
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:~ 2 hours
Content attribution
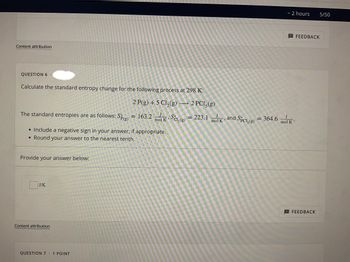
QUESTION 6.
Calculate the standard entropy change for the following process at 298 K:
2 P(g) + 5 Cl₂(g) → 2 PC15(g)
The standard entropies are as follows: Sp(g) = 163.2 mol KSC₂(g) = 223.1 mol and Spcl, (g) = 364.6
J
1
K
;
mol K
• Include a negative sign in your answer, if appropriate.
• Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Provide your answer below:
J/K
Content attribution
QUESTION 7
1 POINT
5/50
FEEDBACK
FEEDBACK
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the ΔG∘rxn for 2ClF (g) + Br2 (g) <------> 2ClBr (g) + F2 (g) _____ kJ/molarrow_forward4.) Determine if each of the following is a spontaneous process, a nonspontaneous process, or an equilibrium process at the specified temperature. Use the following equation: ΔS ΣnS" (products) -ΣnS (reactants (a) H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) at 0°C (b) СаСОз(s) — СаО(s) + CO2(g) at 200°C (с) СаСОз(s) — СаО(:) + CО2(g) at 1000°C (d) Na(s) → Na(1) at 98°C.arrow_forward53. Please show the process of cancelling out the function of ln. thank youarrow_forward
- Discuss the spontaneity of each process in the following scenarios, based on the use of the Gibbs free energy equation: 1. N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) + 2NH3(g), AH = -46.11 kJ/mol 2. An exothermic reaction with an increase in entropy 3. A block of solid carbon dioxide subliming to gaseous carbon dioxidearrow_forwardFor a chemical reaction that has a ∆Go value of +24 kJ/mol, what value must Q have for this system to be at equilibriumarrow_forwardWhat is the change in entropy, AS, for the following reaction? Use Table G in your book for values of standard entropies. Your answer should be in J/K mol. CaCO3(s) + 2 H'(aq) → → Ca² (aq) + H₂O(l) + CO2(g) O 264.9 J/K mol O 118.6 J/K mol 394.3 J/K mol 137.7 J/K mol 2arrow_forward
- Given the values of AH, ASn, and T, determine ASuniy and predict whether or not each reaction is spontaneous. (Assume that all reactants and products are in their standard states.) a. AH = -95 kJ; AS;n = -157 J/K; T = 298 K b. AH = -95 kJ; AS"n = -157 J/K; T = 855 K Calculate the Gibbs free energy for the above sets (a) and (b)arrow_forwardCalculate ΔS when 25.0 g ethanol at 50.0 °C is added to 75.0 g ethanol at 10.0 °C in an insulated container where Cp = 111.5 J/mol K. Calculate the change in entropy of each ethanol sample, and then the total entropy change. Comment on what is happening to each sample, and overall. (answers: warm = -6.11 J/K; cold = +5.69 J/K; total = 0.42 J/K)arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction: C(graphite) + 1/2 O2 (g) → CO(g) Is it spontaneous under standard conditions at 298 K? Answer this question by calculating AS" (system), AS° (surroundings), and AS (universe). (Define reactants and products as the system.) S* (J/mol · K) A¡H° (kJ/mol) at 298 K (kJ/mol) Compound at 298 K C(s, graphite) 5.6 CO(g) 197.674 -110.525 CS2 (g) 237.8 116.7 CCL (e) 214.39 -128.4 Cl2 (g) 223.08 Si(s) 18.82 SİCL, (g) 330.86 -662.75 S(s, rhombic) 32.1 Br2 (e) 152.2 HBr(g) 198.70 -36.29 H2 (g) 130.7 H2O2 (e) 109.6 -187.78 O2 (g) 205.07 O yes O noarrow_forward
- Use the data to calculate the standard entropy change for the following reaction: 5. S°[Mt(s)] 43.2 J/K mol Mt(s) + ½ O2(g) → MtO(s) S°[O2(g)] = 305.1 J/K-mol S°[MtO(s)] 62.6 J/K mol a) -133.2 J/K b) -285.7 J/K c) 285.7 J/K d) 133.2 J/Karrow_forwardWhich one of the following choices of gaseous molecules is rank ordered correctly from lowest standard molar entropy (left hand side) to highest standard molar entropy (right hand side)? He, Ne, CO, SiH4 SiH4 , CO, Ne, He SiH4 , Ne, CO, He CO, SiH4 , Ne, Hearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY