
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
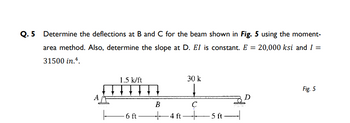
Transcribed Image Text:Q. 5 Determine the deflections at B and C for the beam shown in Fig. 5 using the moment-
area method. Also, determine the slope at D. El is constant. E = 20,000 ksi and I =
31500 in.4.
1.5 k/ft
30 k
↓↓↓↓
Fig. 5
A
B
C
6 ft 4 ft --
-5 ft-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use the moment-area method to determine the slopes and deflections at point C of the beam shown.arrow_forwardPart e) Rotation_at_B Use the principle of virtual work to determine the rotation at Support B. (The positive direction of a rotation is clockwise. Please present your result to 4 decimal places.) Radiansarrow_forwardQ. 4 Determine the slope at the supports for the beam shown below. Also, determine the deflections at B and C. 10 ft I 40 k B 60 k 10 ft 21 E = constant = 29,000 ksi I = 1,000 in.4 10 ft I Q. 4arrow_forward
- The truss shown in Fig.3 is supported by a roller at C and a hinge at D. Use Castigliano's theorem to calculate the horizontal deflection for point B. E-200 B. kN/mm² and A-800 mm² for all members. s) 15 kN 2 m 20 KN B Th 2 m Fig.3arrow_forward1. If the shear at a point 1m from the roller support is equal to -217.65765765766kN, determine the value of "w". 2. Determine the deflection at point 3.2m from the hinge support. 3. Determine the deflection at point 1m from the roller support.arrow_forward2. Determine the vertical deflection at joint B of the truss shown in Fig. below due to a temperature increase of 40° C in members AB and BC, and a temperature drop of 20° C in members AD, DE, EF, and CF. If member BE is 18 mm too long and member BC is 15mm too short. Use the method of virtual work. E 3.5 m D B -6 m- a = 1.2 (10-5)°Carrow_forward
- Helparrow_forwardUse the moment-area method to determine the slope and deflection at point B of the beam.arrow_forwardQ. Determine the slope at the supports of the beam shown in Fig. I using the double integration method. Also, determine the maximum deflection. El is constant. E = 29,000 ksi and I = 3,500 in.4. 2 k/ft ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ Fig. 1 A C B -15 ft- -6 ft-arrow_forward
- Determine the slope and deflection at point B of the steel beam shown. The reactions have been computed. E = 29(103) ksi, I = 800 in4.arrow_forwardUsing the moment-area method find the deflection at point C of the simply supported beam.arrow_forwardQUESTION 2 - BEAM For the beam shown below, determine the vertical deflection at point B by using the virtual work method. EI is constant. -5 ft A -5 ft 12 k Į -5 ft B -5 ft- 70 k-ft Fig. 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning