
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Suppose a pure monopolist is faced with the demand schedule that follows and the same cost data as the competitive producer discussed in question 3 at the end of Chapter 7 . Calculate the missing total-revenue and marginal-revenue amounts, and determine the profit-maximizing
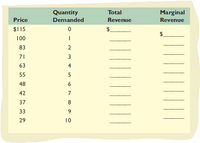
Transcribed Image Text:Marginal
Revenue
Quantity
Total
Price
Demanded
Revenue
$115
$.
100
83
2
71
3
63
4
55
48
6
42
7
37
8
33
29
10
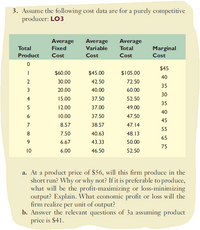
Transcribed Image Text:3. Assume the following cost data are for a purely competitive
producer: LO3
Average
Average
Average
Total
Fixed
Variable
Total
Marginal
Product
Cost
Cost
Cost
Cost
$45
$60.00
$45.00
$105.00
40
2
30.00
42.50
72.50
35
3
20.00
40.00
60.00
30
4
15.00
37.50
52.50
35
5
12.00
37.00
49.00
40
6
10.00
37.50
47.50
45
7
8.57
38.57
47.14
55
8
7.50
40.63
48.13
65
6.67
43.33
50.00
75
10
6.00
46.50
52.50
a. At a product price of $56, will this firm produce in the
short run? Why or why not? If it is preferable to produce,
what will be the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing
output? Explain. What economic profit or loss will the
firm realize per unit of output?
b. Answer the relevant questions of 3a assuming product
price is $41.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Eyeglasslux is a single-price monopolist in the eye-glass frame market. It faces a Market demand given by Q=378-2P. Its Total Cost function is TC=6,422+20Q and Marginal Cost is MC=20. If the government imposes a price ceiling of $27, what is the monopolist's QUANTITY in the SHORT- run?arrow_forwardA monopolist book publisher with a constant marginal cost of 2 and no fixed costs sells novels in only two countries. Assume the inverse demand curve in country 1 is given by P₁ = 10-Q and the inverse demand curve in country 2 is given by P₂ = 18-Q Assuming book shipments across countries are banned so that price discrimination occurs. What is the equilibrium price and quantity of books sold by the monopolist in country 1? Continuing to assume price discrimination, what is the equilibrium price and quantity of books sold by the monopolist in country 2? If book imports are permitted in both countries so that price discrimination is impossible, what is the equilibrium price and quantity sold in the two countries combined? P=1, Q=16 P=1, Q=12 P=4, Q=8 11 P=6, Q=6 P=4. Q=14 P=6, Q=12 P=8, Q=10 P=10, Q=8 P=6, Q=20 P=7, Q=20 P=10, Q=8 P=12, Q=6arrow_forwardConsider a monopolist facing a market demand given by: P = 200 - 4Q. Where P is the price and Q is the quantity. The monopolist produces the good according to the cost function c(Q) = Q2 + 5. Determine the profit maximizing quantity and price the monopolist will offer in the market. Calculate the profits for the monopolist. Calculate the deadweight loss due to a monopoly. Illustrate this in a well labelled diagram. I will thumbs up solution if it is original answer and not from ChatGPT, if ChatGPT is used I will thumbs-down and report to Chegg as ChatGPT returns the incorrect answer here and I'm stuck. Thank you! :)arrow_forward
- Suppose the inverse demand for a monopolist's product is given by P(Q) = 70 – .50 The monopolist can produce output in two plants. The marginal cost of producing in plant 1 is MC, = 3Q, and the marginal cost of producing in plant 2 is MC, = Q2. How much out- put should be produced in each plant to maximize profits, and what price should be charged for the product?arrow_forwarda) Find and highlight the consumer surplus in the monopoly in the diagram.b) Draw a possible marginal cost curve for the monopolist into the diagram that is consistentwith all the other curves that are already given. c) Based on the marginal cost curve that you constructed in part (b), find and highlight themonopolist’s total costs at the monopoly price in the diagram. d) Briefly (200 words max) explain the shape of the marginal revenue curve as compared tothe demand curve in the diagram.arrow_forwardConsider the case of a monopolist who has the ability to perfectly price discriminate by charging each one of its customers a two-part tariff. Suppose for simplicity that there are only two consumers, Mary and Terry. Mary demand for the good is 2/3 of the aggregate demand. The aggregate demand is given by Q=550-3p, where Q denotes the total quantity demanded at price p. The firm's total cost of producing Q units is given by the function C(Q) = 5 Q + 100 Find the two-part tariff that the firm will charge Mary in order to maximize its profit. Then enter the fee of this two-part tariff below. (As usual, you must enter a number below, not a ratio, not an expression with symbols..., just a number.)arrow_forward
- A monopolist serves a market with five potential buyers, each of whom would buy at most one piece of the monopolist's good. Anna would be willing to pay up to £50 for it, Bob up to £70, Chloe up to £90, Dave up to £110 and Elizabeth up to £130. The monopolist's variable cost function is given in below table. [Note: In parts (a) and (b), working outs only need to be shown for at least one result per line of the table.] Quantity 1 Marginal Costs 50 Price Marg. Revenue 2 55 3 60 d) Find the total surplus maximising (i.e., socially optimal) quantity. e) Quantify the Deadweight Loss! 4 65 5 70arrow_forwardA monopolist has a cost function c(q) = 5q+800 and faces aggregate demand q=3000 - 120p. Suppose first that monopolist sells q=400 units. The monopolist's revenue would be The monopolist profit would be The absolute value of the price elasticity of demand would be The consumer surplus would be Now suppose that the monopolist chooses q to maximize its profit. The monopolist's revenue would be The monopolist profit would be The absolute value of the price elasticity of demand would be The consumer surplus would bearrow_forwardThe function Q= 14 - P represent the market demand. The cost function of the monopolist is C= 2Q. a) Find quantity, price and profit of the monopolist. b) Given the results of point (a), what is the firm's percentage mark-up of price over marginal cost? c) Suppose that now we have a market demand with elasticity equal to -2. If the price is 8, what should be the marginal cost of the last unit produced?arrow_forward
- Consider the case of a monopolist who charges the same price to all consumers. The demand for the good is given by Q=813-7p, where Q denotes the quantity demanded at price p. The firm's total cost of producing Q units is given by the function C(Q) = 7 Q What is the profit maximizing price for this monopolist? (As usual, you must enter a number below, not a ratio, not an expression with symbols..., just a number.)arrow_forwardAssume you were provided the following information for a monopolist: Inverse Demand Function: P = 100 - 2Q Total Cost Function: TC = 10 + 2Q The monopolist has a constant marginal cost of $2. What is the profit maximizing level of output?arrow_forwardA single price monopolist has a cost function of c(Q) = 10 + Q, where Q is output. It faces the following demand curve: Q°(p) = 0, if p > 24 and Q°(p) = 120/p, if p s 24. What is the profit-maximizing choice of output? The profit maximizing choice of output is = At this optimum level of output, calculate the consumer surplus. In addition, by drawing a graph, show the area representing the producer surplus (label it by PS) and the area representing the deadweight loss (label it by DWL). Calculate the values of producer surplus and deadweight loss.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education