
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

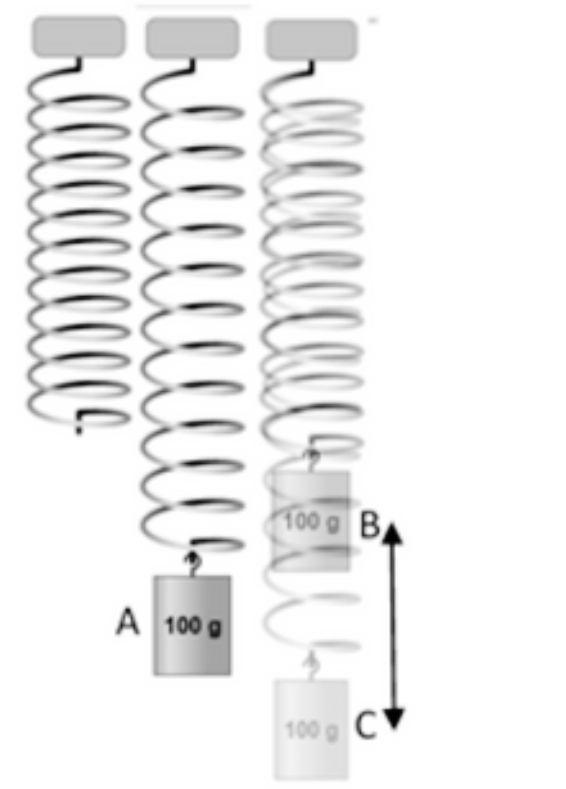
Transcribed Image Text:Questions 2-5 reference the picture of a mass attached to a spring shown. The leftmost picture gives the spring in its relaxed (equilibrium) position. The mass is lifted to point "B" and let go such that it oscillates up and down as shown in the rightmost position. Positions B and C are its highest and lowest points while bouncing. Point A is where the mass is traveling the fastest. Neglect air drag.
*Diagram Explanation:*
The diagram illustrates a spring attached to a 100 g mass. There are three marked positions:
- Position A (equilibrium position): The spring is at its natural length with no external forces applied.
- Position B (highest position): The spring is compressed, indicating the mass was lifted.
- Position C (lowest position): The spring is stretched, indicating the mass has descended as the spring oscillates.
*Question:*
At what point will the mass have the largest elastic (spring) potential energy?
- ○ A
- ○ B
- ○ C
- ○ All points will have the same amount of elastic potential energy.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given : mass attached to spring, m = 100 g
Spring Oscillating between point B and point C.
B is highest point of bouncing.
C is lowest point of bouncing.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Questions 6-13 refer to the figure below. The graph represents the position as a function of time for a small 1.20 kg object attached to a light spring that is oscillating on a smooth horizontal surface. n 0.4 Time (s) 0 0.2 6. What is the amplitude of the motion (in cm)? 7. What is the period of the motion (in s)? 8. What is the frequency of the motion (in Hz)? 9. What is the angular frequency of the motion (in rad/s)? 0.6 11. What is the maximum speed of the object (in m/s)? 10. What is the spring constant of the spring (in N/m)? (Be aware of units!) 0.8 12. What is the maximum acceleration of the object (in m/s²)? 13. If instead of attaching the 1.20 kg mass to the spring, we attach a mass of 2.4 kg. What is the new period (in s) of the motion?arrow_forwardFor an oscillating air-track glider (Figure 1), the force constant of the spring is k=200N/m and the glider mass is m=0.50kg. Now let's find the angular frequency, frequency, and period of the glider's motion. a)suppose we could "tune" this system by varying the mass. What mass would be required for a period of 2.0 s? Express your answer in kilograms.arrow_forwardA conical pendulum consists of a weight fixed on the end of a string suspended from a privet. Instead of swing back and forth it moves in a constant speed around in a circle tracing a cone shape with the string. a. Draw a force diagram for a conical pendulum. b.Find a relationship between the length of the string and the time the weight would take to complete a full circle. c. If the system was dampened discuss the energy and period of the pendulum.arrow_forward
- a. What is the translational velocity of the bottom tip of the pendulum at the moment that gravitational potential energy is 50% of its maximum? b. What effect would doubling the mass and length of the physical pendulum have on the answer to part (a) of the problem? c. Draw graphs of angular acceleration, tangential translational acceleration, and centripetal acceleration as functions of the instantaneous angle that the pendulum makes with the vertical. In all three graphs show the behavior of the acceleration from release with theta =38.4 degree until the pendulum is vertical and theta =0 degree.arrow_forwardAt what time does the oscillator shown below first reach its Equilibrium Position? A в D E F t=0.0 s t=0.30s t=0.45 s t=0.90 s t=1.35 s t=1.80 s +0.10 m---- -0.10 m (Unit = s) %3D wwarrow_forwardChapter 15, Problem 083 The scale of a spring balance that reads from 0 to 26.2 kg is 14.6 cm long. A package suspended from the balance is found to oscillate vertically with a frequency of 2.25 Hz. (a) What is the spring constant? (b) How much does the package weigh? (a) Number Units (b) Number Units Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Workarrow_forward
