
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Question 2 A pendulum consisting of a bar “B” and a mass “C” is suspended from a fixed pivot at “O” as shown in figure 2– a. A light spring is attached to the pendulum at point “P” and is anchored at a fixed point “Q”. When the pendulum is in equilibrium the line OC is at 450 from the vertical and the angle OPQ is 900. Calculate the natural frequency of the pendulum for small oscillations about the equilibrium position. The following data is available: Bar “B” Mass “C” Spring PQ mass 1 kg 6 kg centre of gravity G1 G2 radius of gyration about the centre of gravity 0,1 m 0,025 m spring stiffness 700 N/m
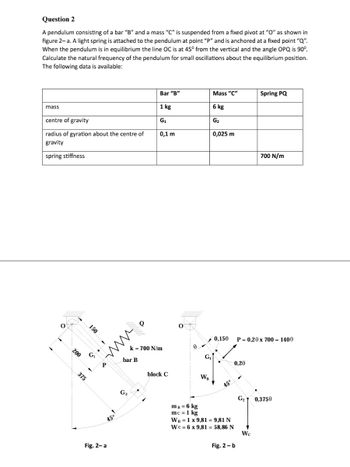
Transcribed Image Text:Question 2
A pendulum consisting of a bar "B" and a mass "C" is suspended from a fixed pivot at "O" as shown in
figure 2-a. A light spring is attached to the pendulum at point "P" and is anchored at a fixed point "Q".
When the pendulum is in equilibrium the line OC is at 45° from the vertical and the angle OPQ is 90°.
Calculate the natural frequency of the pendulum for small oscillations about the equilibrium position.
The following data is available:
mass
centre of gravity
radius of gyration about the centre of
gravity
spring stiffness
0
200
150
G₁
375
.
P
45°
Fig. 2-a
bar B
G₂
Q
Bar "B"
1 kg
G₁
0,1 m
k = 700 N/m
block C
0
G₁
WB
Mass "C"
6 kg
G₂
0,025 m
0,150
45°
mB = 6 kg
mc = 1 kg
WB = 1 x 9,81 = 9,81 N
Wc = 6 x 9,81 = 58,86 N
0,20
Fig. 2-b
Spring PQ
P = 0,20 x 700 = 1400
700 N/m
Wc
G₂ 0,3750
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A wooden plank of mass M is placed on the top of two identical, homogeneous cylinders, each of mass m. The plank is attached to a verti-cal wall with a horizontal ideal spring of stiffness k (see figure). Find the period of small oscillations of the plank. Assume that the coefficient of static friction is large enough so the cylinders don’t slip neither on the horizontal surface nor on the plank.arrow_forwardRefer to Figure Q2. A tray of mass mı is supported by 3 springs as shown in Figure 3(a). The natural frequency fa is 5.0Hz. An additional mass motor of m2 = 3.0kg (in OFF condition) is placed at the center on top of the mass, the natural frequency is observed to be 2.5Hz. a) Calculate the mass mı. The motor m2 is ON and it rotates at the speed of 600 rpm. Calculate: a) The transmissibility b) Attenuation c) Explain what will happen if the system run at Resonant Frequency m2 m1 Figure 2(a): Original system Figure 2(b): system with m2 addedarrow_forwardPls see question in the attached image and solve the question by hand written notes and figure.arrow_forward
- Q1: The system shown has two masses. Beam of mass (Jo#m L² kg.m²) rotates about fixed point (O) and its free end is connected to disk rotates about fixed point (O₂). Consider all connecting links are massless and rigid. Find 1- The displacements of points A, B, and C in addition to the rotations of masses, all in terms of 0. 2- Find the equation of motion (EOM) in terms of 0. 3- What is the natural frequency of the system? L/2 A Jo=m L² k L/2 Joz-m R² full 0₂ R U B Carrow_forwardA pendulum is made up of a spring with a mass attached to the end. The spring is arranged to lie in a straight line, by wrapping the spring around a massless bar. The equilibrium length of the bar is “l”. Using lagrange’s equations, find the equations of motion.arrow_forwardQUESTION 2. A smooth rod with a length of 21 is bent as in Figure 2 and small oscillations are made around the frictionless pin in B. If the period of minor oscillations is denoted by To when B = 0, find the beta angle where the period of minor oscillations is 2To. hand written plz B 7 Figure 2.arrow_forward
- Vibrationarrow_forward+ b 3. A tuning fork is an example of a "resonant system", that is, one that has a low damping ratio. A model of a (half) tuning fork is rod of mass m with air drag modeled as a damper connected approximately at its middle, and a torsional spring at the base of the cantilever. Assume the cantilever rotates back and forth about its pivot by a small angle o. Because other forces are much larger, you can reasonably neglect the effect of gravity in this model. The moment of inertia of a cantilevered beam pinned at one end is equal to ml2, where I is its length. (a) What is the natural frequency of this system if m= 0.1 kg and k = 2548 Nm/rad, and 1 = 0.1 m. Please give the value in rad/s and Hz. (b) Find an upper bound on the damping coefficient b that insures that the damping ratio of the tuning fork is no greater than = 0.01. (c) For this damping ratio, what is the damped natural frequency of the system? (d) For this damping ratio, what is the decay rate (the size of the exponent…arrow_forwardFigure below shows a rod with mass M = 100 kg, cross section area A = 10 cm². The rod is supported by 4 springs having stiffnesses of k = 1 MN/m. A tip mass with m = 120 kg is attached to the rod. Assume x is the degree of freedom of the equivalent system. The Young's modulus, E, is not known. If the natural frequency of the equivalent mass-spring system is 40 Hz, determine the Young's modulus, E. Assume the length of the rod is L = 5 m. Find the nearest answer. k ww E, A, M k F @www.ww wint L 195 GPa 179 GPa 116 GPa 45 GPa 236 GPa 000 00arrow_forward
- A body weighing 5kg is attached to a very light bar as depicted below. The set-up is free to rotate in the vertical plane about pin support O. The force applied at point C makes the bar oscillate(via small rotation) about the position of equilibrium illustrated below a. Derive the differential equation of motion for the steady state angular displacement (theta) of the bararrow_forward0.5m 1m The figure shows a slender rod with a mass of 6 kg. Attached to the rod is a spring of stiffness k = 250 N /m .A moveable point mass m1= 1 kg is position at a distance x from the pivot point. You can assume small angle oscillations from the equilibrium position shown in the figure.arrow_forwardProblem (1): Derive the equation of motion of the system shown in Figure and find: • The natural frequency of vibration • The damping ratio • The free damped frequency of vibration If m= 10 kg, c = 50 N-s/m, k = 1000 N/m, L= 1 m 44 3k Uniform rigid bar, mass m 2 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY