
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
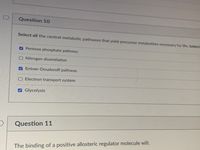
Transcribed Image Text:Question 10
Select all the central metabolic pathways that yield precursor metabolites necessary for life. (select.
Pentose phosphate pathway
ONitrogen dissimilation
A Entner-Doudoroff pathway
O Electron transport system
Glycolysis
Question 11
The binding of a positive allosteric regulator molecule will:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- question 20arrow_forwardQuestion 11 The breakdown of large molecules by the enzymatic addition of water is an example of what kind of reaction? O 1. oxidation O 2. reduction O 3. condensation O 4. hydrolysis O 5. decarboxylation A Moving to another question will save this response. W AR SONY ASSIST BUtton, Onetoucharrow_forwardQuestion 16 In the skeletal muscle, insulin increases fatty acid synthesis by up regulation of which pathway? O A. Oxidative phosphorylation O B. Glycolysis O C. Glycogenesis O D. Lipolysis O E. B oxidizationarrow_forward
- 17arrow_forwardQuestion 29 Which enzymes produce 2 ATP's for every glucose? hexokinase O phosphoglyceromutase O Triose phosphate dehydrogenase O phosphofructokinase O pyruvate kinasearrow_forwardQuestion 28 Which enzyme breaks glucose into 2 molecules of 3 carbons each? O pyruvate deydrogenase O phosphoglycerokinase Aldolase O phosphoglucoisomerase O Hexokinasearrow_forward
- Question 1: In some microorganisms, carbon fixation occurs by reversal of the citric acid cycle. This reversal is accomplished in part by the use of a strong reductant (ferredoxin) to drive the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase reaction in the reductive direction. Part a: ΔG°‘ for reaction as it occurs in the ‘normal’ (oxidative) citric acid cycle is -30.1 kJ/mol. The standard reduction potential for NADH is -0.32 V. In order to drive the reaction in the reverse direction, the reductant (a ferredoxin) must have a lower reduction potential than NADH/NAD+. Remembering that this is a two-electron reduction, and using the numbers given just above, compute the value of the ferredoxin reduction potential that would be needed to make the standard free energy zero (so that the reductive reaction is enegetically just as favorable as the oxidative reaction). Assume that all of the other reactants are the same in the reductive as in the oxidative reaction. Write out the steps in your calculation;…arrow_forwardQuestion 9 Match the enzyme with a phrase about it. v Catalyzes a substrate lovei phosphorylation 3. Pyruvate kinaise v breaks down sucrose to glucose and fructose b. phosphovylase e phosphohaxesa semerase (ato called giasose-6 phosphete samerane) v is a type of isomerase v removes one glucose residue from glycogen d. Sucrase A Muving to another question will save this responsearrow_forwardi really need the right answer pleasearrow_forward
- Question attachedarrow_forwardQuestion 11 Which reaction in glycolysis produces NADH? O oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate O oxidation of 1,3-biphosphoglycerate isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate O cleavage of glyceraldehydes 3-phosphate O phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphatearrow_forwardQuestion 1 a. What enzyme works on glucose-6-P when the energy charge is 0.80? b. What enzyme works on glucose-6-P when the energy charge is 0.97? c. What enzyme works on glycogen when the energy charge is 0.80?d. d. What enzyme works on glycogen when the energy charge is 0.97? e. What enzyme works on pyruvate when the energy charge is 0.80 (assume high O2)? f. What enzyme works on pyruvate when the energy charge is 0.97?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education