- A 2.6kg mass is a attached to a spring with a stiffness of 410N/m. In the picture on the left side, the system is in equilibrium. A student then displaces the spring downward to the position as shown. Neglect friction and drag. What is the period of the harmonic motion? unit What is the frequency of the harmonic motion? unit How many cycles would the system make in 55s? (You may answer with a decimal) 37cm What is the minimum length (L) of the spring as it oscillates? cm How far does the mass travel during one period? cm 44cm 00000arrow_forwardA 240 g air-track glider is attached to a spring. The glider is pushed in 9.60 cm and released. A student with a stopwatch finds that 14.0 oscillations take 12.5 s. You may want to review (Pages 400 - 402) For help with math skills, you may want to review: Solving Radical Equations For general problem-solving tips and strategies for this topic, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Mass on a spring. Part A What is the spring constant? Express your answer with the appropriate units. 122 Submit μA N m ? Previous Answers Request Answer * Incorrect; Try Again: 5 attempts remainingarrow_forwardA peg on a turntable moves with a constant tangential speed of 0.67 m/s in a circle of radius 0.26m. The peg casts a shadow on a wall. Find the following quantities related to the motion of the shadow.1) Find the period. Express your answer using two significant figures. T=(?)s2) Find the amplitude. A=(?)m3) Find the Max Speed Vmax= (?) m/s4) Find the maximum magnitude of the acceleration. aMax=(?)m/s^2arrow_forward
- 3 Neha gives an explanation for the Electromotive Brain Transducer 3000 shown below. She says that when you shake the pencil with a period of 6.0 seconds, the long paperclip will swing with a large amplitude, but the shorter paperclip will not swing much at all. What is the technical term for what causes the long paperclip to vibrate with a large amplitude, but not the short paperclip? 1 Period: 3 s Period: 6 sarrow_forwardA block with mass M rests on a frictionless surface and is connected to a horizontal spring with a force constant k. The other end of the spring is attached to a wall (see figure). A second block with mass mm rests on top of the first block. The coefficient of static friction between the blocks is μs. Find the maximum amplitude of oscillation such that the top block will not slip on the bottom block.arrow_forwardGrandfather clocks keep time by advancing the hands a set amount per oscillation of the pendulum. Therefore, the pendulum needs to have a very accurate period for the clock to keep time accurately. As a fine adjustment of the pendulum’s period, many grandfather clocks have an adjustment nut on a bolt at the bottom of the pendulum disk. Screwing this nut inward or outward changes the mass distribution of the pendulum by moving the pendulum disk closer to or farther from the axis of rotation at O. Let mp = 0.7 kg and r = 0.1 m Model the pendulum as a uniform disk of radius r and mass mp at the end of a rod of negligible mass and length L – r, and assume that the oscillations of θ are small. If the pendulum disk is initially at a distance L = 0.85 m from the pin at O, how much would the period of the pendulum change if the adjustment nut with a lead of 0.5 mm was rotated four complete rotations closer to the disk? In addition, how much time would the clock gain or lose in a 24 h…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON