
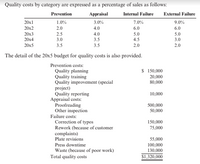
Iona Company, a large printing company, is in its fourth year of a five-year, quality improvement program. The program began in 20x0 with an internal study that revealed the quality costs being incurred. In that year, a five-year plan was developed to lower quality costs to 10 percent of sales by the end of 20x5. Sales and quality costs for each year are as follows:
Sales Revenues Quality Costs
20x1 $10,000,000 $2,000,000
20x2 10,000,000 1,800,000
20x3 11,000,000 1,815,000
20x4 12,000,000 1,680,000
20x5* 12,000,000 1,320,000
Required:
1. Prepare an interim quality cost performance report for 20x5 that compares actual quality costs with budgeted quality costs. Comment on the firm’s ability to achieve its quality goals
for the year.
2. Prepare a one-period quality performance report for 20x5 that compares the actual quality costs of 20x4 with the actual costs of 20x5. How much did profits change because of
improved quality?
3. Prepare a graph that shows the trend in total quality costs as a percentage of sales since the inception of the quality improvement program.
4. Prepare a graph that shows the trend for all four quality cost categories for 20x1 through 20x5. How does this graph help management know that the reduction in total quality costs
is attributable to quality improvements?
5. Assume that the company is preparing a second five-year plan to reduce quality costs to 2.5 percent of sales. Prepare a long-range quality cost performance report assuming sales of
$15 million at the end of five years. Assume that the final planned relative distribution of quality costs is as follows: proofreading, 50 percent; other inspection, 13 percent; quality
training, 30 percent; and quality reporting, 7 percent.

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 7 images

- Oakmont Company has an opportunity to manufacture and sell a new product for a four-year period. The company's discount rate is 17%. After careful study, Oakmont estimated the following costs and revenues for the new product: Cost of equipment needed Working capital needed) Overhaul of the equipment in two years. Salvage value of the equipment in four years Annual revenues and costs: Sales revenues $ 275,000 $ 86,000 $10,000 $ 13,000 $ 420,000 Variable expenses $ 205,000 Fixed out-of-pocket operating costs $ 87,000 When the project concludes in four years the working capital will be released for investment elsewhere within the company. Click here to view Exhibit 148-1 and Exhibit 148-2. to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. Required: Calculate the net present value of this investment opportunity. (Round your final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.)arrow_forwardCasey Nelson Is a divisional manager for Pigeon Company. His annual pay ralses are largely determined by his division's return on Investment (ROI), which has been above 23% each of the last three years. Casey is considering a capital budgeting project that would require a $4,100,000 Investment in equipment with a useful life of five years and no salvage value. Pigeon Company's discount rate is 19%. The project would provide net operating Income each year for five years as follows: Sales $ 4,000, 000 1,840, e0e Variable expenses Contribution margin 2,160,000 Fixed expenses: Advertising, salaries, and other fixed out- of-pocket costs $ 760, 000 820, 000 Depreciation Total fixed expenses 1,580, e00 Net operating income $ 580, 000 Click here to view Exhibit 12B-1 and Exhibit 12B-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. Requlred: 1. What is the project's net present value? 2. What is the project's Internal rate of return to the nearest whole percent? 3. What Is the…arrow_forwardGodoarrow_forward
- Lou Barlow, a divisional manager for Sage Company, has an opportunity to manufacture and sell one of two new products for a five- year period. His annual pay raises are determined by his division's return on investment (ROI), which has exceeded 19% each of the last three years. He computed the following cost and revenue estimates for each product: Product A Product B Initial investment: Cost of equipment (zero salvage value) $ 190,000 $ 400,000 Annual revenues and costs: Sales revenues $ 270,000 $ 370,000 Variable expenses $ 128,000 $ 178,000 Depreciation expense $ 38,000 $ 80,000 Fixed out-of-pocket operating costs $ 72,000 $ 52,000 The company's discount rate is 17%. Click here to view Exhibit 14B-1 and Exhibit 14B-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. Required: 1. Calculate each product's payback period. 