
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
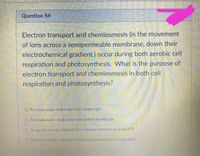
Transcribed Image Text:Question 54
Electron transport and chemiosmosis (is the movement
of ions across a semipermeable membrane, down their
electrochemical gradient.) occur during both aerobic cell
respiration and photosynthesis. What is the purpose of
electron transport and chemiosmosis in both cell
respiration and photosynthesis?
O To create sugar molecules from oxygen gas
O To create water molecules from carbon dioxide gas
OTo use the energy released from slowing electrons to build ATP
OTo usc he energy released from slowing electrons to create light
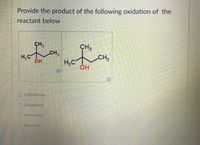
Transcribed Image Text:Provide the product of the following oxidation of the
reactant below
CH,
CH3
CH3
H;C
CH3
H,C
ОН
O2-Pentanone
O 2-Butanone
ONo reaction
Butanone
31
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 5 Which of the following subunits of ATP synthase is correctly described? a: site of ATP synthesis y: protons are transferred to this subunit, determines the number of protons transferred per ATP formed a: contains two half channels for transferring protons across the membranearrow_forwardQuestion 23 2 pts As it turns out, arsenic is a competitive inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Suppose you add arsenic to human muscle tissue in a laboratory. What results would you expect to observe? I. Decreased ability of the tissue to relax after contraction II. Increased concentration of ADP in the mitochondrial matrix III. Increased concentration of lactic acid in the cytosol IV. Increased concentration of NADH and FADH2 in the mitochondrial matrix I, II, and IV II, III, IV I and II I and IV I, II, and IIIarrow_forwardQUESTION 52 An organism is discovered that thrives in both the presence and absence of oxygen in the air. Curiously, the consumption of sugar increases as oxygen is removed from the organism's environment, even though the organism does not gain much weight. This organism O a. is photosynthetic O b. is a normal member of the animal kingdom O c. must utilize a molecule other than oxygen to accept electrons from the electron transport chain O d. only performs fermentation to make ATParrow_forward
- Question 8 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of aerobic metabolism? O A. Carbon dioxide is produced in the matrix of the mitochondria. O B. Oxygen is reduced to water by the electron transport chain. C. Lactic acid is produced in the cytoplasm. OD. ATP synthase requires a pH gradient O E. The electron transport chain functions as hydrogen ion pumps. mennes Mausantara **** Eminemarrow_forwardQuestion 29 Sponges (Porifera) All of the above pump water through their sponge material with the movement of collar cells Have larvae that swim using cilia Extract oxygen from the sea water Are assemblies of cells that work together cooperatively as one organismarrow_forwardQuestion 9 - Under anaerobic conditions in the muscle, lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction converting pyruvate to lactate. What is the metabolic reason for this fermentation reaction? It is necessary to reduce pyruvate before it can be converted to acetyl-CoA and enter the citric acid cycle in muscle. NAD* must be replenished for glycolysis to continue. The reaction creates NADH which can produce additional energy in the electron transport chain. O Lactate is more oxidized than pyruvate.arrow_forward
- Question 8 There are six basic categories of enzymes. Which enzymes remove electrons from, or add electrons to, various substrates? They are used in both catabolic and anabolic pathways. (do not capitalize your answer) erarrow_forwardQuestion 18 In a photosynthetic cell undergoing cell expansion and growth involving active synthesis of multiple proteins, which of the following would you expect to be false? O photo-respiratory activity would increase O Nucleolar activity would be elevated O All of the possible answers are true O Mitochondrial activity will increase O Non-Cyclic electron transport would be greater than cyclic electron transportarrow_forwardQuestion 1: The amount of energy effectively stored in each ATP (the actual energy of ATP hydolysis) will depend on the concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Pi, according to equations discussed in class and in the book. If the ATP synthase is operating at close to equilibrium (as might be the case if ATP is being used slowly), we can compute the maximum possible energy of ATP hydrolysis by assuming balance between the energy provided by the proton gradient and the energy used to make the ATP. (Since we care about the magnitude of the energy it’s convenient to talk in terms of absolute values; the maximum possible ATP hydrolysis energy is then the most negative value possible.) Using what you know about the mechanism of the ATP synthase, and assuming that the membrane gradient consists of a Δψ of -.15V and a ΔpH of 1 unit (alkaline inside), compute the maximum possible ATP-hydrolysis energies for synthases with: a.) 8 c-subunits b.) 13 c-subunitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON