
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
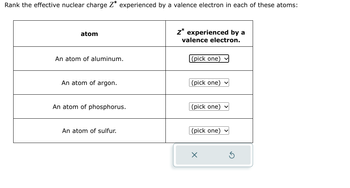
Transcribed Image Text:Rank the effective nuclear charge Z* experienced by a valence electron in each of these atoms:
atom
Z* experienced by a
valence electron.
An atom of aluminum.
(pick one)
An atom of argon.
(pick one)
An atom of phosphorus.
(pick one)
An atom of sulfur.
(pick one)
☑
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- (ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE AND CHEMICAL BONDING Understanding periodic trends in effective nuclear charge Rank the effective nuclear charge Z experienced by a valence electron in each of these atoms: atom An atom of palladium. An atom of molybdenum. An atom of cadmium. An atom of niobium. z experienced by a valence electron. (pick one) (pick one) (pick one) ✓ (pick one) X Śarrow_forwardConsider As and Br. Which would have a higher effective nuclear charge and why? O O Arsenic (As) because it has fewer electrons than bromine. Bromine (Br) because it has more electrons than arsenic. Arsenic (As) because both have the same number of core electrons, but Arsenic has fewer protons. Bromine (Br) because both have the same number of core electrons, but bromine has more protons. They have the same effective nuclear charge because they are in the same row.arrow_forward1-An atomic cation with a charge of +2 has the following electron configuration: [He] 2s22p4 What is the chemical symbol for the ion? How many electrons does the ion have? How many 2s electrons are in the ion? 2- Ammonium perchlorate (NH4ClO4) is powerful solid rocket fuel, used in the Space Shuttle boosters. It decomposes into nitrogen (N2) gas, chlorine (Cl2) gas, oxygen (O2) gas, and water vapor, releasing a great deal of energy. Calculate the moles of chlorine produced by the reaction of 0.90mol of ammonium perchlorate. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to the correct number of significant digits. _____________ 3-How many protons and neutrons are in an atom of Th-229 ? Number of protons= ________ Number of neutrons= _______ 4- The chemical formula for beryllium sulfide is BeS. A chemist determined by measurements that 0.055 moles of beryllium sulfide…arrow_forward
- Which specific electrons are added/removed, in this order, to form the ion?arrow_forward1) In the past you have learned that bismuth (Bi) is a metal that can lose 3 electrons and become Bi* . Actually, Bismuth is able to form 3 ions! The charges for each of the ions are 3-, 3+ and 5+. Propose electron configurations (long form only) for each ion. Explain the reasoning behind your configurations. Be sure to include the electron configuration of the neutral atom. Atom/ Electron Configuration (shorthand only) Reasoning for electron configuration of each ion Ion Bi (neutral) Bi3- Bi3+ Bi5+arrow_forwardThe periodic table lists all known elements arranged by atomic number. Atomic number is the nuclear charge, the number of protons in the nucleus of an an atom of a particular element. For a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Each column of the table, called a group, contains elements with the same number of valence electrons that are in different quantum levels. Each row of the table, called a period, contains elements with differing numbers of valence electrons that are in the same principal quantum level. The four main blocks of the table (s, p, d, and f) contain elements whose highest energy electrons have the same azimuthal quantum number (ℓ).arrow_forward
- Co forms two monatomic ions, Co³t and Co²+. From which sublevels do you expect electrons are lost in forming these ions? (Hint: It is possible for electrons other than those in the s and p sublevels to be involved in forming ions.) In forming the Co3+ ion are: electron(s) lost from the 4s orbital? electron(s) lost from the 3d orbital? To support your answer, complete the following. It is OK to use the noble gas core notation. (Express your answer as a series of orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of Li would be entered in complete form as 1s 2 2s 1 or in condensed form as [He]2s '.) Electron configuration of Co: 3+ Electron configuration of Co*arrow_forwardThe Periodic Table shows the common charges of ions that group elements form. Using the information in the Periodic Table, how would you rank the elements rubidium (Rb), antimony (Sb), and iodine (I) in order of increasing number of valence electrons? A Antimony has a greater number of valence electrons than iodine but a lower number than rubidium. B Antimony has a lower number of valence electrons than iodine but a greater number than rubidium. C Iodine has a lower number of valence electrons than rubidium but a greater number than antimony. D Rubidium has a greater number of valence electrons than antimony but a lower number than iodine.arrow_forwardHow many valence electrons are there in an atom of As (Z = 33)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:9781559539418
Author:Angelica Stacy
Publisher:MAC HIGHER

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning