Question
this is a physics course question
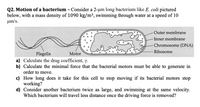
Transcribed Image Text:Q2. Motion of a bacterium - Consider a 2-µm long bacterium like E. coli pictured
below, with a mass density of 1090 kg/m3, swimming through water at a speed of 10
um/s.
Outer membrane
-Inner membrane
Chromosome (DNA)
Ribosome
Flagella
Motor
a) Calculate the drag coefficient, y.
b) Calculate the minimal force that the bacterial motors must be able to generate in
order to move.
c) How long does it take for this cell to stop moving
working?
d) Consider another bacterium twice as large, and swimming at the same velocity.
Which bacterium will travel less distance once the driving force is removed?
its bacterial motors stop
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Physics Please help me with this Physics homework question. This is a practice homework question. Please help me.arrow_forwardThe force exerted by an electric charge at the origin on a charged particle at the point (x, y, z) with position Kr = (x, y, z) is F(F) = where K is constant. vector 7= 3' 171³ Assume K = 30. Find the work done as the particle moves along a straight line from (3,0,0) to (3,4,2).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios