
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
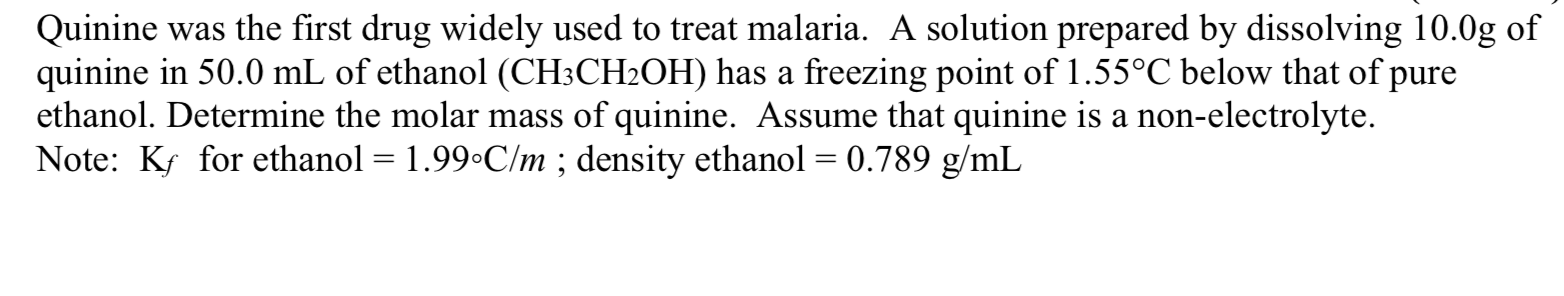
Transcribed Image Text:Quinine was the first drug widely used to treat malaria. A solution prepared by dissolving 10.0g of
quinine in 50.0 mL of ethanol (CH;CH2OH) has a freezing point of 1.55°C below that of pure
ethanol. Determine the molar mass of quinine. Assume that quinine is a non-electrolyte.
Note: Ks for ethanol = 1.99•C/m ; density ethanol = 0.789 g/mL
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- When 224. mg of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 45.0 g of cyclohexane (C6H₁2), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 6.5 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on cyclohexane, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to 1 significant digit.arrow_forwardThe freezing point of ethanol, CH3CH2OH, is -117.300 °C at 1 atmosphere. Kf(ethanol) = 1.99 °C/mIn a laboratory experiment, students synthesized a new compound and found that when 13.34 grams of the compound were dissolved in 212.8 grams of ethanol, the solution began to freeze at -117.981 °C. The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non-electrolyte.What is the molecular weight they determined for this compound?arrow_forwardThe freezing point of benzene, C,Hg, is 5.500 °C at 1 atmosphere. Kf(benzene) = 5.12 °C/m In a laboratory experiment, students synthesized a new compound and found that when 13.39 grams of the compound were dissolved in 298.4 grams of benzene, the solution began to freeze at 4.703 °C. The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non-electrolyte. What is the molecular weight they determined for this compound? g/molarrow_forward
- The solubility of Ne in water at 25 °C is 2.1 × 10⁻⁴ M when the partial pressure of Ne is 0.20 atm. What is the value of the Henry's law constant for Ne?arrow_forwardA solid consists of a mixture of NaNO3 and Mg(NO3)2. When 6.50 g of the solid is dissolved in 50.0 g of water, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 5.04°C. What is the composition by mass of the solid?arrow_forwardAn aqueous solution containing 10.0 g of starch per liter has an osmotic pressure of 3.8 mm Hg at 25 °C. What is the average molar mass of starch? (Becausenot all starch molecules are identical, the result will be an average.) What is the freezing point of the solution? Would it be easy to determine the molecular weight of starch by measuring the freezing point depression? (Assume that the molarity and molality are the same for this solution.)arrow_forward
- Which solution has the lower freezing point, 0.20 M NaOH or 0.20 M Ba(OH)2? Both NaOH and Ba(OH)2 are strong electrolytes. Perform any calculations necessary then answer using full sentences.arrow_forward13.69 g of protein are dissolved in 200.0 mL of water at 28.3 ∘C. The osmotic pressure of the solution is 1.999 mmHg. Find the molar mass of the protein.arrow_forwardWhen 911. mg of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 35.0 g of benzene (C,H6), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 2.5 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on benzene, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Ox10 미□arrow_forward
- When 60.1 mg of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 70.0 g of benzene (CH), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 5.4 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on benzene, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to 1 significant digit. 0 ☐ X x10 Śarrow_forwardSuppose a group of students tell you that they added solid sodium chloride NaCls to 35 mL of deionized water and they did not record how many grams of NaCl they added but they got a freezing point depression of 1.25°C. Calculate how many grams of NaCl the students added. The pure freezing point of water is 0.00°C and the freezing point depression constant (K) of water is 1.858 °C/m. Remember that NaCl is a solid salt and an ionic compound therefore it contributes a negligible amount to the overall additive volume and keep track of its van't Hoff factor. The density of water at 20°C is 0.9982 g/mL.arrow_forwardWhat is the freezing point of an aqueous FeCl₃ solution made to be 0.81 m FeCl₃? (Kf for water is 1.86 °C/m)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY