 0.90
(C) 0.80
(D) 0.75
(E) decreasing as real disposable income
increases
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Utility Optimization Problem Suppose a household has the following lifetime utility function: (a) Finding Partial Derivatives of Utility U = c1/2 + Bc1/2 Find expressions for the partial derivatives of lifetime utility, U, with respect to period t and period t + 1 consumption. Is marginal utility of consumption in both periods always positive? (b) Finding Second Derivatives of Utility a²U Find expressions for the second derivatives of lifetime utility with respect to period t and t + 1 consumption, i.e., 321 and 227. Are these second derivatives always negative for any positive values of period t and t+1 consumption? c) Deriving Indifference Curve Expression Derive an expression for the indifference curve associated with lifetime utility level Uo (i.e., derive an expression for C++1 as a function of U₁ and c). What is the slope of the indifference curve? How does the magnitude of the slope vary with the value of Ę? d) Combining Budget Constraints Suppose that the household faces two…arrow_forward4) Distinguish between the short-run and long-run factors that affect residential investment.arrow_forwardQ4) Refer to the information provided in table below to answer the questions that follow. Y C S 0 100 180 190 1. Find the consumption, if the consumption function is: C= 120 +0.2Y. 2. Find aggregate saving. 3. Illustrate that by graph from the information provided in table.arrow_forward
- Suppose that Maria spends 84,500 on consumption, her disposable income is $90,000 and her Marginal Propensity to Save is .15. What does Maria's autonomous consumption equal? Select one: a. $5,500 b. $6,500 c. $7,000 d. $8,000arrow_forward61)If the marginal propensity to save is 0.2, then a $10,000 decrease in disposable income will Select one: a. increase consumption by $2,000. b. increase consumption by $8,000. c. decrease consumption by $8,000. d. decrease consumption by $2,000.arrow_forwardPlease help! Thank you very much for your time. If your disposable income increases from $12,000 to $17,000 and your consumption increases from $10,000 to $14,500, your MPC is_____ A. 0.2. B. 0.4. C. 0.6. D. 0.9.arrow_forward
- This problem has been solved! See the answer Explain the relationship between the aggregate expenditures model in graph (A) below and the aggregate demand–aggregate supply model in graph (B) below. In other words, explain how points 1, 2, and 3 are related to points 1’, 2’, and 3’.arrow_forwardIn an economy MPC equals to 0.85 if investment is increased by $20 how more would be the increase in incomearrow_forwardIncome choices: a. What will a 2% increase in tax rates do to disposable income? b. If Eduardo’s disposable income increases from $1,200 to $1,700 and his level of saving increases from minus $100 to a plus $100, his marginal propensity to save is:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education