
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Question 71
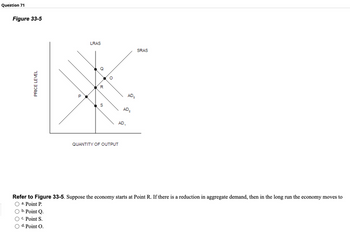
Figure 33-5
PRICE LEVEL
LRAS
R
S
O
AD₁
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT
AD₂
AD₂
SRAS
Refer to Figure 33-5. Suppose the economy starts at Point R. If there is a reduction in aggregate demand, then in the long run the economy moves to
a. Point P.
b. Point Q.
c. Point S.
d. Point O.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following causes the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the right? O A. an increase in the expected price of an important natural resource B. a positive technological change O C. a higher expected future price level O D. a decrease in the capital stockarrow_forwardFigure 34-3 PRICE LEVEL a a a LRAS Y, Y₂ QUANTITY OF OUTPUT SRAS. SRAS. AD Refer to Figure 34-3. Starting from point B and assuming that aggregate demand is held constant, in the long run the economy is likely to experience a falling price level and a falling level of output, as the economy moves to point C. falling price level and a rising level of output, as the economy moves to point A. rising price level and a falling level of output, as the economy moves to point A. Orising price level and a rising level of output, as the economy moves to point C.arrow_forwardFigure 6 PRICE LEVEL LRAS Y, Y₂ QUANTITY OF OUTPUT SRAS; SRAS, AD 15. Refer to Figure 6. Starting from point A and assuming that aggregate demand is held constant, in the long run the economy is likely to experience a a. falling price level and a falling level of output, as the economy moves to point C. b. rising price level and a falling level of output, as the economy moves to point B. c. falling price level and a rising level of output, as the economy moves to point B. d. rising price level and a rising level of output, as the economy moves to point C.arrow_forward
- Consider an economy with the following aggregate demand (AD) and short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) schedules. Decision-makers have previously made decisions anticipat- ing that the price level during the current period will be p 105° a. Indicate the quantity of GDP that will be produced during the period.arrow_forwardSolutions for c,d and earrow_forward28. Which of the following are determinants of aggregate demand? Choose all that apply. A. a spike in net exports B. the Federal Reserve lowering its interest rates C. a change in technology D. growing consumer confidencearrow_forward
- Which of the following would cause the Aggregate Supply curve to move from AS to AS2 in the graph below? A) A general increase in energy and labor cost for businesses. B) A general decrease in labor cost for businesses. C) An increase in productivity. D) A federal government increase in spending.arrow_forwardIn the intermediate range of an aggregate supply curve an increase in total demand will O cause unemployment and deflation. cause employment to fall, but the price level to rise. increase employment, output, and the price level. O increase employment and output but not the price level.arrow_forwardStarting at long run equilibrium, ceteris paribus, an increase in the costs of widely used factors of production would most likely O Increase short run aggregate supply and create an inflationary gap. O Decrease long run aggregate supply and create a recessionary gap. O Decrease short run aggregate supply and create a recessionary gap. O Decrease aggregate demand and create a recessionary gap.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education