
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
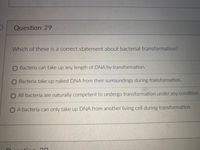
Transcribed Image Text:Question 29
Which of these is a correct statement about bacterial transformation?
Bacteria can take up any length of DNA by transformation.
O Bacteria take up naked DNA from their surroundings during transformation.
O All bacteria are naturally competent to undergo transformation under any condition.
O A bacteria can only take up DNA from another living cell during transformation.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Introduction :-
DNA that isn't protected by lipids, proteins, or any other molecule is referred to as naked DNA. The release of genetic material into the surrounding environment, such as from bursting cells, results in naked DNA.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question #3: CRISPR has been used to cure an individual from sickle cell. Below is a Sanger electropherogram of a sequence from a patient without sickle cell and one with sickle cell. Sequence from a normal individual mmmm Sequence from the diseased individual G T GIIC A GC A Se SCIENCEphe A G A SCIENCE SCIENCEphoto G a) Where is the change in the sequence and what is the consequence to the protein sequence of this mutation? b) Below is an image of the normal and diseased quaternary hemoglobin protein. What is different about the protein shape and why does that structure have a huge impact on its function (please name the function!)? Adult haemogBRAR G G G G A G Sickle Cell haemoglobin S Structure a s RARY COLIBRARY c) If you were to use CRISPR to modify the genome of a diseased individual, to which nucleotides might you design your guide RNA? Why? d) RNA Seq is used to determine off-target effects of Cas9 cleavage. Why is this an appropriate tool to determine these effects? e) Data on…arrow_forwardQUESTION 20 Which of the following polymerases is found in the nucleolus? O A. DNA polymerase III O B. RNA polymerase III O C. RNA polymerase I D. RNA polymerase II - O E. Both A and Barrow_forwardQUESTION 3 which of the following is true for methyl directed repair O A. methyl directed repair cannot distinguish the template strand from the newly replicated strand. O B. methyl directed repair changes both the template strand and the newly replicated strand. O C. methyl directed repair corrects the DNA strand that is methylated. O D. methyl directed repair corrects the mismatch by changing the newly replicated strand. O E. methyl directed repair corrects the mismatch by changing the template strand.arrow_forward
- Question 36 Which of these is not considered a method of DNA extraction? organic filtration differential purification all of the above are extraction methodsarrow_forwardQUESTION 11 Which of the following statements about RNA interference pathways and mechanisms is FALSE? O A Investigators can load RISC and/or RITS complexes with artificial, designed RNAS in order to specifically target and silence a gene of interest as a way to see what the effect of that gene is when its expression is silenced. O B. Only a small section of a small interfering RNA, called the 'seed' sequence, is actually used to identify nucleic acid targets that are to be silenced. OC. Eukaryotic RNA interference pathways do not regulate genes from the genome itself (i.e. endogenous genes), they only respond to external infection events such as invading viruses. The piRNA pathway processes small RNAS out of long noncoding RNA transcripts and is important for suppression of repetitive element movement in germ cells. OD. O E. The micro (n RNA pathway and the short interfering (si) pathways load small RNAS into RISC or RITS complexes.arrow_forwardQuestion 16 Why can't SNPS be detected by PCR and Gel Electrophoresis? O Because Gel Electrophoresis detects size differences in DNA and SNPS do not change the size of the DNA strand. O Because SNPS cause deletions so large that they are beyond the limits of this technique to detect. O Because SNPS affect proteins and PCR only works on DNA. O Because SNPS are too complicated to detect with this technology.arrow_forward
- QUESTION 5 Based on the plasmid shown, what will you have to use to to distinguish and isolate the bacteria that successfully took up the plasmid? O Lactose O Tetracycline O Ampicillin O UV light to identify the glowing colonies O Xgalarrow_forwardQUESTION 2 Within a few weeks of treatment for herpes virus with the drug isonazide, a patient's herpes virus population consists entirely of isonazide-resistant viruses. How can this result best be explained? O A. The drug caused the HIV RNA genome to change O B. The isonazide drug spontaeously converted to a form ineffective against the virus. O C HIV began making drug-resistant versions of reverse transcriptase (a viral enzyme) in response to the drug O D. None of the abovearrow_forwardQuestion 92 True or False? A conjugative R plasmid permits a living bacterial donor to transfer antibiotic resistance genes and genes for conjugation to a recipient bacterium. O True O Falsearrow_forward
- QUESTION 2 Which of the following would be classified as non-coding DNA? (mark all applicable answers) The cytochrome oxidase Il gene found on the human mitochondrion Introns of the alpha hemoglobin gene found on human chromosome 16 Exons of the alpha hemoglobin gene found on human chromosome 16 U The DNA between genes in the human genome (also referred to as intergenic regions or IGRS)arrow_forwardQUESTION 27 Microtubules are made of tubulin. When tubulin is bound to GTP, it has a higher affinity for other tubulin molecules, so microtubules grow. When tubulin is bound to GDP, the affinity is lower so microtubules shrink. We would say that tubulin is regulated by O Ubiquitylation O Phosphorylation O Small molecule binding O Protein-protein interactionsarrow_forwardQUESTION 1 Which of the following more common terms is closest in meaning to pluripotent? O Stem cell O Genetically Modified Organism O Subspecies O Tissue type O Antibodyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education