
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Choose the best reagents to complete the following reactions.
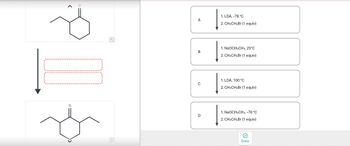
Transcribed Image Text:Q
Q
1. LDA, -78 °C
A
2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv)
1. NaOCH2CH3, 25°C
B
2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv)
1. LDA, 100 °C
C
2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv)
1. NaOCH2CH3, -78 °C
D
2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv)
Done
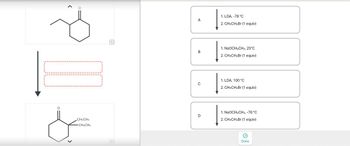
Transcribed Image Text:CH2CH3
⚫CH2CH3
@
Q
1. LDA, -78 °C
A
2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv)
1. NaOCH2CH3, 25°C
B
2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv)
1. LDA, 100 °C
C
2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv)
1. NaOCH2CH3, -78 °C
D
2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv)
Done
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 9.96 Most first aid "cold packs" are based on the endothermic dissolution of ammonium nitrate in water: NH4NO3(s)NH4+(aq)+NO3(aq) H= 25.69 kJ A particular cold pack contains 50.0 g of NH4NO3 and 125.0 g of water. When the pack is squeezed, the NH4NO3dissolves in the water. If the pack and its contents are initially at 24.0°C, what is the lowest temperature that this bag could reach? (Assume that the ammonium nitrate solution has a specific heat of 4.25J g-l K-l, and that the heat capacity of the bag itself is small enough to be neglected.)arrow_forwardIdentify the best reagents to complete the following reaction. O ZI H ZIarrow_forwardwhat are the answers?arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardWhat is Keg for the reaction 2S03(g) = 2S0,(g) + 02(g)? OA. K [So, f10,1 [So,P O B. Ke 2(SO,] 2[SO, ||0,] [So, F [SO, P10,1 C. Kea O D. Karrow_forwardWhich reaction will have a pressure equilibrium constant (Kp) that is greater than the concentration equilibrium constant (K)? O CH3 COOH(aq) + H20(1)=H30*(aq)+ CH3 CO0 (aq) O 2H,0;(g)=2H,0() + O2(g) O 2503(9) = 250,(g) +O2(g) O l2(g) + H2(g)=2HI(g)arrow_forward
- Please choose the correct expression and circle it.arrow_forwardHow many Calories should there be in three grams of pure sucrose?A.4B. 12C. 18D. 8E. None of the above.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium reaction of propyl alcohol (C3H,OH) and acetic acid (CH3COOH) resulting from the hydrolysis of propyl acetate (CH3COOC3H;) is given below. CH3COOC3H, + H20 CH3COOH + C3H5OH Which of the following is the equilibrium (K) constant? O a. K = [CH3COOHJ [C3H7OH] / [CH3COOC3H;] [H2O] O b. K = [CH§COOH] [C3H;OH] / [CH3COOC3H;] O c. K= [CH3CO0C3H7] [H20] / [CH3COOH] [C3H7OH] O d. K = [CH3COOC3H;] / [CH3COOH] [C3H;OH]arrow_forward
- 7 4 (a) Calculate the value of Kc for the reaction: PC15 (2) PC13 (g) + Cl2 (g) AH = Positive Given that when 8.4 mol of PCls (g) is mixed with 1.8 mol of PC13 (g) and allowed to come to equilibrium in a 10 dm³ container the amount of PCls (g) at equilibrium is 7.2 mol. Kc = (b) Explain the effect of the following changes below on the value of Kc: (1) Increasing temperature (ii) Lowering the concentration of chlorine (Cl2) (iii) Addition of a catalystarrow_forwardDetermine AGrxn for 2 A(g) + B₂(g) → 2 AB(g) A. -400 kJ B. -250 kJ C. -200 kJ D. -100 kJ E. -50 kJ Compound(state) AG (kJ/mol) A(g) B₂(g) AB(g) 0 -100 -150arrow_forwardAt a specific temperature, the reaction: has Keq = 1.40 x 10-4. At the same temperature, determine Keq for the reaction:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305446021
Author:Lampman
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT