
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
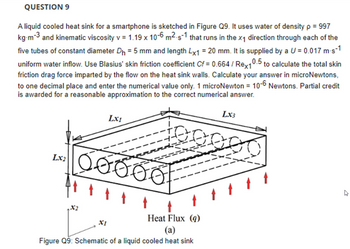
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 9
A liquid cooled heat sink for a smartphone is sketched in Figure Q9. It uses water of density p = 997
kg m-3 and kinematic viscosity v = 1.19 x 10-6 m²-s-1 that runs in the x₁ direction through each of the
five tubes of constant diameter D₁ = 5 mm and length Lx1 = 20 mm. It is supplied by a U = 0.017 m-s-1
uniform water inflow. Use Blasius' skin friction coefficient Cf = 0.664 / Rex1
0.5 to calculate the total skin
friction drag force imparted by the flow on the heat sink walls. Calculate your answer in microNewtons,
to one decimal place and enter the numerical value only. 1 microNewton = 10-6 Newtons. Partial credit
is awarded for a reasonable approximation to the correct numerical answer.
Lx₂
X2
Lx1
X1
Ő ve
Heat Flux (9)
(a)
Figure Q9: Schematic of a liquid cooled heat sink
LX3
4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 6-1: The Reynolds number is an engineering parameter that relates to the volume flow rate of a fluid 4Q where vis πνd m² through a tube of diameter d as Red the fluid kinematic viscosity. Determine the Reynolds number and its uncertainty by general analysis given d = 50.4 ±0.1 mm, Q = 0.213 +0.005 S v = 0.999 × 10-6 ± 0.005 × 10-6 m². Which variable contributes the most to the overall uncertainty? Assume uncertainties are at 95 % confidence. Sarrow_forwardProblem 2 The apparatus sketched in the figure below serves as a viscometer i.e. it can be used to measure the viscosity of a liquid. In the drawing, D is a large reservoir containing a viscous liquid A and E is a cylindrical tube of radius R, open at both ends, surrounding and coaxial with B, which is a cylindrical "bob" of radius êR that is dragged up through the fluid by a frictionless pulley system (C) utilizing a weight W. Determine a design equation that relates the viscosity of the liquid to the geometry of the system and the weight W. Hint: you can assume that the length of the cylindrical tube is sufficiently long for the flow to reach steady state. W E D Barrow_forwardPlease help me question 2.6arrow_forward
- Working for an engineering consultancy firm, your knowledge of fluid dynamics is required to design a new safety feature for a high-pressure air line in a factory. The air line takes the form of a cylindrical pipe of diameter 150 mm, which is designed to operate between 0.45 MPa and 0.76 MPa. At the end of the pipe a burs9ng disk is placed so that, if the pressure exceeds the maximum opera9ng pressure, the air is vented to atmosphere rather than over-pressuring the chemical reac9on vessel (Figures 4a and 4b). In this ques9on, you should treat the flow as quasione-dimensional and inviscid. The air in the surrounding atmosphere is at 101 kPa and 298 K. a) You have a choice of five disks which can withstand the following forces across them before burs9ng: 10.5 kN, 11.0 kN, 11.5 kN, 12.0 kN, 12.5 kN. Which of these burs9ng disks would you recommend, and why? b) Due to an over-pressurisa9on of the air line, the disk bursts at 9me t = 0. At what pressure in the air line will this occur? c)…arrow_forwardPlease help, will give helpful ratings if correct!!!arrow_forwardCorection the following number k=.02625,Kinematic viscosity(fancy v)=16.55*10^-6m^2/s,Pr=.7 Re(x=L)=54380 Nu(x)=170.1 h(x=L)=29.8 Ts(l)=54.9Carrow_forward
- Example(1-13): steam and water flow through 75 mm inside diameter pipe at flow rate of 0.05 and 1.5 m³/s respectivily. If the mean temperature and pressure are 330 K and 120 kpa, what is the pressure drop per unit length of pipe. Where the pipe roughness 0.00015 mm, liquid and gas viscosities are 0.52x10³ pa.s and 0.0133x10-³ pa.s.arrow_forwardProblem 2 For this problem, use the graph below, also given at the end of the notes on stress concentration. Determine the stress concentration factor in a 0.2 inch thick flat bar with two symmetric grooves (semi-circular notches) of radius 0.3 inches and width 2.6 inches. Use the graph in Fig. 2. 3.0 Nolched rectangular bar in lension or simple compression. a0 = F/A, where A = dt and is the thickness. 2.6 2.2 1.2 K, 1.1 1.8 1,05 14 1.0 0,05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 rld Fig. 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY