
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
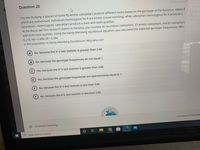
Transcribed Image Text:Question 20
You are studying a species of butterfly whose caterpillars produce different toxins based on the genotype of the Tox locus. Alleles E
and N are codominant. Individuals homozygous for E are emetic (cause vomiting), while caterpillars homozygous for N produce a
neurotoxin. Heterozygotic caterpillars produce a toxin with both qualities.
At the Bocas del Toro research station in Panama, you counted 45 neurotoxic caterpillars, 57 emetic caterpillars, and 82 caterpillars
with both toxic qualities. Using the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium equation, you calculated the expected genotypic frequencies: NN=
0.218, NE= 0.498, EE= 0.284.
Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium? Why/why not?
A) No, because the X^2 test statistic is greater than 3.84.
B) No, because the genotype frequencies do not equal 1.
c) Yes, because the X^2 test statistic is greater than 3.84.
D Yes, because the genotype frequencies are approximately equal to 1.
E) No, because the X^2 test statistic is less than 3.84.
F) Yes, because the X^2 test statistic is less than 3.84.
Last saved 1:10:05 PM
70 minutes remaining
P Type here to search
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Hardy Weinberg equilibrium or Hardy Weinberg model states that genotypic as well as allelic frequencies do not change from generation to further generation unless there is some evolutionary influence. The evolutionary influences include mate choice, genetic drift, natural selection, mutation, sexual selection, assortative mating, genetic hitchhiking, founder effect, population bottleneck, inbreeding, gene flow, and meiotic drive.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 5 Assume you discovered two new genetic traits in drosophila caused by two different mutations. In the first trait, you can clearly distinguish that the flies can have either 2 or 3 stripes on their body. For the other trait, you can distinguish yellow bodies in some flies and white bodies in others. You hypothesize that the stripe trait is controlled by 1 gene (where 2 stripes (S) is dominant over 3 stripes (s)) and that a different gene determines the body color (where white (W) is dominant over yellow (w)). You hypothesize that the genes are on different chromosomes. You set out to test your hypothesis, by crossing F1 heterozygote (in other words, dihybrids) male and female flies. Below is a table as it appears in YOUR lab book. You have already indicated the number of flies you have obtained for each combination of phenotypes. Perform a chi²-test by completing the table below to determine if your data is consistent with your hypotheses. Provide your reasoning by showing…arrow_forwardQuestion 17 You and your laboratory partner began to conduct a dihybrid cross of pea plants before the pandemic, using two traits that sort independently. The traits you studied were leaf shape (S-smooth, s=ridgy) and leaf color (C-green, c=red). You and your lab partner put on your masks and took a socially distanced trip to see your experiment in the greenhouse, where you counted 112 plants from the F1 generation of your experiment. As you expected, every plant in the F1 had smooth, green leaves. What are the allele frequencies in the F1 generation of your experiment? A Ss=50%, Cc=50% B S=25%, s=25%, C=25%, c=25% C) S=50%, s=50%, C=50%, c=50% Ss=100%, Cc=100% Last saved 1:29. 52 minutes remaining P Type here to search Home PrtScn F8 *3 F2 DII F3 Esc F5 F6 F7 23 $ % 2 3. 4 6.arrow_forwardQUESTION 7 You are trying to use qPCR to compare gene expression of nitrous oxide reductase (nosZ) in a Pseudomonas sample treated under various conditions. Using the 2-delta deltact method, about how much higher (or lower) is the expression of nitrous oxide reductase (nosZ) in the experimentally treated sample verses the untreated sample? nosZ Ct values for untreated sample (control conditions) Internal housekeeping nosz Ct values for Internal housekeeping gene Ct values for untreated sample (control conditions) gene Ct values for treatment sample experimental treatment sample experimental Replicate 1 21.3 20.0 19.8 20.9 Replicate 2 21.5 20.1 19.7 21.0 Replicate 3 21.4 20.3 19.5 20.7 Replicate 4 21.6 20.2 19.4 21.1 O A. -2 times higher B. -100 times higher C. about 20% as much as the control O D.-3.5 times higher O E. -12 times higher O F. -6 times higher than the controlarrow_forward
- Question 2arrow_forwardQuestion 1 You are doing a genetics experiment with the fruit fly. In the "P" generation, you cross two true-breeding flies. The female parent is brown and wingless and the male parent is black with normal wings. All of the flies in the F1 generation are brown and have normal wings. Indicate the alleles associated with dominant phenotypes by uppercase letters and alleles associated with recessive phenotypes by lowercase letters. Assume the genes are not found on a sex chromosome. Indicate the color alleles as "B" and "b" the wing alleles by the letters "N" and "n". a) The genotypes of the flies in the P generation are: female and male. b) The genotype of the flies in the F1 generation is: c) You now take an F1 female and cross her to a true-breeding black, wingless male. This male's genotype is: d) You count 1600 offspring in the F2 generation. If the wing and the color traits were linked and no recombination occurred, you would expect to count: # of brown, winged flies (of the…arrow_forwardQUESTION 20 All of the following are characteristics of pathogens that allow them to rapidly and effectively evolve, EXCEPT: a. Large genome size b. Large population size c. Short generation time d. High mutation ratearrow_forward
- QUESTION 12 The B gene codes for hair while the b gene codes for hairless. If B is dominant and b is recessive. Which of the following are possible phenotypes and their genotypes? O a. Hair Bb, Hairless BB, Hair bb O b. Hairless bB, Hair BB, Hair Bb OC. Hairless Bb, Hair BB O d. Hair BB, Hair Bb, Hairless bb OCT 28 O etv MacBook Air esc 80 DII DD F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F7 F8 F10 @ #3 2$ & * 1 3 4 7 8 Q W R Y P qe S : os lock H J K L C V > M control option command command optio V -arrow_forwardQUESTION 40 Under what situation would you expect haplotype frequencies to remain unchanged from one generation to the next? a. the recombination rate is zero b. the coefficient of LD is 0.5 c. the two loci are in linkage disequilibrium d. crossing over between two loci occurs regularlyarrow_forwardQUESTION 6 For a trait known to be caused by a mitochondrial gene variant, there may be an occasional female that can transmit different phenotypes to her progeny on an apparently random basis. What situation might you suspect? O She is heterozygous for this trait. She displays heteroplasmy for this trait. O She displays a low rate of mutation. She is the product of a somatic mutation.arrow_forward
- QUESTION 2 Within a few weeks of treatment for herpes virus with the drug isonazide, a patient's herpes virus population consists entirely of isonazide-resistant viruses. How can this result best be explained? O A. The drug caused the HIV RNA genome to change O B. The isonazide drug spontaeously converted to a form ineffective against the virus. O C HIV began making drug-resistant versions of reverse transcriptase (a viral enzyme) in response to the drug O D. None of the abovearrow_forwardQuestion 1 Given a population with the following proportions of each genotype - 0.11 homozygote dominant individuals, 0.21 heterozygotes, determine the total frequency of dominant alleles in the population.arrow_forwardQUESTION 43 Which of the following statements is true about linkage disequilibrium? O a. D= -0.21 indicates that two loci are in greater LD than D= 0.15 O b. New alleles are born into a population in LE with the surrounding loci O c. Divergent populations that experience a sudden large migratory event will be immediately in LE after mixing. O d. Selective sweeps occur randomly along chromosomes as a result of LE and LD alternating at regular intervals.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education