2. Calculate each product's net present value. 3. Calculate each product's internal rate of return. 4. Calculate each product's profitability index. 5.…arrow_forwardCasey Nelson is a divisional manager for Pigeon Company. His annual pay raises are largely determined by his division's return on investment (ROI), which has been above 22% each of the last three years. Casey is considering a capital budgeting project that would require a $3,800,000 investment in equipment with a useful life of five years and no salvage value. Pigeon Company's discount rate is 18%. The project would provide net operating income each year for five years a follows: Sales Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses: Advertising, salaries, and other fixed out-of-pocket costs Depreciation Total fixed expenses Net operating income. EXHIBIT 7B-1 Present Value of $1; Click here to view Exhibit 7B-1 and Exhibit 7B-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. Required: 1. What is the project's net present value? 2. What is the project's internal rate of return to the nearest whole percent? 3. What is the project's simple rate of return? 4-a. Would…arrow_forwardUse an excel spreedsheet to answer this question: The National Potato Cooperative purchased a deskinning machine last year for $150,000. Revenue for the first year was $ 50,000. Over the total estimated life of 8 years, use a spreadsheet to estimate the remaining equivalent annual revenues (years 2 through 8) to ensure breakeven by recovering the investment and a return of 10% per year. Costs are expected to be constant at $42,000 per year and a salvage value of $10,000 is anticipated.arrow_forward
- Oakmont Company has an opportunity to manufacture and sell a new product for a four-year period. The company's discount rate is 17%. After careful study, Oakmont estimated the following costs and revenues for the new product: Cost of equipment needed Working capital needed Overhaul of the equipment in two years Salvage value of the equipment in four years Annual revenues and costs: Sales revenues $ 155,000 $ 65,000 $ 9,000 $ 14,500 $ 300,000 Variable expenses $ 145,000 Fixed out-of-pocket operating costs $ 75,000 When the project concludes in four years the working capital will be released for investment elsewhere within the company. Click here to view Exhibit 7B-1 and Exhibit 7B-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. Net present value Required: Calculate the net present value of this investment opportunity. Note: Round your final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.arrow_forwardAria Acoustics, Incorporated (AAI), projects unit sales for a new seven-octave voice emulation implant as follows: Year 12345 Unit Sales 73,400 86,400 105,500 97,600 67,500 Production of the implants will require $1,600,000 in net working capital to start and additional net working capital investments each year equal to 15 percent of the projected sales increase for the following year. Total fixed costs are $3,400,000 per year, variable production costs are $257 per unit, and the units are priced at $381 each. The equipment needed to begin production has an installed cost of $16,900,000. Because the implants are intended for professional singers, this equipment is considered industrial machinery and thus qualifies as seven-year MACRS property. In five years, this equipment can be sold for about 20 percent of its acquisition cost. The tax rate is 22 percent and the required return is 14 percent. MACRS schedule a. What is the NPV of the project? Note: Do not round intermediate…arrow_forwardOakmont Company has an opportunity to manufacture and sell a new product for a four-year period. The company's discount rate is 15%. After careful study, Oakmont estimated the following costs and revenues for the new product: Cost of equipment needed Working capital needed Overhaul of the equipment in two years Salvage value of the equipment in four years Annual revenues and costs: Sales revenues Variable expenses Fixed out-of-pocket operating costs $ 130,000 $ 60,000 8,000 $ 12,000 $ When the project concludes in four years the working capital will be released for investment elsewhere within the company. $250,000 $ 120,000 $ 70,000 Click here to view Exhibit 13B-1 and Exhibit 13B-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. $ Required: Calculate the net present value of this investment opportunity. (Round discount factor(s) to 3 decimal places.) Net present value 3arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





