
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Two metal disks, one with radius R1 = 2.59 cm and mass M1 = 0.850 kg and the other with radius R2 = 5.08 cm and mass M2 = 1.61 kg , are welded together and mounted on a frictionless axis through their common center. (Figure 1).
(A) A light string is wrapped around the edge of the smaller disk, and a 1.50-kg block, suspended from the free end of the string. If the block is released from rest at a distance of 2.10 m above the floor, what is its speed just before it strikes the floor?
(B) Repeat the calculation of part (A), this time with the string wrapped around the edge of the larger disk.
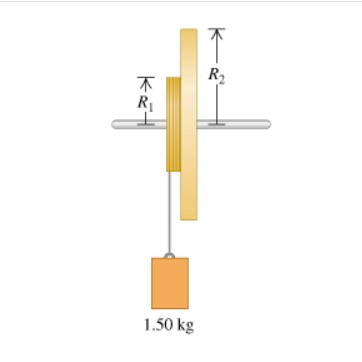
Transcribed Image Text:R2
R
1.50 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two identical masses are attached to frictionless pulleys by very light strings wrapped around the rim of the pulley and are released from rest. Both pulleys have the same mass and same diameter, but one is solid and the other is a hoop. As the masses fall, in which case is the tension in the string greater, or is it the same in both cases? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardAssume y= 0 + p. Be m A A beam, uniform in mass, M = 27 kg and length L = 28 m, hangs by a cable supported at point B, and rotates without friction around point A. On the end far of the beam, an object of mass m = 14 kg is hanging. The beam is making an angle of e = 35° at point A with respect to the + x- axis. The cable makes an angle o = 21° with respect to the - x-axis at B. Assume w = 0 + Q. What is the vertical force Sy that the wall exerts on the beam at point A in terms of the tension T, given parameters, and variables available in the palette?arrow_forwardA string goes over a solid pulley (1 = (1/2)mR2) which has a mass 8.0 kg and a radius of 0.200 m . two masses (10.0 kg and 20.0 kg) are attached to the ends of the string and hang freely. When the system relea to move. Determine the acceleration of the massesarrow_forward
- A uniform beam weighing 10 N sits at rest across two triangular stands. The beam has a length of 1.0 m. Assume the left end of the beam is at origin, the left stand is at position 0.10 m and the right stand is at position 0.80 m. What is the magnitude of the normal force of the left stand acting on the beam, in Newtons? (Hint: Clearly draw a diagram with the pivot, forces, and r associated with each force.) Your answer needs to have 2 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forwardTo loosen a pipe fitting, a plumber slips a piece of scrap pipe (a "cheater") over his wrench handle. He stands on the end of the cheater, applying his 900 N weight at a point 0.80 m from the center of the fitting. The wrench handle and cheater make an angle of 19° with the horizontal. Find the magnitude and direction of the torque he applies about the center of the fitting. (680 Nm) F-900Narrow_forwardA coin of mass m=10.00 g is placed at R=16.00 cm from the center of a rotating, horizontal turntable. The coin has static and kinetic coefficients of friction with the turntable surface of u =0.90 and HK = 0.72, respectively. (a) If the turntable is sping at an angular velocity of 5.20 rad/s, how much is the friction between the coin and the turntable? Answer: (b) What is the maximum angular velocity at which the turntable can spin without the coin sliding? Answer: rad/s.arrow_forward
- A child's top is held in place upright on a frictionless surface. The axle has a radius of r = 3.21 mm. Two strings are wrapped around the axle, and the top is set spinning by T T applying T = 1.40N of constant tension to each string. If it takes 0.590 s for the string to unwind, how much angular 2r momentum L does the top acquire? Assume that the strings do not slip as the tension is applied. R P h kg-m? %3D S Point P is located on the outer surface of the top, a distance h = 27.0 mm above the ground. The angle that the outer surface of the top makes with the rotation axis of the top is 0 = 22.0°. If the final tangential speed v, of point P is 1.95 m/s, what is the top's moment of inertia I? 2r T. I = kg-m?arrow_forwardA thin rod of mass 0.650 kg and length 1.48 m is at rest, hanging vertically from a strong, fixed hinge at its top end. Suddenly, a horizontal impulsive force 16.7 N is applied to it. Suppose the force acts at the bottom end of the rod. Find the acceleration of its center of mass.arrow_forwardA sphere of mass 5 kg and a block of mass m2 =3 kg are connected by a light cord that passes over a pulley as shown in Figure. The radius of the pulley is R=20 cm, and the mass of the thin rim is 1 kg. The spokes of the pulley have negligible mass. The block slides on a horizontal surface. The kinetic coefficient of friction between block and horizontal surface is 0.1 Find for the linear acceleration of the two objects,arrow_forward
- If the distance h is 1.52 m , what is the vertical component of the force exerted on the wheel A by the track? If the distance h is 1.52 m , what is the vertical component of the force exerted on the wheel B by the track? Find the maximum value h can have without causing one wheel to leave the track. Thank you!arrow_forwardhe wheels of a wagon can be approximated as the combination of a thin outer hoop, of radius ?h=0.421 mrh=0.421 m and mass 5.27 kg5.27 kg, and two thin crossed rods of mass 7.37 kg7.37 kg each. A farmer would like to replace his wheels with uniform disks ?d=0.0588 mtd=0.0588 m thick, made out of a material with a density of 6450 kg6450 kg per cubic meter. If the new wheel is to have the same moment of inertia about its center as the old wheel about its center, what should the radius of the disk be?arrow_forwardCan somebody help pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON